| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Acetylcysteinamide" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (December 2020) |
 | |
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.211.696 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
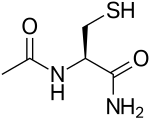
| Formula | C5H10N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 162.21 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.227 g/cm |
| Boiling point | 308 °C (586 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 22 mg/mL (20 °C) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
N-Acetylcysteine amide (abbrev. NACA, AD4 and also known as acetylcysteinamide) is an amide derivative of N-acetylcysteine that appears to have better blood–brain barrier permeability and bioavailability and a similar antioxidant capability.
References
- Sunitha K, Hemshekhar M, Thushara RM, Santhosh MS, Yariswamy M, Kemparaju K, et al. (May 2013). "N-Acetylcysteine amide: a derivative to fulfill the promises of N-Acetylcysteine". Free Radical Research. 47 (5): 357–367. doi:10.3109/10715762.2013.781595. PMID 23472882. S2CID 207517783.
This pharmacology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |