| The topic of this article may not meet Misplaced Pages's general notability guideline. Please help to demonstrate the notability of the topic by citing reliable secondary sources that are independent of the topic and provide significant coverage of it beyond a mere trivial mention. If notability cannot be shown, the article is likely to be merged, redirected, or deleted. Find sources: "Kaniadakis Gaussian distribution" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Probability density function | |||
Cumulative distribution function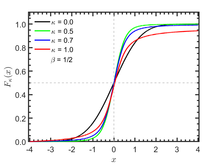 | |||
| Parameters |
shape (real) rate (real) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | |||
| Median | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| Skewness | |||
| Excess kurtosis | |||
The Kaniadakis Gaussian distribution (also known as κ-Gaussian distribution) is a probability distribution which arises as a generalization of the Gaussian distribution from the maximization of the Kaniadakis entropy under appropriated constraints. It is one example of a Kaniadakis κ-distribution. The κ-Gaussian distribution has been applied successfully for describing several complex systems in economy, geophysics, astrophysics, among many others.
The κ-Gaussian distribution is a particular case of the κ-Generalized Gamma distribution.
Definitions
Probability density function
The general form of the centered Kaniadakis κ-Gaussian probability density function is:
where is the entropic index associated with the Kaniadakis entropy, is the scale parameter, and
is the normalization constant.
The standard Normal distribution is recovered in the limit
Cumulative distribution function
The cumulative distribution function of κ-Gaussian distribution is given by
where
is the Kaniadakis κ-Error function, which is a generalization of the ordinary Error function as .
Properties
Moments, mean and variance
The centered κ-Gaussian distribution has a moment of odd order equal to zero, including the mean.
The variance is finite for and is given by:
Kurtosis
The kurtosis of the centered κ-Gaussian distribution may be computed thought:
which can be written as
Thus, the kurtosis of the centered κ-Gaussian distribution is given by:
or
κ-Error function
| κ-Error function | |
|---|---|
 Plot of the κ-error function for typical κ-values. The case κ=0 corresponds to the ordinary error function. Plot of the κ-error function for typical κ-values. The case κ=0 corresponds to the ordinary error function. | |
| General information | |
| General definition | |
| Fields of application | Probability, thermodynamics |
| Domain, codomain and image | |
| Domain | |
| Image | |
| Specific features | |
| Root | |
| Derivative | |
The Kaniadakis κ-Error function (or κ-Error function) is a one-parameter generalization of the ordinary error function defined as:
Although the error function cannot be expressed in terms of elementary functions, numerical approximations are commonly employed.
For a random variable X distributed according to a κ-Gaussian distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation , κ-Error function means the probability that X falls in the interval .
Applications
The κ-Gaussian distribution has been applied in several areas, such as:
- In economy, the κ-Gaussian distribution has been applied in the analysis of financial models, accurately representing the dynamics of the processes of extreme changes in stock prices.
- In inverse problems, Error laws in extreme statistics are robustly represented by κ-Gaussian distributions.
- In astrophysics, stellar-residual-radial-velocity data have a Gaussian-type statistical distribution, in which the K index presents a strong relationship with the stellar-cluster ages.
- In nuclear physics, the study of Doppler broadening function in nuclear reactors is well described by a κ-Gaussian distribution for analyzing the neutron-nuclei interaction.
- In cosmology, for interpreting the dynamical evolution of the Friedmann–Robertson–Walker Universe.
- In plasmas physics, for analyzing the electron distribution in electron-acoustic double-layers and the dispersion of Langmuir waves.
See also
- Giorgio Kaniadakis
- Kaniadakis statistics
- Kaniadakis distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Exponential distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Gamma distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Weibull distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Logistic distribution
- Kaniadakis κ-Erlang distribution
References
- Moretto, Enrico; Pasquali, Sara; Trivellato, Barbara (2017). "A non-Gaussian option pricing model based on Kaniadakis exponential deformation". The European Physical Journal B. 90 (10): 179. Bibcode:2017EPJB...90..179M. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2017-80112-x. ISSN 1434-6028. S2CID 254116243.
- ^ da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E. F.; Carvalho, Pedro Tiago C.; de Araújo, João M.; Corso, Gilberto (2020-05-27). "Full-waveform inversion based on Kaniadakis statistics". Physical Review E. 101 (5): 053311. Bibcode:2020PhRvE.101e3311D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.101.053311. ISSN 2470-0045. PMID 32575242. S2CID 219746493.
- ^ Kaniadakis, G. (2021-01-01). "New power-law tailed distributions emerging in κ-statistics (a)". Europhysics Letters. 133 (1): 10002. arXiv:2203.01743. Bibcode:2021EL....13310002K. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/133/10002. ISSN 0295-5075. S2CID 234144356.
- Moretto, Enrico; Pasquali, Sara; Trivellato, Barbara (2017). "A non-Gaussian option pricing model based on Kaniadakis exponential deformation". The European Physical Journal B. 90 (10): 179. Bibcode:2017EPJB...90..179M. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2017-80112-x. ISSN 1434-6028. S2CID 254116243.
- Wada, Tatsuaki; Suyari, Hiroki (2006). "κ-generalization of Gauss' law of error". Physics Letters A. 348 (3–6): 89–93. arXiv:cond-mat/0505313. Bibcode:2006PhLA..348...89W. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2005.08.086. S2CID 119003351.
- da Silva, Sérgio Luiz E.F.; Silva, R.; dos Santos Lima, Gustavo Z.; de Araújo, João M.; Corso, Gilberto (2022). "An outlier-resistant κ -generalized approach for robust physical parameter estimation". Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications. 600: 127554. arXiv:2111.09921. Bibcode:2022PhyA..60027554D. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2022.127554. S2CID 248803855.
- Carvalho, J. C.; Silva, R.; do Nascimento jr., J. D.; Soares, B. B.; De Medeiros, J. R. (2010-09-01). "Observational measurement of open stellar clusters: A test of Kaniadakis and Tsallis statistics". EPL (Europhysics Letters). 91 (6): 69002. Bibcode:2010EL.....9169002C. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/91/69002. ISSN 0295-5075. S2CID 120902898.
- Carvalho, J. C.; Silva, R.; do Nascimento jr., J. D.; De Medeiros, J. R. (2008). "Power law statistics and stellar rotational velocities in the Pleiades". EPL (Europhysics Letters). 84 (5): 59001. arXiv:0903.0836. Bibcode:2008EL.....8459001C. doi:10.1209/0295-5075/84/59001. ISSN 0295-5075. S2CID 7123391.
- Guedes, Guilherme; Gonçalves, Alessandro C.; Palma, Daniel A.P. (2017). "The Doppler Broadening Function using the Kaniadakis distribution". Annals of Nuclear Energy. 110: 453–458. doi:10.1016/j.anucene.2017.06.057.
- de Abreu, Willian V.; Gonçalves, Alessandro C.; Martinez, Aquilino S. (2019). "Analytical solution for the Doppler broadening function using the Kaniadakis distribution". Annals of Nuclear Energy. 126: 262–268. doi:10.1016/j.anucene.2018.11.023. S2CID 125724227.
- Gougam, Leila Ait; Tribeche, Mouloud (2016). "Electron-acoustic waves in a plasma with a κ -deformed Kaniadakis electron distribution". Physics of Plasmas. 23 (1): 014501. Bibcode:2016PhPl...23a4501G. doi:10.1063/1.4939477. ISSN 1070-664X.
- Chen, H.; Zhang, S. X.; Liu, S. Q. (2017). "The longitudinal plasmas modes of κ -deformed Kaniadakis distributed plasmas". Physics of Plasmas. 24 (2): 022125. Bibcode:2017PhPl...24b2125C. doi:10.1063/1.4976992. ISSN 1070-664X.









 is the entropic index associated with the
is the entropic index associated with the 



 as
as  .
.
 and is given by:
and is given by:









 , κ-Error function means the probability that X falls in the interval
, κ-Error function means the probability that X falls in the interval  .
.