This article is about historical Iron Age kingdom. For the mythological kingdom, see Matsya Kingdom. For the avatar of the Hindu god Viṣṇu, see Matsya. For other uses, see Matsya (disambiguation).
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Matsya" tribe – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (February 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Kingdom of MatsyaMacchā | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 1400 BCE–c. 350 BCE | |||||||
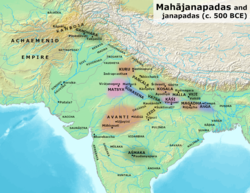 Matsya Kingdom and other Mahajanapadas in the Post Vedic period. Matsya Kingdom and other Mahajanapadas in the Post Vedic period. | |||||||
| Capital | Virāṭanagara | ||||||
| Common languages | Prakrits | ||||||
| Religion | Historical Vedic religion | ||||||
| Demonym(s) | Mātsyeya | ||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||
| Raja | |||||||
| Historical era | Iron Age | ||||||
| • Established | c. 1400 BCE | ||||||
| • Disestablished | c. 350 BCE | ||||||
| |||||||
| Today part of | India | ||||||
Matsya (Pali: Macchā) was an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe of central India whose existence is attested during the Iron Age. The members of the Matsya tribe were called the Mātsyeyas and were organised into a kingdom called the Matsya kingdom.
Etymology
Macchā in Pāli and Matsya in Sanskrit mean "fish".
Location
 Location of the Matsyas among the Vedic tribes
Location of the Matsyas among the Vedic tribes Location of Matsya during the late Vedic period
Location of Matsya during the late Vedic period Location of Matsya during the post-Vedic period
Location of Matsya during the post-Vedic period
The kingdom of the Mātsyeyas covered an extensive territory, with the Sarasvatī river and the forests skirting it as its western border, and its southern boundaries being the hills near the Chambal River. Most of the kingdom comprised parts of present-day North-eastern Rajasthan. The neighbours of the Matsya state were Kuru in the north, and Sūrasena in the east.
The capital of Matsya was Virāṭanagara, which corresponds to the modern-day Bairāṭ in Jaipur district of Rajasthan.
History
The Matsya tribe was first mentioned in the Ṛgveda, where they appear as one of the opponents of Sudās during the Battle of the Ten Kings.
According to the Śatapatha Brāhmaṇa, the Mātsyeya king Dhvasan Dvaitavana performed an aśvamedha sacrifice near the Sarasvatī river. A forest on the banks of the Sarasvatī and a lake were both named after the king Dvaitavana.
Vedic texts such as the Gopatha Brāhmaṇa mention the Mātsyeyas along with the Śālva tribe, and the Kauśītaki Upaniṣad connects them with the Kuru-Pañcālas. Later Puranic texts such as the Mahābhārata connects them with the Trigartas and the Caidyas, and the Manu-Saṃhitā lists the countries of the Mātsyeyas, the Śūrasenakas, the Pañcālas, and of Kuru-kṣetra, as forming the Brahmarṣi-deśa (the holy enclave of the brāhmaṇa sages).
The later history of Matsya is not known, although the Buddhist Aṅguttara Nikāya included it among the sixteen Mahājanapadas ("great realms"), which were the most powerful states of India immediately before the birth of the Buddha. The Matsya state in the Mahājanapada period archaeologically corresponds to the Northern Black Polished Ware archaeological culture which in the western part of the Gaṅgā-Yamunā Doab region succeeded the earlier Painted Grey Ware culture, and is associated with the Kuru, Pañcāla, Matsya, Surasena and Vatsa Mahājanapadas.
Unlike other states of central India who abandoned the kingdom form for a gaṇasaṅgha (aristocratic republic) mode of government during the late Iron Age, Matsya maintained a monarchical system.
Matsya was eventually conquered by the empire of Magadha.
Legacy
After the Indian independence in 1947, the princely states of Bharatpur, Dholpur, Alwar and Karauli were temporarily put together from 1947 to 1949 as the ″United States of Matsya″, and later in March 1949 after these princely states signed the Instrument of Accession they were merged with the present state of Rajasthan.
The Matsya Festival is held in Alwar every year in the last week of November to celebrate culture and adventure.
See also
- Vedic period
- Janapadas
- Mahajanapadas
- Cemetery H culture
- Painted Grey Ware culture
- Northern Black Polished Ware
- Kingdoms of Ancient India
References
- ^ Raychaudhuri 1953, p. 66-68.
- Monier-Williams, Monier (1899). A Sanskrit-English Dictionary: Etymologically and Philologically Arranged with Special Reference to Cognate Indo-European Languages. Oxford, England, United Kingdom: Clarendon Press. p. 776.
- Apte, Vaman Shivram (1890). The Practical Sanskrit-English Dictionary. Motilal Banarsidass Publishers. p. 735. ISBN 978-8-120-81568-1.
- Mayrhofer, Manfred (1996). Entry “mátsya-”. In: Etymologisches Wörterbuch des Altindoarischen Volume II. Heidelberg: Carl Winter Universitätsverlag, 1996. pp. 297-298. (In German)
- ^ Raychaudhuri 1953, p. 137-138.
- Bhan, Suraj (1 December 2006). "North Indian Protohistory and Vedic Aryans". Ancient Asia. 1: 173. doi:10.5334/aa.06115. ISSN 2042-5937.
- NWR tourist places
- Times Travel Editor (November 2018). "All about Alwar Matsya Festival". Times of India. Alwar, Rajasthan, India.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help).
Sources
- Raychaudhuri, Hemchandra (1953). Political History of Ancient India: From the Accession of Parikshit to the Extinction of Gupta Dynasty. University of Calcutta.
| Mahajanapadas | |
|---|---|
| Great Indian Kingdoms (c. 600 BCE–c. 300 BCE) | |
| Historical regions of North India | |
|---|---|
