| Part of a series on |
| Strategy |
|---|
 |
| Analysis methods |
| Major thinkers |
| Concepts |
| Frameworks and tools |
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational decision making in humans, animals, and computers.
Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was followed by Theory of Games and Economic Behavior (1944), co-written with Oskar Morgenstern, which considered cooperative games of several players. The second edition provided an axiomatic theory of expected utility, which allowed mathematical statisticians and economists to treat decision-making under uncertainty.
Game theory was developed extensively in the 1950s, and was explicitly applied to evolution in the 1970s, although similar developments go back at least as far as the 1930s. Game theory has been widely recognized as an important tool in many fields. John Maynard Smith was awarded the Crafoord Prize for his application of evolutionary game theory in 1999, and fifteen game theorists have won the Nobel Prize in economics as of 2020, including most recently Paul Milgrom and Robert B. Wilson.
History
Earliest results
In 1713, a letter attributed to Charles Waldegrave, an active Jacobite and uncle to British diplomat James Waldegrave, analyzed a game called "le her". Waldegrave provided a minimax mixed strategy solution to a two-person version of the card game, and the problem is now known as the Waldegrave problem.
In 1838, Antoine Augustin Cournot provided a model of competition in oligopolies. Though he did not refer to it as such, he presented a solution that is the Nash equilibrium of the game in his Recherches sur les principes mathématiques de la théorie des richesses (Researches into the Mathematical Principles of the Theory of Wealth). In 1883, Joseph Bertrand critiqued Cournot's model as unrealistic, providing an alternative model of price competition which would later be formalized by Francis Ysidro Edgeworth.
In 1913, Ernst Zermelo published Über eine Anwendung der Mengenlehre auf die Theorie des Schachspiels (On an Application of Set Theory to the Theory of the Game of Chess), which proved that the optimal chess strategy is strictly determined.
Foundation

The work of John von Neumann established game theory as its own independent field in the early-to-mid 20th century, with von Neumann publishing his paper On the Theory of Games of Strategy in 1928. Von Neumann's original proof used Brouwer's fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. Von Neumann's work in game theory culminated in his 1944 book Theory of Games and Economic Behavior, co-authored with Oskar Morgenstern. The second edition of this book provided an axiomatic theory of utility, which reincarnated Daniel Bernoulli's old theory of utility (of money) as an independent discipline. This foundational work contains the method for finding mutually consistent solutions for two-person zero-sum games. Subsequent work focused primarily on cooperative game theory, which analyzes optimal strategies for groups of individuals, presuming that they can enforce agreements between them about proper strategies.
In his 1938 book Applications aux Jeux de Hasard and earlier notes, Émile Borel proved a minimax theorem for two-person zero-sum matrix games only when the pay-off matrix is symmetric and provided a solution to a non-trivial infinite game (known in English as Blotto game). Borel conjectured the non-existence of mixed-strategy equilibria in finite two-person zero-sum games, a conjecture that was proved false by von Neumann.

In 1950, John Nash developed a criterion for mutual consistency of players' strategies known as the Nash equilibrium, applicable to a wider variety of games than the criterion proposed by von Neumann and Morgenstern. Nash proved that every finite n-player, non-zero-sum (not just two-player zero-sum) non-cooperative game has what is now known as a Nash equilibrium in mixed strategies.
Game theory experienced a flurry of activity in the 1950s, during which the concepts of the core, the extensive form game, fictitious play, repeated games, and the Shapley value were developed. The 1950s also saw the first applications of game theory to philosophy and political science. The first mathematical discussion of the prisoner's dilemma appeared, and an experiment was undertaken by mathematicians Merrill M. Flood and Melvin Dresher, as part of the RAND Corporation's investigations into game theory. RAND pursued the studies because of possible applications to global nuclear strategy.
Prize-winning achievements
In 1965, Reinhard Selten introduced his solution concept of subgame perfect equilibria, which further refined the Nash equilibrium. Later he would introduce trembling hand perfection as well. In 1994 Nash, Selten and Harsanyi became Economics Nobel Laureates for their contributions to economic game theory.
In the 1970s, game theory was extensively applied in biology, largely as a result of the work of John Maynard Smith and his evolutionarily stable strategy. In addition, the concepts of correlated equilibrium, trembling hand perfection and common knowledge were introduced and analyzed.
In 1994, John Nash was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in the Economic Sciences for his contribution to game theory. Nash's most famous contribution to game theory is the concept of the Nash equilibrium, which is a solution concept for non-cooperative games, published in 1951. A Nash equilibrium is a set of strategies, one for each player, such that no player can improve their payoff by unilaterally changing their strategy.
In 2005, game theorists Thomas Schelling and Robert Aumann followed Nash, Selten, and Harsanyi as Nobel Laureates. Schelling worked on dynamic models, early examples of evolutionary game theory. Aumann contributed more to the equilibrium school, introducing equilibrium coarsening and correlated equilibria, and developing an extensive formal analysis of the assumption of common knowledge and of its consequences.
In 2007, Leonid Hurwicz, Eric Maskin, and Roger Myerson were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics "for having laid the foundations of mechanism design theory". Myerson's contributions include the notion of proper equilibrium, and an important graduate text: Game Theory, Analysis of Conflict. Hurwicz introduced and formalized the concept of incentive compatibility.
In 2012, Alvin E. Roth and Lloyd S. Shapley were awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics "for the theory of stable allocations and the practice of market design". In 2014, the Nobel went to game theorist Jean Tirole.
Different types of games
See also: List of games in game theoryCooperative / non-cooperative
Main articles: Cooperative game theory and Non-cooperative gameA game is cooperative if the players are able to form binding commitments externally enforced (e.g. through contract law). A game is non-cooperative if players cannot form alliances or if all agreements need to be self-enforcing (e.g. through credible threats).
Cooperative games are often analyzed through the framework of cooperative game theory, which focuses on predicting which coalitions will form, the joint actions that groups take, and the resulting collective payoffs. It is different from non-cooperative game theory which focuses on predicting individual players' actions and payoffs by analyzing Nash equilibria.
Cooperative game theory provides a high-level approach as it describes only the structure and payoffs of coalitions, whereas non-cooperative game theory also looks at how strategic interaction will affect the distribution of payoffs. As non-cooperative game theory is more general, cooperative games can be analyzed through the approach of non-cooperative game theory (the converse does not hold) provided that sufficient assumptions are made to encompass all the possible strategies available to players due to the possibility of external enforcement of cooperation.
Symmetric / asymmetric
| E | F | |
| E | 1, 2 | 0, 0 |
| F | 0, 0 | 1, 2 |
| An asymmetric game | ||
A symmetric game is a game where each player earns the same payoff when making the same choice. In other words, the identity of the player does not change the resulting game facing the other player. Many of the commonly studied 2×2 games are symmetric. The standard representations of chicken, the prisoner's dilemma, and the stag hunt are all symmetric games.
The most commonly studied asymmetric games are games where there are not identical strategy sets for both players. For instance, the ultimatum game and similarly the dictator game have different strategies for each player. It is possible, however, for a game to have identical strategies for both players, yet be asymmetric. For example, the game pictured in this section's graphic is asymmetric despite having identical strategy sets for both players.
Zero-sum / non-zero-sum
| A | B | |
| A | –1, 1 | 3, −3 |
| B | 0, 0 | –2, 2 |
| A zero-sum game | ||
Zero-sum games (more generally, constant-sum games) are games in which choices by players can neither increase nor decrease the available resources. In zero-sum games, the total benefit goes to all players in a game, for every combination of strategies, and always adds to zero (more informally, a player benefits only at the equal expense of others). Poker exemplifies a zero-sum game (ignoring the possibility of the house's cut), because one wins exactly the amount one's opponents lose. Other zero-sum games include matching pennies and most classical board games including Go and chess.
Many games studied by game theorists (including the famed prisoner's dilemma) are non-zero-sum games, because the outcome has net results greater or less than zero. Informally, in non-zero-sum games, a gain by one player does not necessarily correspond with a loss by another.
Furthermore, constant-sum games correspond to activities like theft and gambling, but not to the fundamental economic situation in which there are potential gains from trade. It is possible to transform any constant-sum game into a (possibly asymmetric) zero-sum game by adding a dummy player (often called "the board") whose losses compensate the players' net winnings.
Simultaneous / sequential
Main articles: Simultaneous game and Sequential gameSimultaneous games are games where both players move simultaneously, or instead the later players are unaware of the earlier players' actions (making them effectively simultaneous). Sequential games (or dynamic games) are games where players do not make decisions simultaneously, and player's earlier actions affect the outcome and decisions of other players. This need not be perfect information about every action of earlier players; it might be very little knowledge. For instance, a player may know that an earlier player did not perform one particular action, while they do not know which of the other available actions the first player actually performed.
The difference between simultaneous and sequential games is captured in the different representations discussed above. Often, normal form is used to represent simultaneous games, while extensive form is used to represent sequential ones. The transformation of extensive to normal form is one way, meaning that multiple extensive form games correspond to the same normal form. Consequently, notions of equilibrium for simultaneous games are insufficient for reasoning about sequential games; see subgame perfection.
In short, the differences between sequential and simultaneous games are as follows:
| Sequential | Simultaneous | |
|---|---|---|
| Normally denoted by | Decision trees | Payoff matrices |
| Prior knowledge of opponent's move? |
Yes | No |
| Time axis? | Yes | No |
| Also known as | Extensive-form game Extensive game |
Strategy game Strategic game |
Perfect information and imperfect information
Main article: Perfect information
An important subset of sequential games consists of games of perfect information. A game with perfect information means that all players, at every move in the game, know the previous history of the game and the moves previously made by all other players. An imperfect information game is played when the players do not know all moves already made by the opponent such as a simultaneous move game. Examples of perfect-information games include tic-tac-toe, checkers, chess, and Go.
Many card games are games of imperfect information, such as poker and bridge. Perfect information is often confused with complete information, which is a similar concept pertaining to the common knowledge of each player's sequence, strategies, and payoffs throughout gameplay. Complete information requires that every player know the strategies and payoffs available to the other players but not necessarily the actions taken, whereas perfect information is knowledge of all aspects of the game and players. Games of incomplete information can be reduced, however, to games of imperfect information by introducing "moves by nature".
Bayesian game
Main article: Bayesian gameOne of the assumptions of the Nash equilibrium is that every player has correct beliefs about the actions of the other players. However, there are many situations in game theory where participants do not fully understand the characteristics of their opponents. Negotiators may be unaware of their opponent's valuation of the object of negotiation, companies may be unaware of their opponent's cost functions, combatants may be unaware of their opponent's strengths, and jurors may be unaware of their colleague's interpretation of the evidence at trial. In some cases, participants may know the character of their opponent well, but may not know how well their opponent knows his or her own character.
Bayesian game means a strategic game with incomplete information. For a strategic game, decision makers are players, and every player has a group of actions. A core part of the imperfect information specification is the set of states. Every state completely describes a collection of characteristics relevant to the player such as their preferences and details about them. There must be a state for every set of features that some player believes may exist.
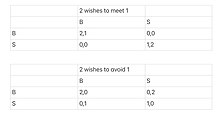
For example, where Player 1 is unsure whether Player 2 would rather date her or get away from her, while Player 2 understands Player 1's preferences as before. To be specific, supposing that Player 1 believes that Player 2 wants to date her under a probability of 1/2 and get away from her under a probability of 1/2 (this evaluation comes from Player 1's experience probably: she faces players who want to date her half of the time in such a case and players who want to avoid her half of the time). Due to the probability involved, the analysis of this situation requires to understand the player's preference for the draw, even though people are only interested in pure strategic equilibrium.
Combinatorial games
Games in which the difficulty of finding an optimal strategy stems from the multiplicity of possible moves are called combinatorial games. Examples include chess and Go. Games that involve imperfect information may also have a strong combinatorial character, for instance backgammon. There is no unified theory addressing combinatorial elements in games. There are, however, mathematical tools that can solve some particular problems and answer some general questions.
Games of perfect information have been studied in combinatorial game theory, which has developed novel representations, e.g. surreal numbers, as well as combinatorial and algebraic (and sometimes non-constructive) proof methods to solve games of certain types, including "loopy" games that may result in infinitely long sequences of moves. These methods address games with higher combinatorial complexity than those usually considered in traditional (or "economic") game theory. A typical game that has been solved this way is Hex. A related field of study, drawing from computational complexity theory, is game complexity, which is concerned with estimating the computational difficulty of finding optimal strategies.
Research in artificial intelligence has addressed both perfect and imperfect information games that have very complex combinatorial structures (like chess, go, or backgammon) for which no provable optimal strategies have been found. The practical solutions involve computational heuristics, like alpha–beta pruning or use of artificial neural networks trained by reinforcement learning, which make games more tractable in computing practice.
Discrete and continuous games
Much of game theory is concerned with finite, discrete games that have a finite number of players, moves, events, outcomes, etc. Many concepts can be extended, however. Continuous games allow players to choose a strategy from a continuous strategy set. For instance, Cournot competition is typically modeled with players' strategies being any non-negative quantities, including fractional quantities.
Differential games
Main article: Differential gameDifferential games such as the continuous pursuit and evasion game are continuous games where the evolution of the players' state variables is governed by differential equations. The problem of finding an optimal strategy in a differential game is closely related to the optimal control theory. In particular, there are two types of strategies: the open-loop strategies are found using the Pontryagin maximum principle while the closed-loop strategies are found using Bellman's Dynamic Programming method.
A particular case of differential games are the games with a random time horizon. In such games, the terminal time is a random variable with a given probability distribution function. Therefore, the players maximize the mathematical expectation of the cost function. It was shown that the modified optimization problem can be reformulated as a discounted differential game over an infinite time interval.
Evolutionary game theory
Main article: Evolutionary game theoryEvolutionary game theory studies players who adjust their strategies over time according to rules that are not necessarily rational or farsighted. In general, the evolution of strategies over time according to such rules is modeled as a Markov chain with a state variable such as the current strategy profile or how the game has been played in the recent past. Such rules may feature imitation, optimization, or survival of the fittest.
In biology, such models can represent evolution, in which offspring adopt their parents' strategies and parents who play more successful strategies (i.e. corresponding to higher payoffs) have a greater number of offspring. In the social sciences, such models typically represent strategic adjustment by players who play a game many times within their lifetime and, consciously or unconsciously, occasionally adjust their strategies.
Stochastic outcomes (and relation to other fields)
Individual decision problems with stochastic outcomes are sometimes considered "one-player games". They may be modeled using similar tools within the related disciplines of decision theory, operations research, and areas of artificial intelligence, particularly AI planning (with uncertainty) and multi-agent system. Although these fields may have different motivators, the mathematics involved are substantially the same, e.g. using Markov decision processes (MDP).
Stochastic outcomes can also be modeled in terms of game theory by adding a randomly acting player who makes "chance moves" ("moves by nature"). This player is not typically considered a third player in what is otherwise a two-player game, but merely serves to provide a roll of the dice where required by the game.
For some problems, different approaches to modeling stochastic outcomes may lead to different solutions. For example, the difference in approach between MDPs and the minimax solution is that the latter considers the worst-case over a set of adversarial moves, rather than reasoning in expectation about these moves given a fixed probability distribution. The minimax approach may be advantageous where stochastic models of uncertainty are not available, but may also be overestimating extremely unlikely (but costly) events, dramatically swaying the strategy in such scenarios if it is assumed that an adversary can force such an event to happen. (See Black swan theory for more discussion on this kind of modeling issue, particularly as it relates to predicting and limiting losses in investment banking.)
General models that include all elements of stochastic outcomes, adversaries, and partial or noisy observability (of moves by other players) have also been studied. The "gold standard" is considered to be partially observable stochastic game (POSG), but few realistic problems are computationally feasible in POSG representation.
Metagames
These are games the play of which is the development of the rules for another game, the target or subject game. Metagames seek to maximize the utility value of the rule set developed. The theory of metagames is related to mechanism design theory.
The term metagame analysis is also used to refer to a practical approach developed by Nigel Howard, whereby a situation is framed as a strategic game in which stakeholders try to realize their objectives by means of the options available to them. Subsequent developments have led to the formulation of confrontation analysis.
Mean field game theory
Main article: Mean field game theoryMean field game theory is the study of strategic decision making in very large populations of small interacting agents. This class of problems was considered in the economics literature by Boyan Jovanovic and Robert W. Rosenthal, in the engineering literature by Peter E. Caines, and by mathematicians Pierre-Louis Lions and Jean-Michel Lasry.
Representation of games
The games studied in game theory are well-defined mathematical objects. To be fully defined, a game must specify the following elements: the players of the game, the information and actions available to each player at each decision point, and the payoffs for each outcome. (Eric Rasmusen refers to these four "essential elements" by the acronym "PAPI".) A game theorist typically uses these elements, along with a solution concept of their choosing, to deduce a set of equilibrium strategies for each player such that, when these strategies are employed, no player can profit by unilaterally deviating from their strategy. These equilibrium strategies determine an equilibrium to the game—a stable state in which either one outcome occurs or a set of outcomes occur with known probability.
Most cooperative games are presented in the characteristic function form, while the extensive and the normal forms are used to define noncooperative games.
Extensive form
Main article: Extensive form game
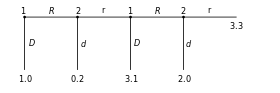
The extensive form can be used to formalize games with a time sequencing of moves. Extensive form games can be visualized using game trees (as pictured here). Here each vertex (or node) represents a point of choice for a player. The player is specified by a number listed by the vertex. The lines out of the vertex represent a possible action for that player. The payoffs are specified at the bottom of the tree. The extensive form can be viewed as a multi-player generalization of a decision tree. To solve any extensive form game, backward induction must be used. It involves working backward up the game tree to determine what a rational player would do at the last vertex of the tree, what the player with the previous move would do given that the player with the last move is rational, and so on until the first vertex of the tree is reached.
The game pictured consists of two players. The way this particular game is structured (i.e., with sequential decision making and perfect information), Player 1 "moves" first by choosing either F or U (fair or unfair). Next in the sequence, Player 2, who has now observed Player 1's move, can choose to play either A or R (accept or reject). Once Player 2 has made their choice, the game is considered finished and each player gets their respective payoff, represented in the image as two numbers, where the first number represents Player 1's payoff, and the second number represents Player 2's payoff. Suppose that Player 1 chooses U and then Player 2 chooses A: Player 1 then gets a payoff of "eight" (which in real-world terms can be interpreted in many ways, the simplest of which is in terms of money but could mean things such as eight days of vacation or eight countries conquered or even eight more opportunities to play the same game against other players) and Player 2 gets a payoff of "two".
The extensive form can also capture simultaneous-move games and games with imperfect information. To represent it, either a dotted line connects different vertices to represent them as being part of the same information set (i.e. the players do not know at which point they are), or a closed line is drawn around them. (See example in the imperfect information section.)
Normal form
| Player 2 chooses Left |
Player 2 chooses Right | |
| Player 1 chooses Up |
4, 3 | –1, –1 |
| Player 1 chooses Down |
0, 0 | 3, 4 |
| Normal form or payoff matrix of a 2-player, 2-strategy game | ||
The normal (or strategic form) game is usually represented by a matrix which shows the players, strategies, and payoffs (see the example to the right). More generally it can be represented by any function that associates a payoff for each player with every possible combination of actions. In the accompanying example there are two players; one chooses the row and the other chooses the column. Each player has two strategies, which are specified by the number of rows and the number of columns. The payoffs are provided in the interior. The first number is the payoff received by the row player (Player 1 in our example); the second is the payoff for the column player (Player 2 in our example). Suppose that Player 1 plays Up and that Player 2 plays Left. Then Player 1 gets a payoff of 4, and Player 2 gets 3.
When a game is presented in normal form, it is presumed that each player acts simultaneously or, at least, without knowing the actions of the other. If players have some information about the choices of other players, the game is usually presented in extensive form.
Every extensive-form game has an equivalent normal-form game, however, the transformation to normal form may result in an exponential blowup in the size of the representation, making it computationally impractical.
Characteristic function form
Main article: Cooperative game theoryIn cooperative game theory the characteristic function lists the payoff of each coalition. The origin of this formulation is in John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern's book.
Formally, a characteristic function is a function from the set of all possible coalitions of players to a set of payments, and also satisfies . The function describes how much collective payoff a set of players can gain by forming a coalition.
Alternative game representations
See also: Succinct gameAlternative game representation forms are used for some subclasses of games or adjusted to the needs of interdisciplinary research. In addition to classical game representations, some of the alternative representations also encode time related aspects.
| Name | Year | Means | Type of games | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congestion game | 1973 | functions | subset of n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
| Sequential form | 1994 | matrices | 2-person games of imperfect information | No |
| Timed games | 1994 | functions | 2-person games | Yes |
| Gala | 1997 | logic | n-person games of imperfect information | No |
| Graphical games | 2001 | graphs, functions | n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
| Local effect games | 2003 | functions | subset of n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
| GDL | 2005 | logic | deterministic n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
| Game Petri-nets | 2006 | Petri net | deterministic n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
| Continuous games | 2007 | functions | subset of 2-person games of imperfect information | Yes |
| PNSI | 2008 | Petri net | n-person games of imperfect information | Yes |
| Action graph games | 2012 | graphs, functions | n-person games, simultaneous moves | No |
General and applied uses
As a method of applied mathematics, game theory has been used to study a wide variety of human and animal behaviors. It was initially developed in economics to understand a large collection of economic behaviors, including behaviors of firms, markets, and consumers. The first use of game-theoretic analysis was by Antoine Augustin Cournot in 1838 with his solution of the Cournot duopoly. The use of game theory in the social sciences has expanded, and game theory has been applied to political, sociological, and psychological behaviors as well.
Although pre-twentieth-century naturalists such as Charles Darwin made game-theoretic kinds of statements, the use of game-theoretic analysis in biology began with Ronald Fisher's studies of animal behavior during the 1930s. This work predates the name "game theory", but it shares many important features with this field. The developments in economics were later applied to biology largely by John Maynard Smith in his 1982 book Evolution and the Theory of Games.
In addition to being used to describe, predict, and explain behavior, game theory has also been used to develop theories of ethical or normative behavior and to prescribe such behavior. In economics and philosophy, scholars have applied game theory to help in the understanding of good or proper behavior. Game-theoretic approaches have also been suggested in the philosophy of language and philosophy of science. Game-theoretic arguments of this type can be found as far back as Plato. An alternative version of game theory, called chemical game theory, represents the player's choices as metaphorical chemical reactant molecules called "knowlecules". Chemical game theory then calculates the outcomes as equilibrium solutions to a system of chemical reactions.
Description and modeling
The primary use of game theory is to describe and model how human populations behave. Some scholars believe that by finding the equilibria of games they can predict how actual human populations will behave when confronted with situations analogous to the game being studied. This particular view of game theory has been criticized. It is argued that the assumptions made by game theorists are often violated when applied to real-world situations. Game theorists usually assume players act rationally, but in practice, human rationality and/or behavior often deviates from the model of rationality as used in game theory. Game theorists respond by comparing their assumptions to those used in physics. Thus while their assumptions do not always hold, they can treat game theory as a reasonable scientific ideal akin to the models used by physicists. However, empirical work has shown that in some classic games, such as the centipede game, guess 2/3 of the average game, and the dictator game, people regularly do not play Nash equilibria. There is an ongoing debate regarding the importance of these experiments and whether the analysis of the experiments fully captures all aspects of the relevant situation.
Some game theorists, following the work of John Maynard Smith and George R. Price, have turned to evolutionary game theory in order to resolve these issues. These models presume either no rationality or bounded rationality on the part of players. Despite the name, evolutionary game theory does not necessarily presume natural selection in the biological sense. Evolutionary game theory includes both biological as well as cultural evolution and also models of individual learning (for example, fictitious play dynamics).
Prescriptive or normative analysis
| Cooperate | Defect | |
| Cooperate | -1, −1 | -10, 0 |
| Defect | 0, −10 | -5, −5 |
| The prisoner's dilemma | ||
Some scholars see game theory not as a predictive tool for the behavior of human beings, but as a suggestion for how people ought to behave. Since a strategy, corresponding to a Nash equilibrium of a game constitutes one's best response to the actions of the other players – provided they are in (the same) Nash equilibrium – playing a strategy that is part of a Nash equilibrium seems appropriate. This normative use of game theory has also come under criticism.
Economics
Game theory is a major method used in mathematical economics and business for modeling competing behaviors of interacting agents. Applications include a wide array of economic phenomena and approaches, such as auctions, bargaining, mergers and acquisitions pricing, fair division, duopolies, oligopolies, social network formation, agent-based computational economics, general equilibrium, mechanism design, and voting systems; and across such broad areas as experimental economics, behavioral economics, information economics, industrial organization, and political economy.
This research usually focuses on particular sets of strategies known as "solution concepts" or "equilibria". A common assumption is that players act rationally. In non-cooperative games, the most famous of these is the Nash equilibrium. A set of strategies is a Nash equilibrium if each represents a best response to the other strategies. If all the players are playing the strategies in a Nash equilibrium, they have no unilateral incentive to deviate, since their strategy is the best they can do given what others are doing.
The payoffs of the game are generally taken to represent the utility of individual players.
A prototypical paper on game theory in economics begins by presenting a game that is an abstraction of a particular economic situation. One or more solution concepts are chosen, and the author demonstrates which strategy sets in the presented game are equilibria of the appropriate type. Economists and business professors suggest two primary uses (noted above): descriptive and prescriptive.
Managerial economics
Game theory also has an extensive use in a specific branch or stream of economics – Managerial Economics. One important usage of it in the field of managerial economics is in analyzing strategic interactions between firms. For example, firms may be competing in a market with limited resources, and game theory can help managers understand how their decisions impact their competitors and the overall market outcomes. Game theory can also be used to analyze cooperation between firms, such as in forming strategic alliances or joint ventures. Another use of game theory in managerial economics is in analyzing pricing strategies. For example, firms may use game theory to determine the optimal pricing strategy based on how they expect their competitors to respond to their pricing decisions. Overall, game theory serves as a useful tool for analyzing strategic interactions and decision making in the context of managerial economics.
Business
The Chartered Institute of Procurement & Supply (CIPS) promotes knowledge and use of game theory within the context of business procurement. CIPS and TWS Partners have conducted a series of surveys designed to explore the understanding, awareness and application of game theory among procurement professionals. Some of the main findings in their third annual survey (2019) include:
- application of game theory to procurement activity has increased – at the time it was at 19% across all survey respondents
- 65% of participants predict that use of game theory applications will grow
- 70% of respondents say that they have "only a basic or a below basic understanding" of game theory
- 20% of participants had undertaken on-the-job training in game theory
- 50% of respondents said that new or improved software solutions were desirable
- 90% of respondents said that they do not have the software they need for their work.
Project management
Sensible decision-making is critical for the success of projects. In project management, game theory is used to model the decision-making process of players, such as investors, project managers, contractors, sub-contractors, governments and customers. Quite often, these players have competing interests, and sometimes their interests are directly detrimental to other players, making project management scenarios well-suited to be modeled by game theory.
Piraveenan (2019) in his review provides several examples where game theory is used to model project management scenarios. For instance, an investor typically has several investment options, and each option will likely result in a different project, and thus one of the investment options has to be chosen before the project charter can be produced. Similarly, any large project involving subcontractors, for instance, a construction project, has a complex interplay between the main contractor (the project manager) and subcontractors, or among the subcontractors themselves, which typically has several decision points. For example, if there is an ambiguity in the contract between the contractor and subcontractor, each must decide how hard to push their case without jeopardizing the whole project, and thus their own stake in it. Similarly, when projects from competing organizations are launched, the marketing personnel have to decide what is the best timing and strategy to market the project, or its resultant product or service, so that it can gain maximum traction in the face of competition. In each of these scenarios, the required decisions depend on the decisions of other players who, in some way, have competing interests to the interests of the decision-maker, and thus can ideally be modeled using game theory.
Piraveenan summarizes that two-player games are predominantly used to model project management scenarios, and based on the identity of these players, five distinct types of games are used in project management.
- Government-sector–private-sector games (games that model public–private partnerships)
- Contractor–contractor games
- Contractor–subcontractor games
- Subcontractor–subcontractor games
- Games involving other players
In terms of types of games, both cooperative as well as non-cooperative, normal-form as well as extensive-form, and zero-sum as well as non-zero-sum are used to model various project management scenarios.
Political science
The application of game theory to political science is focused in the overlapping areas of fair division, political economy, public choice, war bargaining, positive political theory, and social choice theory. In each of these areas, researchers have developed game-theoretic models in which the players are often voters, states, special interest groups, and politicians.
Early examples of game theory applied to political science are provided by Anthony Downs. In his 1957 book An Economic Theory of Democracy, he applies the Hotelling firm location model to the political process. In the Downsian model, political candidates commit to ideologies on a one-dimensional policy space. Downs first shows how the political candidates will converge to the ideology preferred by the median voter if voters are fully informed, but then argues that voters choose to remain rationally ignorant which allows for candidate divergence. Game theory was applied in 1962 to the Cuban Missile Crisis during the presidency of John F. Kennedy.
It has also been proposed that game theory explains the stability of any form of political government. Taking the simplest case of a monarchy, for example, the king, being only one person, does not and cannot maintain his authority by personally exercising physical control over all or even any significant number of his subjects. Sovereign control is instead explained by the recognition by each citizen that all other citizens expect each other to view the king (or other established government) as the person whose orders will be followed. Coordinating communication among citizens to replace the sovereign is effectively barred, since conspiracy to replace the sovereign is generally punishable as a crime. Thus, in a process that can be modeled by variants of the prisoner's dilemma, during periods of stability no citizen will find it rational to move to replace the sovereign, even if all the citizens know they would be better off if they were all to act collectively.
A game-theoretic explanation for democratic peace is that public and open debate in democracies sends clear and reliable information regarding their intentions to other states. In contrast, it is difficult to know the intentions of nondemocratic leaders, what effect concessions will have, and if promises will be kept. Thus there will be mistrust and unwillingness to make concessions if at least one of the parties in a dispute is a non-democracy.
However, game theory predicts that two countries may still go to war even if their leaders are cognizant of the costs of fighting. War may result from asymmetric information; two countries may have incentives to mis-represent the amount of military resources they have on hand, rendering them unable to settle disputes agreeably without resorting to fighting. Moreover, war may arise because of commitment problems: if two countries wish to settle a dispute via peaceful means, but each wishes to go back on the terms of that settlement, they may have no choice but to resort to warfare. Finally, war may result from issue indivisibilities.
Game theory could also help predict a nation's responses when there is a new rule or law to be applied to that nation. One example is Peter John Wood's (2013) research looking into what nations could do to help reduce climate change. Wood thought this could be accomplished by making treaties with other nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, he concluded that this idea could not work because it would create a prisoner's dilemma for the nations.
Defence science and technology
Game theory has been used extensively to model decision-making scenarios relevant to defence applications. Most studies that has applied game theory in defence settings are concerned with Command and Control Warfare, and can be further classified into studies dealing with (i) Resource Allocation Warfare (ii) Information Warfare (iii) Weapons Control Warfare, and (iv) Adversary Monitoring Warfare. Many of the problems studied are concerned with sensing and tracking, for example a surface ship trying to track a hostile submarine and the submarine trying to evade being tracked, and the interdependent decision making that takes place with regards to bearing, speed, and the sensor technology activated by both vessels. Ho et al. provides a concise summary of the state-of-the-art with regards to the use of game theory in defence applications and highlights the benefits and limitations of game theory in the considered scenarios.
Biology
| Hawk | Dove | |
| Hawk | 20, 20 | 80, 40 |
| Dove | 40, 80 | 60, 60 |
| The hawk-dove game | ||
Unlike those in economics, the payoffs for games in biology are often interpreted as corresponding to fitness. In addition, the focus has been less on equilibria that correspond to a notion of rationality and more on ones that would be maintained by evolutionary forces. The best-known equilibrium in biology is known as the evolutionarily stable strategy (ESS), first introduced in (Maynard Smith & Price 1973). Although its initial motivation did not involve any of the mental requirements of the Nash equilibrium, every ESS is a Nash equilibrium.
In biology, game theory has been used as a model to understand many different phenomena. It was first used to explain the evolution (and stability) of the approximate 1:1 sex ratios. (Fisher 1930) suggested that the 1:1 sex ratios are a result of evolutionary forces acting on individuals who could be seen as trying to maximize their number of grandchildren.
Additionally, biologists have used evolutionary game theory and the ESS to explain the emergence of animal communication. The analysis of signaling games and other communication games has provided insight into the evolution of communication among animals. For example, the mobbing behavior of many species, in which a large number of prey animals attack a larger predator, seems to be an example of spontaneous emergent organization. Ants have also been shown to exhibit feed-forward behavior akin to fashion (see Paul Ormerod's Butterfly Economics).
Biologists have used the game of chicken to analyze fighting behavior and territoriality.
According to Maynard Smith, in the preface to Evolution and the Theory of Games, "paradoxically, it has turned out that game theory is more readily applied to biology than to the field of economic behaviour for which it was originally designed". Evolutionary game theory has been used to explain many seemingly incongruous phenomena in nature.
One such phenomenon is known as biological altruism. This is a situation in which an organism appears to act in a way that benefits other organisms and is detrimental to itself. This is distinct from traditional notions of altruism because such actions are not conscious, but appear to be evolutionary adaptations to increase overall fitness. Examples can be found in species ranging from vampire bats that regurgitate blood they have obtained from a night's hunting and give it to group members who have failed to feed, to worker bees that care for the queen bee for their entire lives and never mate, to vervet monkeys that warn group members of a predator's approach, even when it endangers that individual's chance of survival. All of these actions increase the overall fitness of a group, but occur at a cost to the individual.
Evolutionary game theory explains this altruism with the idea of kin selection. Altruists discriminate between the individuals they help and favor relatives. Hamilton's rule explains the evolutionary rationale behind this selection with the equation c < b × r, where the cost c to the altruist must be less than the benefit b to the recipient multiplied by the coefficient of relatedness r. The more closely related two organisms are causes the incidences of altruism to increase because they share many of the same alleles. This means that the altruistic individual, by ensuring that the alleles of its close relative are passed on through survival of its offspring, can forgo the option of having offspring itself because the same number of alleles are passed on. For example, helping a sibling (in diploid animals) has a coefficient of 1⁄2, because (on average) an individual shares half of the alleles in its sibling's offspring. Ensuring that enough of a sibling's offspring survive to adulthood precludes the necessity of the altruistic individual producing offspring. The coefficient values depend heavily on the scope of the playing field; for example if the choice of whom to favor includes all genetic living things, not just all relatives, we assume the discrepancy between all humans only accounts for approximately 1% of the diversity in the playing field, a coefficient that was 1⁄2 in the smaller field becomes 0.995. Similarly if it is considered that information other than that of a genetic nature (e.g. epigenetics, religion, science, etc.) persisted through time the playing field becomes larger still, and the discrepancies smaller.
Computer science and logic
Game theory has come to play an increasingly important role in logic and in computer science. Several logical theories have a basis in game semantics. In addition, computer scientists have used games to model interactive computations. Also, game theory provides a theoretical basis to the field of multi-agent systems.
Separately, game theory has played a role in online algorithms; in particular, the k-server problem, which has in the past been referred to as games with moving costs and request-answer games. Yao's principle is a game-theoretic technique for proving lower bounds on the computational complexity of randomized algorithms, especially online algorithms.
The emergence of the Internet has motivated the development of algorithms for finding equilibria in games, markets, computational auctions, peer-to-peer systems, and security and information markets. Algorithmic game theory and within it algorithmic mechanism design combine computational algorithm design and analysis of complex systems with economic theory.
Game theory has multiple applications in the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning. It is often used in developing autonomous systems that can make complex decisions in uncertain environment. Some other areas of application of game theory in AI/ML context are as follows - multi-agent system formation, reinforcement learning, mechanism design etc. By using game theory to model the behavior of other agents and anticipate their actions, AI/ML systems can make better decisions and operate more effectively.
Philosophy
| Stag | Hare | |
| Stag | 3, 3 | 0, 2 |
| Hare | 2, 0 | 2, 2 |
| Stag hunt | ||
Game theory has been put to several uses in philosophy. Responding to two papers by W.V.O. Quine (1960, 1967), Lewis (1969) used game theory to develop a philosophical account of convention. In so doing, he provided the first analysis of common knowledge and employed it in analyzing play in coordination games. In addition, he first suggested that one can understand meaning in terms of signaling games. This later suggestion has been pursued by several philosophers since Lewis. Following Lewis (1969) game-theoretic account of conventions, Edna Ullmann-Margalit (1977) and Bicchieri (2006) have developed theories of social norms that define them as Nash equilibria that result from transforming a mixed-motive game into a coordination game.
Game theory has also challenged philosophers to think in terms of interactive epistemology: what it means for a collective to have common beliefs or knowledge, and what are the consequences of this knowledge for the social outcomes resulting from the interactions of agents. Philosophers who have worked in this area include Bicchieri (1989, 1993), Skyrms (1990), and Stalnaker (1999).
The synthesis of game theory with ethics was championed by R. B. Braithwaite. The hope was that rigorous mathematical analysis of game theory might help formalize the more imprecise philosophical discussions. However, this expectation was only materialized to a limited extent.
In ethics, some (most notably David Gauthier, Gregory Kavka, and Jean Hampton) authors have attempted to pursue Thomas Hobbes' project of deriving morality from self-interest. Since games like the prisoner's dilemma present an apparent conflict between morality and self-interest, explaining why cooperation is required by self-interest is an important component of this project. This general strategy is a component of the general social contract view in political philosophy (for examples, see Gauthier (1986) and Kavka (1986)).
Other authors have attempted to use evolutionary game theory in order to explain the emergence of human attitudes about morality and corresponding animal behaviors. These authors look at several games including the prisoner's dilemma, stag hunt, and the Nash bargaining game as providing an explanation for the emergence of attitudes about morality (see, e.g., Skyrms (1996, 2004) and Sober and Wilson (1998)).
Epidemiology
Since the decision to take a vaccine for a particular disease is often made by individuals, who may consider a range of factors and parameters in making this decision (such as the incidence and prevalence of the disease, perceived and real risks associated with contracting the disease, mortality rate, perceived and real risks associated with vaccination, and financial cost of vaccination), game theory has been used to model and predict vaccination uptake in a society.
Well known examples of games
Prisoner's dilemma
Main article: Prisoner's dilemma| BA | B stays silent |
B betrays |
|---|---|---|
| A stays silent |
−2−2 | 0−10 |
| A betrays |
−100 | −5−5 |
William Poundstone described the game in his 1993 book Prisoner's Dilemma:
Two members of a criminal gang, A and B, are arrested and imprisoned. Each prisoner is in solitary confinement with no means of communication with their partner. The principal charge would lead to a sentence of ten years in prison; however, the police do not have the evidence for a conviction. They plan to sentence both to two years in prison on a lesser charge but offer each prisoner a Faustian bargain: If one of them confesses to the crime of the principal charge, betraying the other, they will be pardoned and free to leave while the other must serve the entirety of the sentence instead of just two years for the lesser charge.
The dominant strategy (and therefore the best response to any possible opponent strategy), is to betray the other, which aligns with the sure-thing principle. However, both prisoners staying silent would yield a greater reward for both of them than mutual betrayal.
Battle of the sexes
Main article: Battle of the sexes (game theory)The "battle of the sexes" is a term used to describe the perceived conflict between men and women in various areas of life, such as relationships, careers, and social roles. This conflict is often portrayed in popular culture, such as movies and television shows, as a humorous or dramatic competition between the genders. This conflict can be depicted in a game theory framework. This is an example of non-cooperative games.
An example of the "battle of the sexes" can be seen in the portrayal of relationships in popular media, where men and women are often depicted as being fundamentally different and in conflict with each other. For instance, in some romantic comedies, the male and female protagonists are shown as having opposing views on love and relationships, and they have to overcome these differences in order to be together.
In this game, there are two pure strategy Nash equilibria: one where both the players choose the same strategy and the other where the players choose different options. If the game is played in mixed strategies, where each player chooses their strategy randomly, then there is an infinite number of Nash equilibria. However, in the context of the "battle of the sexes" game, the assumption is usually made that the game is played in pure strategies.
Ultimatum game
Main article: Ultimatum gameThe ultimatum game is a game that has become a popular instrument of economic experiments. An early description is by Nobel laureate John Harsanyi in 1961.
One player, the proposer, is endowed with a sum of money. The proposer is tasked with splitting it with another player, the responder (who knows what the total sum is). Once the proposer communicates his decision, the responder may accept it or reject it. If the responder accepts, the money is split per the proposal; if the responder rejects, both players receive nothing. Both players know in advance the consequences of the responder accepting or rejecting the offer. The game demonstrates how social acceptance, fairness, and generosity influence the players decisions.
Ultimatum game has a variant, that is the dictator game. They are mostly identical, except in dictator game the responder has no power to reject the proposer's offer.
Trust game
The Trust Game is an experiment designed to measure trust in economic decisions. It is also called "the investment game" and is designed to investigate trust and demonstrate its importance rather than "rationality" of self-interest. The game was designed by Berg Joyce, John Dickhaut and Kevin McCabe in 1995.
In the game, one player (the investor) is given a sum of money and must decide how much of it to give to another player (the trustee). The amount given is then tripled by the experimenter. The trustee then decides how much of the tripled amount to return to the investor. If the recipient is completely self interested, then he/she should return nothing. However that is not true as the experiment conduct. The outcome suggest that people are willing to place a trust, by risking some amount of money, in the belief that there would be reciprocity.
Cournot Competition
Main article: Cournot competitionThe Cournot competition model involves players choosing quantity of a homogenous product to produce independently and simultaneously, where marginal cost can be different for each firm and the firm's payoff is profit. The production costs are public information and the firm aims to find their profit-maximizing quantity based on what they believe the other firm will produce and behave like monopolies. In this game firms want to produce at the monopoly quantity but there is a high incentive to deviate and produce more, which decreases the market-clearing price. For example, firms may be tempted to deviate from the monopoly quantity if there is a low monopoly quantity and high price, with the aim of increasing production to maximize profit. However this option does not provide the highest payoff, as a firm's ability to maximize profits depends on its market share and the elasticity of the market demand. The Cournot equilibrium is reached when each firm operates on their reaction function with no incentive to deviate, as they have the best response based on the other firms output. Within the game, firms reach the Nash equilibrium when the Cournot equilibrium is achieved.
Bertrand Competition
Main article: Bertrand competitionThe Bertrand competition assumes homogenous products and a constant marginal cost and players choose the prices. The equilibrium of price competition is where the price is equal to marginal costs, assuming complete information about the competitors' costs. Therefore, the firms have an incentive to deviate from the equilibrium because a homogenous product with a lower price will gain all of the market share, known as a cost advantage.
In popular culture
- Based on the 1998 book by Sylvia Nasar, the life story of game theorist and mathematician John Nash was turned into the 2001 biopic A Beautiful Mind, starring Russell Crowe as Nash.
- The 1959 military science fiction novel Starship Troopers by Robert A. Heinlein mentioned "games theory" and "theory of games". In the 1997 film of the same name, the character Carl Jenkins referred to his military intelligence assignment as being assigned to "games and theory".
- The 1964 film Dr. Strangelove satirizes game theoretic ideas about deterrence theory. For example, nuclear deterrence depends on the threat to retaliate catastrophically if a nuclear attack is detected. A game theorist might argue that such threats can fail to be credible, in the sense that they can lead to subgame imperfect equilibria. The movie takes this idea one step further, with the Soviet Union irrevocably committing to a catastrophic nuclear response without making the threat public.
- The 1980s power pop band Game Theory was founded by singer/songwriter Scott Miller, who described the band's name as alluding to "the study of calculating the most appropriate action given an adversary ... to give yourself the minimum amount of failure".
- Liar Game, a 2005 Japanese manga and 2007 television series, presents the main characters in each episode with a game or problem that is typically drawn from game theory, as demonstrated by the strategies applied by the characters.
- The 1974 novel Spy Story by Len Deighton explores elements of game theory in regard to cold war army exercises.
- The 2008 novel The Dark Forest by Liu Cixin explores the relationship between extraterrestrial life, humanity, and game theory.
- Joker, the prime antagonist in the 2008 film The Dark Knight presents game theory concepts—notably the prisoner's dilemma in a scene where he asks passengers in two different ferries to bomb the other one to save their own.
- In the 2018 film Crazy Rich Asians, the female lead Rachel Chu is a professor of economics and game theory at New York University. At the beginning of the film she is seen in her NYU classroom playing a game of poker with her teaching assistant and wins the game by bluffing; then in the climax of the film, she plays a game of mahjong with her boyfriend's disapproving mother Eleanor, losing the game to Eleanor on purpose but winning her approval as a result.
- In the 2017 film Molly's Game, Brad, an inexperienced poker player, makes an irrational betting decision without realizing and causes his opponent Harlan to deviate from his Nash Equilibrium strategy, resulting in a significant loss when Harlan loses the hand.
See also
- Applied ethics – Practical application of moral considerations
- Bandwidth-sharing game – Type of resource allocation game
- Chainstore paradox – Game theory paradox
- Collective intentionality – Intentionality that occurs when two or more individuals undertake a task together
- Core (game theory) – term in game theoryPages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Glossary of game theory
- Intra-household bargaining – negotiations between members of a household to reach decisionsPages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Kingmaker scenario – Endgame situation in game theory
- Law and economics – Application of economic theory to analysis of legal systems
- Mutual assured destruction – Doctrine of military strategy
- Outline of artificial intelligence – Overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence
- Parrondo's paradox – Paradox in game theory
- Precautionary principle – Risk management strategy
- Quantum refereed game
- Risk management – Identification, evaluation and control of risks
- Self-confirming equilibrium
- Tragedy of the commons – Self-interests causing depletion of a shared resource
- Traveler's dilemma – non-zero-sum game thought experimentPages displaying wikidata descriptions as a fallback
- Wilson doctrine (economics) – Argument in economic theory
- Compositional game theory
Lists
Notes
- Although common knowledge was first discussed by the philosopher David Lewis in his dissertation (and later book) Convention in the late 1960s, it was not widely considered by economists until Robert Aumann's work in the 1970s.
- Experimental work in game theory goes by many names, experimental economics, behavioral economics, and behavioural game theory are several.
- At JEL:C7 of the Journal of Economic Literature classification codes.
- For a more detailed discussion of the use of game theory in ethics, see the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy's entry game theory and ethics.
References
- ^ Myerson, Roger B. (1991). Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict. Harvard University Press. ISBN 9780674341166.
- Shapley, Lloyd S.; Shubik, Martin (1 January 1971). "Chapter 1, Introduction, The Use of Models". Game Theory in Economics. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Neumann, John von; Morgenstern, Oskar (8 April 2007). Theory of Games and Economic Behavior. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-13061-3. Archived from the original on 28 March 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Nisan (2020). "Book report: Theory of Games and Economic Behavior (von Neumann & Morgenstern)". lesswrong.com.
- Bellhouse, David R. (2007), "The Problem of Waldegrave" (PDF), Journal Électronique d'Histoire des Probabilités et de la Statistique [Electronic Journal of Probability History and Statistics], 3 (2), archived (PDF) from the original on 20 August 2008
- Bellhouse, David R. (2015). "Le Her and Other Problems in Probability Discussed by Bernoulli, Montmort and Waldegrave". Statistical Science. 30 (1). Institute of Mathematical Statistics: 26–39. arXiv:1504.01950. Bibcode:2015arXiv150401950B. doi:10.1214/14-STS469. S2CID 59066805.
- Qin, Cheng-Zhong; Stuart, Charles (1997). "Bertrand versus Cournot Revisited". Economic Theory. 10 (3): 497–507. doi:10.1007/s001990050169. ISSN 0938-2259. JSTOR 25055054. S2CID 153431949.
- Edgeworth, Francis (1889) "The pure theory of monopoly", reprinted in Collected Papers relating to Political Economy 1925, vol.1, Macmillan.
- Zermelo, Ernst (1913). Hobson, E. W.; Love, A. E. H. (eds.). Über eine Anwendung der Mengenlehre auf die Theorie des Schachspiels [On an Application of Set Theory to the Theory of the Game of Chess] (PDF). Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Mathematicians (1912) (in German). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 501–504. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 29 August 2019.
- von Neumann, John (1928). "Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele" [On the Theory of Games of Strategy]. Mathematische Annalen [Mathematical Annals] (in German). 100 (1): 295–320. doi:10.1007/BF01448847. S2CID 122961988.
- von Neumann, John (1959). "On the Theory of Games of Strategy". In Tucker, A. W.; Luce, R. D. (eds.). Contributions to the Theory of Games. Vol. 4. Translated by Bargmann, Sonya. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 13–42. ISBN 0-691-07937-4.
- Mirowski, Philip (1992). "What Were von Neumann and Morgenstern Trying to Accomplish?". In Weintraub, E. Roy (ed.). Toward a History of Game Theory. Durham: Duke University Press. pp. 113–147. ISBN 978-0-8223-1253-6.
- Leonard, Robert (2010), Von Neumann, Morgenstern, and the Creation of Game Theory, New York: Cambridge University Press, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511778278, ISBN 978-0-521-56266-9
- Kim, Sungwook, ed. (2014). Game theory applications in network design. IGI Global. p. 3. ISBN 978-1-4666-6051-9.
- Kuhn, Steven (4 September 1997). Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). "Prisoner's Dilemma". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- Shor, Mike. "Non-Cooperative Game". GameTheory.net. Archived from the original on 1 April 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2016.
- Chandrasekaran, Ramaswamy. "Cooperative Game Theory" (PDF). University of Texas at Dallas. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 April 2016.
- Brandenburger, Adam. "Cooperative Game Theory: Characteristic Functions, Allocations, Marginal Contribution" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 August 2017. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- Shor, Mike (2006). "Symmetric Game". Game Theory.net.
- Owen, Guillermo (1995). Game Theory: Third Edition. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-12-531151-9.
- Chang, Kuang-Hua (2015). "Decisions in Engineering Design". Design Theory and Methods Using CAD/CAE. pp. 39–101. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-398512-5.00002-5. ISBN 978-0-12-398512-5.
- ^ Gibbons, Robert (1992). Game Theory for Applied Economists. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. pp. 14–17. ISBN 0-691-04308-6.
- Ferguson, Thomas S. "Game Theory" (PDF). UCLA Department of Mathematics. pp. 56–57. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 July 2004.
- Mycielski, Jan (1992). "Games with Perfect Information". Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications. Vol. 1. pp. 41–70. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(05)80006-2. ISBN 978-0-4448-8098-7.
- "Infinite Chess". PBS Infinite Series. 2 March 2017. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Perfect information defined at 0:25, with academic sources arXiv:1302.4377 and arXiv:1510.08155.
- Owen, Guillermo (1995). Game Theory: Third Edition. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-12-531151-9.
- Mirman, Leonard J. (1989). "Perfect Information". Game Theory. pp. 194–198. doi:10.1007/978-1-349-20181-5_22. ISBN 978-0-333-49537-7.
- Mirman, Leonard (1989). Perfect Information. London: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 194–195. ISBN 978-1-349-20181-5.
- Shoham & Leyton-Brown (2008), p. 60.
- Osborne, Martin J. (2000). An Introduction to Game Theory. Oxford University Press. pp. 271–272.
- Osborne, Martin J (2020). An Introduction to Game Theory. Oxford University Press. pp. 271–277.
- ^ Jörg Bewersdorff (2005). "31". Luck, logic, and white lies: the mathematics of games. A K Peters, Ltd. pp. ix–xii. ISBN 978-1-56881-210-6.
- Albert, Michael H.; Nowakowski, Richard J.; Wolfe, David (2007), Lessons in Play: In Introduction to Combinatorial Game Theory, A K Peters Ltd, pp. 3–4, ISBN 978-1-56881-277-9
- Beck, József (2008). Combinatorial Games: Tic-Tac-Toe Theory. Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–3. ISBN 978-0-521-46100-9.
- Hearn, Robert A.; Demaine, Erik D. (2009), Games, Puzzles, and Computation, A K Peters, Ltd., ISBN 978-1-56881-322-6
- Jones, M. Tim (2008). Artificial Intelligence: A Systems Approach. Jones & Bartlett Learning. pp. 106–118. ISBN 978-0-7637-7337-3.
- Petrosjan, L. A.; Murzov, N. V. (1966). "Game-theoretic problems of mechanics". Litovsk. Mat. Sb. (in Russian). 6: 423–433.
- Newton, Jonathan (2018). "Evolutionary Game Theory: A Renaissance". Games. 9 (2): 31. doi:10.3390/g9020031. hdl:10419/179191.
- Webb (2007).
- Lozovanu, D; Pickl, S (2015). A Game-Theoretical Approach to Markov Decision Processes, Stochastic Positional Games and Multicriteria Control Models. Springer, Cham. ISBN 978-3-319-11832-1.
- Osborne & Rubinstein (1994).
- ^ McMahan, Hugh Brendan (2006). Robust Planning in Domains with Stochastic Outcomes, Adversaries, and Partial Observability (PDF) (PhD dissertation). Carnegie Mellon University. pp. 3–4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 April 2011.
- Howard (1971).
- ^ Rasmusen, Eric (2007). Games and Information (4th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-1-4051-3666-2.
- ^ Kreps, David M. (1990). Game Theory and Economic Modelling. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/0198283814.001.0001. ISBN 978-0-19-828381-2.
- ^ Aumann, R. J.; Hart, S., eds. (1992). Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-444-89427-4.
- ^ Aumann, Robert J.; Heifetz, Aviad (2002). "Chapter 43 Incomplete information". Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications Volume 3. Vol. 3. pp. 1665–1686. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(02)03006-0. ISBN 978-0-444-89428-1.
- Fudenberg, Drew; Tirole, Jean (1991). Game Theory. MIT Press. p. 67. ISBN 978-0-262-06141-4.
- Williams, Paul D. (2013). Security Studies: an Introduction (second ed.). Abingdon: Routledge. pp. 55–56.
- Shoham & Leyton-Brown (2008), p. 35.
- denotes the power set of .
- Tagiew, Rustam (3 May 2011). "If more than Analytical Modeling is Needed to Predict Real Agents' Strategic Interaction". arXiv:1105.0558 .
- Rosenthal, Robert W. (December 1973). "A class of games possessing pure-strategy Nash equilibria". International Journal of Game Theory. 2 (1): 65–67. doi:10.1007/BF01737559. S2CID 121904640.
- Koller, Daphne; Megiddo, Nimrod; von Stengel, Bernhard (1994). "Fast algorithms for finding randomized strategies in game trees". Proceedings of the twenty-sixth annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing – STOC '94. pp. 750–759. doi:10.1145/195058.195451. ISBN 0-89791-663-8. S2CID 1893272.
- Alur, Rajeev; Dill, David L. (April 1994). "A theory of timed automata". Theoretical Computer Science. 126 (2): 183–235. doi:10.1016/0304-3975(94)90010-8.
- Tomlin, C.J.; Lygeros, J.; Shankar Sastry, S. (July 2000). "A game theoretic approach to controller design for hybrid systems". Proceedings of the IEEE. 88 (7): 949–970. doi:10.1109/5.871303. S2CID 1844682.
- Koller, Daphne; Pfeffer, Avi (July 1997). "Representations and solutions for game-theoretic problems". Artificial Intelligence. 94 (1–2): 167–215. doi:10.1016/S0004-3702(97)00023-4.
- Michael, Michael Kearns; Littman, Michael L. (2001). "Graphical Models for Game Theory". In UAI: 253–260. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.22.5705.
- Kearns, Michael; Littman, Michael L.; Singh, Satinder (7 March 2011). "Graphical Models for Game Theory". arXiv:1301.2281 .
- Leyton-Brown, Kevin; Tennenholtz, Moshe (2005). Local-Effect Games (PDF). Dagstuhl Seminar Proceedings. Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum für Informatik. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- Genesereth, Michael; Love, Nathaniel; Pell, Barney (15 June 2005). "General Game Playing: Overview of the AAAI Competition". AI Magazine. 26 (2): 62. doi:10.1609/aimag.v26i2.1813.
- Clempner, Julio (2006). "Modeling shortest path games with Petri nets: a Lyapunov based theory". International Journal of Applied Mathematics and Computer Science. 16 (3): 387–397.
- Sannikov, Yuliy (September 2007). "Games with Imperfectly Observable Actions in Continuous Time" (PDF). Econometrica. 75 (5): 1285–1329. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0262.2007.00795.x.
- Tagiew, Rustam (December 2008). "Multi-Agent Petri-Games". 2008 International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling Control & Automation. pp. 130–135. doi:10.1109/CIMCA.2008.15. ISBN 978-0-7695-3514-2. S2CID 16679934.
- Tagiew, Rustam (2009). "On Multi-agent Petri Net Models for Computing Extensive Finite Games". New Challenges in Computational Collective Intelligence. Studies in Computational Intelligence. Vol. 244. Springer. pp. 243–254. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-03958-4_21. ISBN 978-3-642-03957-7.
- Bhat, Navin; Leyton-Brown, Kevin (11 July 2012). "Computing Nash Equilibria of Action-Graph Games". arXiv:1207.4128 .
- Larson, Jennifer M. (11 May 2021). "Networks of Conflict and Cooperation". Annual Review of Political Science. 24 (1): 89–107. doi:10.1146/annurev-polisci-041719-102523.
- Friedman, Daniel (1998). "On economic applications of evolutionary game theory" (PDF). Journal of Evolutionary Economics. 8: 14–53. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 February 2014.
- ^ Camerer, Colin F. (2003). "1.1 What Is Game Theory Good For?". Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction. pp. 5–7. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011.
- Bruin, Boudewijn de (September 2005). "Game Theory in Philosophy". Topoi. 24 (2): 197–208. doi:10.1007/s11245-005-5055-3.
- Ross, Don (10 March 2006). "Game Theory". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Retrieved 21 August 2008.
- Velegol, Darrell; Suhey, Paul; Connolly, John; Morrissey, Natalie; Cook, Laura (17 October 2018). "Chemical Game Theory". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research. 57 (41): 13593–13607. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.8b03835. S2CID 105204747.
- Camerer, Colin F. (2003). "Introduction". Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction. pp. 1–25. Archived from the original on 14 May 2011.
- Kadane, Joseph B.; Larkey, Patrick D. (December 1983). "The Confusion of Is and Ought in Game Theoretic Contexts". Management Science. 29 (12): 1365–1379. doi:10.1287/mnsc.29.12.1365.
- Aumann, Robert J. (2008). "game theory". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics (2nd ed.). Archived from the original on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 22 August 2011.
- Shubik, Martin (1981). "Game Theory Models and Methods in Political Economy". In Arrow, Kenneth; Intriligator, Michael (eds.). Handbook of Mathematical Economics, v. 1. 1. Vol. 1. pp. 285–330. doi:10.1016/S1573-4382(81)01011-4. ISBN 978-0-444-86126-9.
- Shapiro, Carl (Spring 1989). "The Theory of Business Strategy". The RAND Journal of Economics. 20 (1). Wiley: 125–137. JSTOR 2555656. PMID 10296625..
- Agarwal, N.; Zeephongsekul, P. (11–12 December 2011). Psychological Pricing in Mergers & Acquisitions using Game Theory (PDF). 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation. Perth. Retrieved 3 February 2023.
- Tesfatsion, Leigh (2006). Agent-Based Computational Economics: A Constructive Approach to Economic Theory. Handbook of Computational Economics. Vol. 2. pp. 831–880. doi:10.1016/S1574-0021(05)02016-2. ISBN 978-0-444-51253-6.
- Joseph Y. Halpern (2008). "computer science and game theory". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics.
- Myerson, Roger B. (2008). "mechanism design". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 4 August 2011.
- Myerson, Roger B. (2008). "revelation principle". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Archived from the original on 16 May 2013. Retrieved 4 August 2011.
- Sandholm, Tuomas (2008). "computing in mechanism design". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 5 December 2011.
- ^ Nisan, Noam; Ronen, Amir (April 2001). "Algorithmic Mechanism Design". Games and Economic Behavior. 35 (1–2): 166–196. doi:10.1006/game.1999.0790.
- ^ Nisan, Noam; Roughgarden, Tim; Tardos, Eva; Vazirani, Vijay V., eds. (2007). Algorithmic Game Theory. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521872829. LCCN 2007014231.
- Brams, Steven J. (1994). Chapter 30 Voting procedures. Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications. Vol. 2. pp. 1055–1089. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(05)80062-1. ISBN 978-0-444-89427-4. and Moulin, Hervé (1994). Chapter 31 Social choice. Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications. Vol. 2. pp. 1091–1125. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(05)80063-3. ISBN 978-0-444-89427-4.
- Smith, Vernon L. (December 1992). "Game Theory and Experimental Economics: Beginnings and Early Influences". History of Political Economy. 24 (Supplement): 241–282. doi:10.1215/00182702-24-Supplement-241.
- Smith, Vernon L. (2001). "Experimental Economics". International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. pp. 5100–5108. doi:10.1016/B0-08-043076-7/02232-4. ISBN 978-0-08-043076-8.
- Plott, Charles R.; Smith, Vernon L., eds. (2008). Handbook of Experimental Economics Results. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-08-088796-8.
- Vincent P. Crawford (1997). "Theory and Experiment in the Analysis of Strategic Interaction," in Advances in Economics and Econometrics: Theory and Applications, pp. 206–242 Archived 1 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Cambridge. Reprinted in Colin F. Camerer et al., ed. (2003). Advances in Behavioral Economics, Princeton. 1986–2003 papers. Description Archived 18 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine, preview, Princeton, ch. 12
- Shubik, Martin (2002). "Chapter 62 Game theory and experimental gaming". Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications Volume 3. Vol. 3. pp. 2327–2351. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(02)03025-4. ISBN 978-0-444-89428-1.
- The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. 2008.Faruk Gul. "behavioural economics and game theory." Abstract. Archived 7 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- Camerer, Colin F. (2008). "behavioral game theory". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. Archived from the original on 23 November 2011. Retrieved 4 August 2011.
- Camerer, Colin F. (1997). "Progress in Behavioral Game Theory". Journal of Economic Perspectives. 11 (4): 172. doi:10.1257/jep.11.4.167.
- Camerer, Colin F. (2003). Behavioral Game Theory. Princeton. Description Archived 14 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine, preview Archived 26 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine (+), and ch. 1 link Archived 4 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine.
- Camerer, Colin F.; Loewenstein, George; Rabin, Matthew, eds. (2011). Advances in Behavioral Economics. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-2911-8.
- Fudenberg, Drew (2006). "Advancing Beyond Advances in Behavioral Economics". Journal of Economic Literature. 44 (3): 694–711. doi:10.1257/jel.44.3.694. JSTOR 30032349. S2CID 3490729.
- Tirole, Jean (1988). The Theory of Industrial Organization. MIT Press. Description and chapter-preview links, pp. vii–ix, "General Organization," pp. 5–6, and "Non-Cooperative Game Theory: A User's Guide Manual,' " ch. 11, pp. 423–59.
- Bagwell, Kyle; Wolinsky, Asher (2002). "Game theory and industrial organization". Handbook of Game Theory with Economic Applications Volume 3. Vol. 3. pp. 1851–1895. doi:10.1016/S1574-0005(02)03012-6. ISBN 978-0-444-89428-1.
- Fels, E. M. (1961). "Review of Strategy and Market Structure: Competition, Oligopoly, and the Theory of Games". Weltwirtschaftliches Archiv. 87: 12–14. JSTOR 40434883.
- Reid, Gavin C. (1982). "Review of Market Structure and Behavior". The Economic Journal. 92 (365): 200–202. doi:10.2307/2232276. JSTOR 2232276.
- Martin Shubik (1981). "Game Theory Models and Methods in Political Economy," in Handbook of Mathematical Economics, v. 1, pp. 285–330 doi:10.1016/S1573-4382(81)01011-4.
- Martin Shubik (1987). A Game-Theoretic Approach to Political Economy. MIT Press. Description. Archived 29 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- Martin Shubik (1978). "Game Theory: Economic Applications," in W. Kruskal and J.M. Tanur, ed., International Encyclopedia of Statistics, v. 2, pp. 372–78.
- Christen, Markus (1 July 1998). "Game-theoretic model to examine the two tradeoffs in the acquisition of information for a careful balancing act". INSEAD. Archived from the original on 24 May 2013. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
- Chevalier-Roignant, Benoît; Trigeorgis, Lenos (15 February 2012). "Options Games: Balancing the trade-off between flexibility and commitment". The European Financial Review. Archived from the original on 20 June 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- Wilkinson, Nick (2005). "Game theory". Managerial Economics. pp. 331–381. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511810534.015. ISBN 978-0-521-81993-0.
- "CIPS and TWS Partners promote game theory on the global stage". 27 November 2020. Archived from the original on 27 November 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- CIPS (2021), Game Theory Archived 11 April 2021 at the Wayback Machine, CIPS in conjunction with TWS Partners, accessed 11 April 2021
- ^ Piraveenan, Mahendra (2019). "Applications of Game Theory in Project Management: A Structured Review and Analysis". Mathematics. 7 (9): 858. doi:10.3390/math7090858.
- "What game theory tells us about politics and society". MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 4 December 2018. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Downs (1957).
- Brams, Steven J. (1 January 2001). "Game theory and the Cuban missile crisis". Plus Magazine. Archived from the original on 24 April 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
- "How game theory explains 'irrational' behavior". MIT Sloan. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Levy, Gilat; Razin, Ronny (March 2004). "It Takes Two: An Explanation for the Democratic Peace". Journal of the European Economic Association. 2 (1): 1–29. doi:10.1162/154247604323015463.
- Fearon, James D. (1 January 1995). "Rationalist Explanations for War". International Organization. 49 (3): 379–414. doi:10.1017/s0020818300033324. JSTOR 2706903. S2CID 38573183.
- Wood, Peter John (February 2011). "Climate change and game theory". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1219 (1): 153–170. Bibcode:2011NYASA1219..153W. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05891.x. PMID 21332497.
- ^ Ho, Edwin; Rajagopalan, Arvind; Skvortsov, Alex; Arulampalam, Sanjeev; Piraveenan, Mahendra (28 January 2022). "Game Theory in Defence Applications: A Review". Sensors. 22 (3): 1032. arXiv:2111.01876. Bibcode:2022Senso..22.1032H. doi:10.3390/s22031032. PMC 8838118. PMID 35161778.
- Harper & Maynard Smith (2003).
- Maynard Smith, John (1974). "The theory of games and the evolution of animal conflicts" (PDF). Journal of Theoretical Biology. 47 (1): 209–221. Bibcode:1974JThBi..47..209M. doi:10.1016/0022-5193(74)90110-6. PMID 4459582.
- Alexander, J. McKenzie (19 July 2009). "Evolutionary Game Theory". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- ^ Okasha, Samir (3 June 2003). "Biological Altruism". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Stanford University. Retrieved 3 January 2013.
- Shoham, Yoav; Leyton-Brown, Kevin (2008). Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-47524-2.
- Ben-David et al. (1994).
- Halpern, Joseph Y. (2008). "Computer science and game theory". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics (2nd ed.).
- Shoham, Yoav (August 2008). "Computer science and game theory". Communications of the ACM. 51 (8): 74–79. doi:10.1145/1378704.1378721.
- Littman, Amy; Littman, Michael L. (2007). "Introduction to the Special Issue on Learning and Computational Game Theory". Machine Learning. 67 (1–2): 3–6. doi:10.1007/s10994-007-0770-1. S2CID 22635389.
- Hanley, John T. (14 December 2021). "GAMES, game theory and artificial intelligence". Journal of Defense Analytics and Logistics. 5 (2): 114–130. doi:10.1108/JDAL-10-2021-0011.
- Albrecht, Stefano V.; Christianos, Filippos; Schäfer, Lukas (2024). Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: Foundations and Modern Approaches. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-04937-5.
- Parashar, Nilesh (15 August 2022). "What is Game Theory in AI?". Medium.
- Hazra, Tanmoy; Anjaria, Kushal (March 2022). "Applications of game theory in deep learning: a survey". Multimedia Tools and Applications. 81 (6): 8963–8994. doi:10.1007/s11042-022-12153-2. PMC 9039031. PMID 35496996.
- Skyrms (1996)
- Grim et al. (2004).
- Ullmann-Margalit, E. (1977), The Emergence of Norms, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-824411-0
- Bicchieri, Cristina (2006), The Grammar of Society: the Nature and Dynamics of Social Norms, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-57372-6
- Bicchieri, Cristina (1989). "Self-Refuting Theories of Strategic Interaction: A Paradox of Common Knowledge". Erkenntnis. 30 (1–2): 69–85. doi:10.1007/BF00184816. S2CID 120848181.
- Bicchieri, Cristina (1993), Rationality and Coordination, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-57444-0
- Skyrms, Brian (1990), The Dynamics of Rational Deliberation, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-21885-7
- Stalnaker, Robert (October 1996). "Knowledge, Belief and Counterfactual Reasoning in Games". Economics and Philosophy. 12 (2): 133–163. doi:10.1017/S0266267100004132.
- Braithwaite, Richard Bevan (1955). Theory of Games as a Tool for the Moral Philosopher. An Inaugural Lecture Delivered in Cambridge on 2 December 1954. University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-11351-9.
- Kuhn, Steven T. (July 2004). "Reflections on Ethics and Game Theory". Synthese. 141 (1): 1–44. doi:10.1023/B:SYNT.0000035846.91195.cb.
- Chang, Sheryl L.; Piraveenan, Mahendra; Pattison, Philippa; Prokopenko, Mikhail (2020). "Game theoretic modelling of infectious disease dynamics and intervention methods: a review". Journal of Biological Dynamics. 14 (1): 57–89. arXiv:1901.04143. Bibcode:2020JBioD..14...57C. doi:10.1080/17513758.2020.1720322. PMID 31996099.
- Roberts, Siobhan (20 December 2020). "'The Pandemic Is a Prisoner's Dilemma Game'". The New York Times.
- Poundstone 1993, pp. 8, 117.
- Rapoport, Anatol (1987). "Prisoner's Dilemma". The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics. pp. 1–5. doi:10.1057/978-1-349-95121-5_1850-1. ISBN 978-1-349-95121-5.
- "Battle of the Sexes | History, Participants, & Facts | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Athenarium (12 August 2020). "Battle of the Sexes – Nash equilibrium in mixed strategies for coordination". Athenarium. Archived from the original on 23 April 2023. Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- Harsanyi, John C. (June 1961). "On the rationality postulates underlying the theory of cooperative games". Journal of Conflict Resolution. 5 (2): 179–196. doi:10.1177/002200276100500205.
- Aoki, Ryuta; Yomogida, Yukihito; Matsumoto, Kenji (January 2015). "The neural bases for valuing social equality". Neuroscience Research. 90: 33–40. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2014.10.020. PMID 25452125.
- Berg, Joyce; Dickhaut, John; McCabe, Kevin (July 1995). "Trust, Reciprocity, and Social History". Games and Economic Behavior. 10 (1): 122–142. doi:10.1006/game.1995.1027.
- Johnson, Noel D.; Mislin, Alexandra A. (October 2011). "Trust games: A meta-analysis". Journal of Economic Psychology. 32 (5): 865–889. doi:10.1016/j.joep.2011.05.007.
- "Cournot (Nash) Equilibrium". OECD. 18 April 2013. Archived from the original on 23 May 2021. Retrieved 20 April 2021.
- Spulber, Daniel F. (1995). "Bertrand Competition when Rivals' Costs are Unknown". The Journal of Industrial Economics. 43 (1): 1–11. doi:10.2307/2950422. JSTOR 2950422.
- Nasar, Sylvia (1998) A Beautiful Mind, Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-81906-6.
- Singh, Simon (14 June 1998). "Between Genius and Madness". The New York Times.
- Heinlein, Robert A. (1959), Starship Troopers
- Dr. Strangelove Or How I Learned to Stop Worrying and Love the Bomb. 29 January 1964. 51 minutes in.
... is that the whole point of the doomsday machine is lost, if you keep it a secret!
- Guzman, Rafer (6 March 1996). "Star on hold: Faithful following, meager sales". Pacific Sun. Archived from the original on 6 November 2013. Retrieved 25 July 2018..
- "Liar Game (manga) – Anime News Network". www.animenewsnetwork.com. Archived from the original on 25 November 2022. Retrieved 25 November 2022.
- Chaffin, Sean (20 August 2018). "Poker and Game Theory Featured in Hit Film 'Crazy Rich Asians'". PokerNews.com. Archived from the original on 5 November 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- Bean, Travis (8 February 2019). "Game theory in Crazy Rich Asians: explaining the Mahjong showdown between Rachel and Eleanor". Colossus. Archived from the original on 5 November 2022. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- "An Analysis of the Applications of Networks in "Molly's Game" : Networks Course blog for INFO 2040/CS 2850/Econ 2040/SOC 2090". Archived from the original on 8 April 2023. Retrieved 8 April 2023.
Sources
- Ben-David, S.; Borodin, A.; Karp, R.; Tardos, G.; Wigderson, A. (January 1994). "On the power of randomization in on-line algorithms". Algorithmica. 11 (1): 2–14. doi:10.1007/BF01294260. S2CID 26771869.
- Downs, Anthony (1957), An Economic theory of Democracy, New York: Harper
- Fisher, Sir Ronald Aylmer (1930). The Genetical Theory of Natural Selection. Clarendon Press.
- Gauthier, David (1986), Morals by agreement, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-824992-4
- Grim, Patrick; Kokalis, Trina; Alai-Tafti, Ali; Kilb, Nicholas; St Denis, Paul (2004), "Making meaning happen", Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 16 (4): 209–243, doi:10.1080/09528130412331294715, S2CID 5737352
- Harper, David; Maynard Smith, John (2003), Animal signals, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-852685-8
- Howard, Nigel (1971), Paradoxes of Rationality: Games, Metagames, and Political Behavior, Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, ISBN 978-0-262-58237-7
- Kavka, Gregory S. (1986). Hobbesian Moral and Political Theory. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-02765-4.
- Lewis, David (1969), Convention: A Philosophical Study, ISBN 978-0-631-23257-5 (2002 edition)
- Maynard Smith, John; Price, George R. (1973), "The logic of animal conflict", Nature, 246 (5427): 15–18, Bibcode:1973Natur.246...15S, doi:10.1038/246015a0, S2CID 4224989
- Osborne, Martin J.; Rubinstein, Ariel (1994), A course in game theory, MIT Press, ISBN 978-0-262-65040-3. A modern introduction at the graduate level.
- Poundstone, William (1993). Prisoner's Dilemma (1st Anchor Books ed.). New York: Anchor. ISBN 0-385-41580-X.
- Quine, W.v.O (1967), "Truth by Convention", Philosophica Essays for A.N. Whitehead, Russel and Russel Publishers, ISBN 978-0-8462-0970-6
- Quine, W.v.O (1960), "Carnap and Logical Truth", Synthese, 12 (4): 350–374, doi:10.1007/BF00485423, S2CID 46979744
- Skyrms, Brian (1996), Evolution of the social contract, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-55583-8
- Skyrms, Brian (2004), The stag hunt and the evolution of social structure, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-53392-8
- Sober, Elliott; Wilson, David Sloan (1998), Unto others: the evolution and psychology of unselfish behavior, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-93047-6
- Webb, James N. (2007), Game theory: decisions, interaction and evolution, Undergraduate mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-84628-423-6 Consistent treatment of game types usually claimed by different applied fields, e.g. Markov decision processes.
Further reading
Textbooks and general literature
- Aumann, Robert J (1987), "game theory", The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics, vol. 2, pp. 460–82.
- Camerer, Colin (2003), "Introduction", Behavioral Game Theory: Experiments in Strategic Interaction, Russell Sage Foundation, pp. 1–25, ISBN 978-0-691-09039-9, archived from the original on 14 May 2011, retrieved 9 February 2011, Description.
- Dutta, Prajit K. (1999), Strategies and games: theory and practice, MIT Press, ISBN 978-0-262-04169-0. Suitable for undergraduate and business students.
- Fernandez, L F.; Bierman, H S. (1998), Game theory with economic applications, Addison-Wesley, ISBN 978-0-201-84758-1. Suitable for upper-level undergraduates.
- Gaffal, Margit; Padilla Gálvez, Jesús (2014). Dynamics of Rational Negotiation: Game Theory, Language Games and Forms of Life. Springer.
- Gibbons, Robert D. (1992), Game theory for applied economists, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-00395-5. Suitable for advanced undergraduates.
- Published in Europe as Gibbons, Robert (2001), A Primer in Game Theory, London: Harvester Wheatsheaf, ISBN 978-0-7450-1159-2.
- Gintis, Herbert (2000), Game theory evolving: a problem-centered introduction to modeling strategic behavior, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-00943-8
- Green, Jerry R.; Mas-Colell, Andreu; Whinston, Michael D. (1995), Microeconomic theory, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-507340-9. Presents game theory in formal way suitable for graduate level.
- Joseph E. Harrington (2008) Games, strategies, and decision making, Worth, ISBN 0-7167-6630-2. Textbook suitable for undergraduates in applied fields; numerous examples, fewer formalisms in concept presentation.
- Isaacs, Rufus (1999), Differential Games: A Mathematical Theory With Applications to Warfare and Pursuit, Control and Optimization, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 978-0-486-40682-4
- Maschler, Michael; Solan, Eilon; Zamir, Shmuel (2013), Game Theory, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-1-108-49345-1. Undergraduate textbook.
- Miller, James H. (2003), Game theory at work: how to use game theory to outthink and outmaneuver your competition, New York: McGraw-Hill, ISBN 978-0-07-140020-6. Suitable for a general audience.
- Shoham, Yoav; Leyton-Brown, Kevin (2009), Multiagent Systems: Algorithmic, Game-Theoretic, and Logical Foundations, New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-89943-7, retrieved 8 March 2016
- Watson, Joel (2013), Strategy: An Introduction to Game Theory (3rd edition), New York: W.W. Norton and Co., ISBN 978-0-393-91838-0. A leading textbook at the advanced undergraduate level.
- McCain, Roger A. (2010). Game Theory: A Nontechnical Introduction to the Analysis of Strategy. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-4289-65-8.
Historically important texts
- Aumann, R. J.; Shapley, L. S. (1974), Values of Non-Atomic Games, Princeton University Press
- Cournot, A. Augustin (1838), "Recherches sur les principles mathematiques de la théorie des richesses", Libraire des Sciences Politiques et Sociales
- Edgeworth, Francis Y. (1881), Mathematical Psychics, London: Kegan Paul
- Farquharson, Robin (1969), Theory of Voting, Blackwell (Yale U.P. in the U.S.), ISBN 978-0-631-12460-3
- Luce, R. Duncan; Raiffa, Howard (1957), Games and decisions: introduction and critical survey, New York: Wiley
- reprinted edition: R. Duncan Luce; Howard Raiffa (1989), Games and decisions: introduction and critical survey, New York: Dover Publications, ISBN 978-0-486-65943-5
- Maynard Smith, John (1982), Evolution and the theory of games, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-28884-2
- Nash, John (1950), "Equilibrium points in n-person games", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 36 (1): 48–49, Bibcode:1950PNAS...36...48N, doi:10.1073/pnas.36.1.48, PMC 1063129, PMID 16588946
- Shapley, L.S. (1953), A Value for n-person Games, In: Contributions to the Theory of Games volume II, H. W. Kuhn and A. W. Tucker (eds.)
- Shapley, L. S. (October 1953). "Stochastic Games". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 39 (10): 1095–1100. Bibcode:1953PNAS...39.1095S. doi:10.1073/pnas.39.10.1095. PMC 1063912. PMID 16589380.
- von Neumann, John (1928), "Zur Theorie der Gesellschaftsspiele", Mathematische Annalen, 100 (1): 295–320, doi:10.1007/bf01448847, S2CID 122961988 English translation: "On the Theory of Games of Strategy," in A. W. Tucker and R. D. Luce, ed. (1959), Contributions to the Theory of Games, v. 4, p. 42. Princeton University Press.
- von Neumann, John; Morgenstern, Oskar (1944), "Theory of games and economic behavior", Nature, 157 (3981), Princeton University Press: 172, Bibcode:1946Natur.157..172R, doi:10.1038/157172a0, S2CID 29754824
- Zermelo, Ernst (1913), "Über eine Anwendung der Mengenlehre auf die Theorie des Schachspiels", Proceedings of the Fifth International Congress of Mathematicians, 2: 501–4
Other material
- Allan Gibbard, "Manipulation of voting schemes: a general result", Econometrica, Vol. 41, No. 4 (1973), pp. 587–601.
- McDonald, John (1950–1996), Strategy in Poker, Business & War, W. W. Norton, ISBN 978-0-393-31457-1. A layman's introduction.
- Papayoanou, Paul (2010), Game Theory for Business: A Primer in Strategic Gaming, Probabilistic, ISBN 978-0-9647938-7-3.
- Satterthwaite, Mark Allen (April 1975). "Strategy-proofness and Arrow's conditions: Existence and correspondence theorems for voting procedures and social welfare functions" (PDF). Journal of Economic Theory. 10 (2): 187–217. doi:10.1016/0022-0531(75)90050-2.
- Siegfried, Tom (2006), A Beautiful Math, Joseph Henry Press, ISBN 978-0-309-10192-9
- Skyrms, Brian (1990), The Dynamics of Rational Deliberation, Harvard University Press, ISBN 978-0-674-21885-7
- Thrall, Robert M.; Lucas, William F. (1963), "-person games in partition function form", Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 10 (4): 281–298, doi:10.1002/nav.3800100126
- Dolev, Shlomi; Panagopoulou, Panagiota N.; Rabie, Mikaël; Schiller, Elad M.; Spirakis, Paul G. (2011). "Rationality authority for provable rational behavior". Proceedings of the 30th annual ACM SIGACT-SIGOPS symposium on Principles of distributed computing. pp. 289–290. doi:10.1145/1993806.1993858. ISBN 978-1-4503-0719-2.
- Chastain, Erick; Livnat, Adi; Papadimitriou, Christos; Vazirani, Umesh (June 2014), "Algorithms, games, and evolution", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111 (29): 10620–10623, Bibcode:2014PNAS..11110620C, doi:10.1073/pnas.1406556111, PMC 4115542, PMID 24979793
External links
- James Miller (2015): Introductory Game Theory Videos.
- "Games, theory of", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Paul Walker: History of Game Theory Page.
- David Levine: Game Theory. Papers, Lecture Notes and much more stuff.
- Alvin Roth:"Game Theory and Experimental Economics page". Archived from the original on 15 August 2000. Retrieved 13 September 2003. — Comprehensive list of links to game theory information on the Web
- Adam Kalai: Game Theory and Computer Science — Lecture notes on Game Theory and Computer Science
- Mike Shor: GameTheory.net — Lecture notes, interactive illustrations and other information.
- Jim Ratliff's Graduate Course in Game Theory (lecture notes).
- Don Ross: Review Of Game Theory in the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- Bruno Verbeek and Christopher Morris: Game Theory and Ethics
- Elmer G. Wiens: Game Theory — Introduction, worked examples, play online two-person zero-sum games.
- Marek M. Kaminski: Game Theory and Politics Archived 20 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine — Syllabuses and lecture notes for game theory and political science.
- Websites on game theory and social interactions
- Kesten Green's Conflict Forecasting at the Wayback Machine (archived 11 April 2011) — See Papers for evidence on the accuracy of forecasts from game theory and other methods Archived 15 September 2019 at the Wayback Machine.
- McKelvey, Richard D., McLennan, Andrew M., and Turocy, Theodore L. (2007) Gambit: Software Tools for Game Theory.
- Benjamin Polak: Open Course on Game Theory at Yale Archived 3 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine videos of the course
- Benjamin Moritz, Bernhard Könsgen, Danny Bures, Ronni Wiersch, (2007) Spieltheorie-Software.de: An application for Game Theory implemented in JAVA.
- Antonin Kucera: Stochastic Two-Player Games.
- Yu-Chi Ho: What is Mathematical Game Theory; What is Mathematical Game Theory (#2); What is Mathematical Game Theory (#3); What is Mathematical Game Theory (#4)-Many person game theory; What is Mathematical Game Theory ?( #5) – Finale, summing up, and my own view
| Major mathematics areas | |
|---|---|
| Foundations | |
| Algebra | |
| Analysis | |
| Discrete | |
| Geometry | |
| Number theory | |
| Topology | |
| Applied | |
| Computational | |
| Related topics | |
| Property | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By owner | |||||
| By nature | |||||
| Commons | |||||
| Theory | |||||
| Applications |
| ||||
| Disposession/ redistribution | |||||
| Scholars (key work) | |||||
| |||||

 from the set of all possible coalitions of players to a set of payments, and also satisfies
from the set of all possible coalitions of players to a set of payments, and also satisfies  . The function describes how much collective payoff a set of players can gain by forming a coalition.
. The function describes how much collective payoff a set of players can gain by forming a coalition.
 denotes the
denotes the  .
.
 -person games in partition function form", Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 10 (4): 281–298,
-person games in partition function form", Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, 10 (4): 281–298,