| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Sump" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (April 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
A sump is a low space that collects often undesirable liquids such as water or chemicals. A sump can also be an infiltration basin used to manage surface runoff water and recharge underground aquifers. Sump can also refer to an area in a cave where an underground flow of water exits the cave into the earth.
Examples
One common example of a sump is the lowest point in a basement, into which flows water that seeps in from outside. If this is a regular problem, a sump pump that moves the water outside of the house may be used.
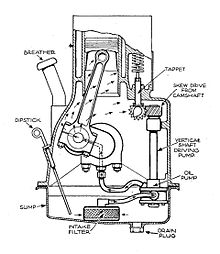
Another example is the oil pan of an engine. The oil is used to lubricate the engine's moving parts and it pools in a reservoir known as its sump, at the bottom of the engine. Use of a sump requires the engine to be mounted slightly higher to make space for it. Often though, oil in the sump can slosh during hard cornering, starving the oil pump. For these reasons, racing motorcycles and piston aircraft engines are "dry sumped" using scavenge pumps and a swirl tank to separate oil from air, which is also sucked up by the pumps.
A sump can also be found in an aquarium, mainly a reef system. The sump sits below the main tank and is used as a filter, as well as a holding place of unsightly equipment such as heaters and protein skimmers. The main advantage of having a sump plumbed into an aquarium is the increase of water in the system, making it more stable and less prone to fluctuations of pH and salinity.
A diving snorkel can have a sump section located below the mouthpiece. This allows excess moisture from the breath and liquid from the ocean to settle and remain in the sump, so that it does not impair the snorkeler's breathing.
In a nuclear power plant's reactor housing, the role of the sump will be to collect any overflow of primary loop coolant; in this case, monitoring and pumping of the sump is an important part of the reactor's safety system.
In mining the term sump is used to describe a hole made in the floor of a level in a working, in the direction of a lower level either for the purpose of testing the trend of an ore vein, or for the purpose of ventilation.
The equivalent of a sump on a boat is the bilge.
In the human eye, the vitreous humour has a minor role as a metabolic sump.
In caving/potholing terminology, a sump is a permanently flooded section of a cave, such that the caver must submerge under water to reach the other side.
Other uses
In a foxhole, a grenade sump is a deeper hole dug inside the foxhole into which live grenades can be kicked to minimize damage from the explosion.
In medieval cosmology, the sump was the center of the cosmos, where the dregs and filth descended, with the celestial sphere far exalted above the world of fallen man.
See also
- Sump pump – Type of pump
References
- Fagin, Dan. "Ancient, Clean, Controversial". Newsday.
- Huneycutt, Jeff (March 2002). "Oil Pans For Power". Circle Track. Retrieved 2006-11-16.
- Batterbury, Mark; Bowling, Brad; Murphy, Conor (2009). Ophthalmology: An Illustrated Colour Text (3rd ed.). Churchill Livingstone. p. 5. ISBN 978-0702030598.
| Internal combustion engine | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Automobile series | |
| Engine block and rotating assembly | |
| Valvetrain and Cylinder head | |
| Forced induction | |
| Fuel system | |
| Ignition | |
| Engine management | |
| Electrical system | |
| Intake system | |
| Exhaust system | |
| Cooling system | |
| Lubrication | |
| Other | |