| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1-(Dimethylamino)-N,N-dimethylmethaniminium chloride | |
| Other names (Dimethylaminomethylene)dimethylammonium chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.312 |
| PubChem CID | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C5H13ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 136.62 g·mol |
| Appearance | Solid |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is the simplest representative of quaternary formamidinium cations of the general formula with a chloride as a counterion in which all hydrogen atoms of the protonated formamidine are replaced by methyl groups.
Deprotonation results in the exceptionally basic bis(dimethylamino)carbene R2N−C̈−NR2.
Preparation
It is generated by protonation of (CH3)3COCH(N(CH3)2)2 (Bredereck's reagent).
- (CH3)3COCH(N(CH3)2)2 + H → (CH3)3COH +
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is also obtained in high yield (95%) in the reaction of dimethylformamide (DMF) with dimethylcarbamoyl chlorideThe conversion of DMF with thionyl chloride in a ratio of 3:1 obtains the product in a is significantly lower yield (72%) which appears, however, more realistic in view of the tricky handling of the chloride salt.
Properties
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is a light yellow, strongly hygroscopic solid.
For drying, the salt is dissolved in dichloromethane and the solution is treated with solid anhydrous sodium sulfate. After several dissolutions in dichloromethane and acetone, and precipitations with tetrahydrofuran, a colorless solid is obtained, which is stable under air and moisture sealing.
The presumption of a mesomeric equilibrium between ionic formamidinium chloride and covalent bis(dimethylamino)chloromethane structure:
could be decided by reaction with germanium dichloride or tin(II) chloride in favour of the presence of N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium chloride.
The hygroscopy of the chloride salt complicates the handling of the compound. Therefore, also syntheses of the much better processible salts N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium methylsulfate (from the dimethylformamide–dimethylsulfate complex) and of N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium p-toluenesulfonate (from dimethylformamide and p-toluenesulfonyl chloride) were investigated.
Applications
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride is useful as a reagent for aminomethylenation (that is, to introduce a =CH−NRR function to CH-acidic compounds). For example, ethyl cyanoacetate reacts with the formamidinium salt in the presence of solid sodium hydroxide to give ethyl (dimethylaminomethylene)cyanoacetate in practically quantitative yields.
The aminomethylenation provides intermediates for the synthesis of heterocycles such as indoles, pyrimidines, pyridines and quinolones.
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride reacts with alkali metal dimethylamides (such as lithium dimethylamide or sodium dimethylamide) to tris(dimethylamino)methane in yields of 55% to 84%.
The reaction product is suited as a reagent for formylation and aminomethylenation.
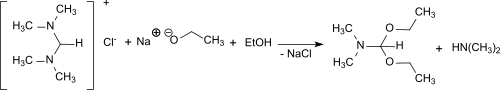
From N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium chloride and sodium ethoxide in ethanol, dimethylformamide diethyl acetal is formed in 68% yield.
In aqueous sodium cyanide, N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium reacts to bis(dimethylamino)acetonitrile.
From N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium and anhydrous hydrogen cyanide, dimethylaminomalonic acid dinitrile is obtained in 92% yield.
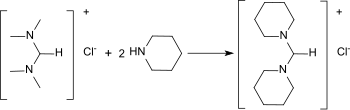
N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium can be regaminated with cyclo-aliphatic amines to the corresponding heterocyclic formamidines.
N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium is a catalyst in the preparation of acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids and phosgene has been reported.
Strong bases (such as phenyllithium) can abstract a proton from the formamidinium cation of N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium forming bis(dimethylamino)carbene.
See also
References
- ^ Alder, R. W.; Blake, M. E.; Bufali, S.; Butts, C. P.; Orpen, A. G.; Schütz, J.; Williams, S. J. (2001). "Preparation of tetraalkylformamidinium salts and related species as precursors to stable carbenes". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 (14): 1586–1593. doi:10.1039/B104110J.
- ^ Magill, A. M.; Cavell, K. J.; Yates, B. F. (2004). "Basicity of nucleophilic carbenes in aqueous and nonaqueous solvents – theoretical predictions". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 126 (28): 8717–24. doi:10.1021/ja038973x. PMID 15250724.
- Kantlehner, Willi; Bowers, Albert (2007). "T-Butoxybis(dimethylamino)methane". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/9780470842898.rb350.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- Arnold, Z. (1959). "The preparation of tetramethylformamidinium salts and their vinylogues". Collection of Czechoslovak Chemical Communications. 24 (3): 760–765. doi:10.1135/cccc19590760.
- Kantlehner, W.; Speh, P. (1971). "Säureamid-Reaktionen. LI. Notiz zur Darstellung von N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidiniumchlorid" [Acyl amide reactions. LI. Note on the presentation of N,N,N′,N′-tetramethylformamidinium chloride]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 104 (11): 3714–3715. doi:10.1002/cber.19711041136.
- ^ DE 1205528, Bredereck, H.; Effenberger, F. & Simchen, G., "Verfahren zur Herstellung von N-substituierten Amidinen oder deren Vinylogen (Process for the preparation of N-substituted amidines or their vinylogues)", issued 1965-11-25, assigned to Bredereck, H.
- Tian, X.; Pape, T.; Mitzel, N. W. (2004). "Formamidinium Salts of Low Valent Metal Halide Anions MX
3 (M = Ge, Sn) and M
2X
6 (M = Ga, In)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung. 59b (11–12): 1524–1531. doi:10.1515/znb-2004-11-1224. - Bredereck, H.; Effenberger, F.; Simchen, G. (1963). "Säureamid-Reaktionen. XXXII. Über Säureamid-Dialkylsulfat-Komplexe" [Acyl amide reactions. XXXII. On acyl amide–dialkylsulfate complexes]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 96 (5): 1350–1355. doi:10.1002/cber.19630960526.
- US 3707553, Bagley, G. E. & Poshkus A. C., "Tetramethylformamidinium arenesulfonates and method of preparation", issued 1972-12-26, assigned to Armstrong Cork Co.
- Schindlbauer, H. (1969). "Reaktionen mit Dimethylformamid. 3. (Mitt.) Die Umsetzung von Arylsulfochloriden und Arylsulfonsäuren mit Dimethylformamid" [Reactions with dimethylformamide. 3. (Comm.) The reaction of arylsulfonyl chlorides and arylsulfonic acids with dimethylformamide]. Monatshefte für Chemie (in German). 100 (5): 1590–1595. doi:10.1007/BF00900174.
- US 5241099, Blank, H.-U. & Kraus, H., "Process for the preparation of aminomethylene compounds", issued 1993-08-31, assigned to Bayer AG
- Bredereck, H.; Effenberger, F.; Brendle, T. (1966). "Synthese und Reaktionen von Trisdimethylaminomethan" [Synthesis and reactions of tris(dimethylamino)methane]. Angewandte Chemie (in German). 78 (2): 147–148. doi:10.1002/ange.19660780212.
- DE 1217391, Bredereck, H., "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Tris-dimethylaminomethan (Process for the preparation of tris(dimethylamino)methane))", issued 1966-12-08, assigned to Bredereck, H.
- Bredereck, H.; Effenberger, F.; Brendle, T.; Muffler, H. (1968). "Orthoamide. V. Synthese von Tris-dialkylamino-methanen" [Orthoamides. V. Synthesis of tris(dialkylamino)methanes]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 101 (5): 1885–1888. doi:10.1002/cber.19681010541.
- Gold, H. (1960). "Die Reaktion von Cyanurchlorid mit Dimethylformamid" [The reaction of cyanuric chloride with dimethylformamide]. Angewandte Chemie (in German). 72 (24): 956–959. doi:10.1002/ange.19600722406.
- Bredereck, H.; Simchen, G.; Kantlehner, W. (1971). "Orthoamide. XVI. Synthese von O.N- und N.N-Acetalen der α-Keto-carbonsäure-nitrile sowie von Iminoestern" [Orthoamides. XVI. Synthesis of O,N- and N,N-acetals of α-keto-carboxylic acid nitriles as well as imino esters]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 104 (3): 924–931. doi:10.1002/cber.19711040331.
- ^ Gold, H.; Bayer, O. (1961). "Die Darstellung basisch substituierter Malonsäure-dinitrile" [Presentation of base-substituted malonic acid dinitriles]. Chemische Berichte (in German). 94 (10): 2594–2596. doi:10.1002/cber.19610941004.
- EP 1124783, Henkelmann, J. & Stamm, A., "Method for producing carboxylic acid chlorides", issued 2001-08-22, assigned to BASF AG