
Erinaceidae is a family of small mammals in the order Eulipotyphla. A member of this family is called an erinaceid, and the family includes hedgehogs and gymnures. Erinaceidae is one of four families in the order Eulipotyphla. They are found in Africa, Europe, and Asia, primarily in forests, shrublands, savannas, and grasslands, though some species can also be found in deserts, rocky areas, or caves. They range in size from the gymnures in the Hylomys genus, at 9 cm (4 in) plus a 1 cm (0.4 in) tail, to the moonrat, at 46 cm (18 in) plus a 30 cm (12 in) tail. Erinaceids are omnivorous and primarily eat insects and small vertebrates such as lizards, though they also consume plants, eggs, and fungi. Hedgehogs all have spines on their backs, while gymnures have fur. No erinaceids have population estimates, but the Hainan gymnure and Dinagat gymnure are categorized as endangered species.
The twenty-four extant species of Erinaceidae are divided into two subfamilies: Erinaceinae, containing sixteen hedgehog species in five genera, and Galericinae, containing eight gymnure species in five genera. A few extinct prehistoric Erinaceidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed.
Conventions
| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (2 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (1 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (1 species) |
| LC | Least concern (19 species) |
| Other categories | |
| DD | Data deficient (1 species) |
| NE | Not evaluated (0 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the erinaceid's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IUCN Red List for that species unless otherwise noted.
Classification
The family Erinaceidae consists of two subfamilies: Erinaceinae, containing sixteen hedgehog species in five genera, and Galericinae, containing eight gymnure species in five genera.
Family Erinaceidae
- Subfamily Erinaceinae
- Genus Atelerix (African hedgehogs): four species
- Genus Erinaceus (woodland hedgehogs): four species
- Genus Hemiechinus (long-eared hedgehogs): two species
- Genus Mesechinus (steppe hedgehogs): two species
- Genus Paraechinus (desert hedgehogs): four species
- Subfamily Galericinae
- Genus Echinosorex (moonrat): one species
- Genus Hylomys (gymnures): three species
- Genus Neohylomys (Hainan gymnure): one species
- Genus Neotetracus (shrew gymnure): one species
- Genus Podogymnura (Philippine gymnures): two species
|
Erinaceids
The following classification is based on the taxonomy described by the reference work Mammal Species of the World (2005), with augmentation by generally accepted proposals made since using molecular phylogenetic analysis, as supported by both the IUCN and the American Society of Mammalogists. The range shown is only for wild populations; domesticated hedgehogs, which are usually four-toed hedgehogs, North African hedgehogs, or hybrids of the two, may live outside these areas.
Subfamily Erinaceinae
Main article: Erinaceinae| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Four-toed hedgehog | A. albiventris (Wagner, 1841) |
Western, central, and eastern Africa
|
Size: 17–23 cm (7–9 in) long Habitat: Savanna and grassland Diet: Invertebrates, as well as plants and small vertebrates |
LC
|
| North African hedgehog | A. algirus (Lereboullet, 1842) Three subspecies
|
Northern Africa
|
Size: 20–25 cm (8–10 in) long Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Omnivorous, including arthropods, small vertebrates, carrion, and fungi |
LC
|
| Somali hedgehog | A. sclateri Anderson, 1895 |
Somalia
|
Size: 20–27 cm (8–11 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 in) tail Habitat: Grassland and savanna Diet: Believed to be omnivorous; primarily insects |
LC
|
| Southern African hedgehog | A. frontalis (Smith, 1831) |
Southern Africa
|
Size: 15–20 cm (6–8 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland Diet: Omnivorous; primarily insects, as well as carrion, vegetables, fungi, and small vertebrates |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amur hedgehog | E. amurensis Schrenk, 1859 |
Eastern Asia
|
Size: 15–29 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Earthworms and other ground invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates and fruit |
LC
|
| European hedgehog | E. europaeus Linnaeus, 1758 |
Europe, northwestern Asia, and New Zealand
|
Size: 13–27 cm (5–11 in) long, plus 2 cm (1 in) tail Habitat: Forest and grassland Diet: Omnivorous; primarily insects, as well as other invertebrates, eggs, small vertebrates, and carrion |
NT
|
| Northern white-breasted hedgehog | E. roumanicus Barrett-Hamilton, 1900 |
Eastern Europe and western Asia (in blue)
|
Size: 13–30 cm (5–12 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Omnivorous; primarily insects, as well as other invertebrates, eggs, small vertebrates, and carrion |
LC
|
| Southern white-breasted hedgehog | E. concolor Martin, 1838 |
Western Asia (in orange)
|
Size: 13–30 cm (5–12 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Omnivorous; primarily insects, as well as other invertebrates, eggs, small vertebrates, and carrion |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indian long-eared hedgehog | H. collaris (Gray, 1830) |
Western India and Pakistan
|
Size: 15–28 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 1–6 cm (0.4–2.4 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Omnivorous; primarily invertebrates and insects, as well as small vertebrates, eggs, carrion, fruit, and seeds |
LC
|
| Long-eared hedgehog | H. auritus (Gmelin, 1770) |
Western and central Asia
|
Size: 12–27 cm (5–11 in) long, plus 1–5 cm (0.4–2.0 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and desert Diet: Omnivorous; primarily invertebrates and insects, as well as eggs, fruit, vegetables, and small vertebrates |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daurian hedgehog
|
M. dauuricus (Sundevall, 1842) |
East-central Asia
|
Size: About 24 cm (9 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail Habitat: Forest and grassland Diet: Beetles and other invertebrates, as well as small reptiles, bird eggs and nestlings, rodents, and carrion |
LC
|
| Hugh's hedgehog | M. hughi (Thomas, 1908) |
Central China
|
Size: About 24 cm (9 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail Habitat: Grassland Diet: Omnivorous; primarily invertebrates and insects, as well as small vertebrates, eggs, carrion, fruit, and seeds |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare-bellied hedgehog | P. nudiventris (Horsfield, 1851) |
Southern India
|
Size: 14–28 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Insects, as well as small vertebrates, eggs, and scorpions |
LC
|
| Brandt's hedgehog | P. hypomelas (Brandt, 1836) |
Western Asia
|
Size: 14–28 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert Diet: Insects, as well as small vertebrates, eggs, and scorpions |
LC
|
| Desert hedgehog | P. aethiopicus (Ehrenberg, 1832) |
Northern Africa and Arabian Peninsula
|
Size: 14–23 cm (6–9 in) long Habitat: Desert, inland wetlands, grassland, shrubland, and savanna Diet: Insects, as well as other invertebrates, amphibians, reptiles, and eggs |
LC
|
| Indian hedgehog | P. micropus (Blyth, 1846) |
Western India and Pakistan
|
Size: 14–28 cm (6–11 in) long, plus 1–4 cm (0.4–1.6 in) tail Habitat: Shrubland and desert Diet: Insects, as well as other invertebrates, small vertebrates, and eggs |
LC
|
Subfamily Galericinae
Main article: Galericinae| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moonrat | E. gymnura (Raffles, 1822) Two subspecies
|
Southeast Asia
|
Size: 26–46 cm (10–18 in) long, plus 16–30 cm (6–12 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Invertebrates, as well as frogs, fish, and fruit |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dwarf gymnure
|
H. parvus Robinson & Kloss, 1916 |
Sumatra island in Indonesia
|
Size: 9–15 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Invertebrates, as well as fruit |
VU
|
| Long-eared gymnure
|
H. megalotis Jenkins & Robinson, 2002 |
Laos
|
Size: 9–15 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and rocky areas Diet: Invertebrates, as well as fruit |
DD
|
| Short-tailed gymnure | H. suillus Müller, 1840 Seven subspecies
|
Southeastern Asia
|
Size: 9–15 cm (4–6 in) long, plus 1–3 cm (0.4–1.2 in) tail Habitat: Forest and shrubland Diet: Invertebrates, as well as fruit |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hainan gymnure | N. hainanensis Shaw & Wong, 1959 |
Hainan island, China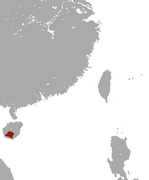
|
Size: 12–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 3–5 cm (1–2 in) tail Habitat: Forest and caves Diet: Insects, worms, and plants |
EN
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shrew gymnure | N. sinensis Trouessart, 1909 |
Southern China
|
Size: 10–13 cm (4–5 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Insects, worms, and plants |
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dinagat gymnure
|
P. aureospinula Heaney & Morgan, 1982 |
Philippines
|
Size: 19–22 cm (7–9 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Insects, worms, and birds |
EN
|
| Mindanao gymnure
|
P. truei Mearns, 1905 |
Philippines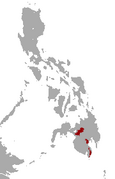
|
Size: 13–15 cm (5–6 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail Habitat: Forest Diet: Insects, worms, and carrion |
LC
|
References
- ^ Wilson, Reeder, pp. 212-219
- "Fossilworks: Erinaceidae". Paleobiology Database. University of Wisconsin–Madison. Archived from the original on January 18, 2023. Retrieved August 29, 2023.
- He, K.; Chen, J.-H.; Gould, G. C.; Yamaguchi, N.; Ai, H.-S.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Jiang, X.-L. (2012). "An Estimation of Erinaceidae Phylogeny: A Combined Analysis Approach". PLoS ONE. 7 (6): e39304. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...739304H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039304. PMC 3380021. PMID 22745729.
- ^ Nichols, Jennifer (2023). "Atelerix albiventris". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Cassola, F. (2017) . "Atelerix albiventris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40602A115174097. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40602A22324217.en.
- ^ Everett, Andrew (2012). "Atelerix algirus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on January 29, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N. (2022). "Atelerix algirus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022: e.T27926A22324424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2022-2.RLTS.T27926A22324424.en.
- ^ Kingdon, p. 36
- ^ Cassola, F. (2017) . "Atelerix sclateri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2275A115061435. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2275A22324040.en.
- ^ King, Wendy (2004). "Atelerix frontalis". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Cassola, F. (2017) . "Atelerix frontalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T2274A115061260. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T2274A22324102.en.
- Smith; Xie, p. 293
- ^ Cassola, F. (2017) . "Erinaceus amurensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40604A115174360. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40604A22325640.en.
- ^ Roberts, Colin (2011). "Erinaceus europaeus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on June 2, 2020. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Amori, G. (2016). "Erinaceus europaeus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T29650A2791303. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T29650A2791303.en.
- ^ Nowak, p. 174
- ^ Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsainas, G.; Palomo, L. (2021) . "Erinaceus roumanicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T136344A197508156. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T136344A197508156.en.
- ^ Nowak, p. 175
- ^ Amori, G.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsainas, G.; Palomo, L. (2021) . "Erinaceus concolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T40605A197506348. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T40605A197506348.en.
- ^ Nowak, pp. 178–179
- ^ Molur, S. (2016). "Hemiechinus collaris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40608A22324478. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T40608A22324478.en.
- ^ Ballenger, Liz (2023). "Hemiechinus auritus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on December 4, 2019. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Stubbe, M.; Samiya, R.; Ariunbold, J.; Buuveibaatar, V.; Dorjderem, S.; Monkhzul, T.; Otgonbaatar, M.; Tsogbadrakh, M.; Zagorodniuk, I.; Hutterer, R.; Kryštufek, B.; Yigit, N.; Mitsainas, G.; Palomo, L. (2021) . "Hemiechinus auritus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T40607A197510528. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T40607A197510528.en.
- ^ Stubbe, M.; Samiya, R.; Ariunbold, J.; Buuveibaatar, V.; Dorjderem, S.; Monkhzul, Ts.; Otgonbaatar, M.; Tsogbadrakh, M.; Tsytsulina, K. (2017) . "Mesechinus dauuricus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40612A115175251. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40612A22325286.en.
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H.; Lunde, D. (2017) . "Mesechinus hughi". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T13209A115111114. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T13209A22325137.en.
- ^ Nowak, p. 177
- ^ Chakraborty, S.; Srinivasulu, C.; Molur, S. (2017). "Paraechinus nudiventris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T39594A22326706. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-2.RLTS.T39594A22326706.en.
- ^ Bhattacharyya, T.; Srinivasulu, C.; Molur, S. (2017) . "Paraechinus hypomelas". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40610A115174910. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40610A22326573.en.
- ^ Hall, Dustin (2002). "Paraechinus aethiopicus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on April 1, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Hutterer, R. (2016). "Paraechinus aethiopicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40606A22326233. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T40606A22326233.en.
- ^ Seitz, Megan (2006). "Paraechinus micropus". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Molur, S. (2016). "Paraechinus micropus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40609A22326424. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T40609A22326424.en.
- Nowak, p. 173
- ^ Cassola, F. (2016). "Echinosorex gymnura". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40603A22326807. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T40603A22326807.en.
- Fox, David L. (2023). "Echinosorex gymnura". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on December 19, 2023. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Nowak, p. 171
- ^ Clayton, E. (2018). "Hylomys parvus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T10589A22325019. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T10589A22325019.en.
- ^ Chiozza, F. (2016). "Hylomys megalotis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T136193A22324783. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136193A22324783.en.
- ^ Chiozza, F. (2017) . "Hylomys suillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T40611A115175083. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T40611A22324887.en.
- ^ Nowak, p. 172
- ^ Johnston, C.; Smith, A. T. (2016). "Neohylomys hainanensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T10588A22326961. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T10588A22326961.en.
- ^ Smith, A. T.; Johnston, C. H. (2016). "Neotetracus sinensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T10590A22325953. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T10590A22325953.en.
- ^ Clayton, E. (2018). "Podogymnura aureospinula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T17829A22326149. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-1.RLTS.T17829A22326149.en.
- ^ Rasmussen, Andrew (2007). "Podogymnura truei". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Archived from the original on February 2, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2023.
- ^ Heaney, L.; Balete, D.; Tabao, M. (2016). "Podogymnura truei". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T17828A22326078. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T17828A22326078.en.
Sources
- Kingdon, Jonathan (2014). Mammals of Africa. Vol. IV: Hedgehogs, Shrews and Bats. A & C Black. ISBN 978-1-4081-8993-1.
- Nowak, Ronald M. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Vol. 1. Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-5789-8.
- Smith, Andrew T.; Xie, Yan, eds. (2010). A Guide to the Mammals of China. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-3411-2.
- Hutterer, Rainer (2005). Wilson, Don E.; Reeder, DeeAnn M. (eds.). Mammal Species of the World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
| Lists of mammal species | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotremes and marsupials |
| ||||||||||||||
| Placental mammals |
| ||||||||||||||


















