In mathematics, addition and subtraction logarithms or Gaussian logarithms can be utilized to find the logarithms of the sum and difference of a pair of values whose logarithms are known, without knowing the values themselves.
Their mathematical foundations trace back to Zecchini Leonelli and Carl Friedrich Gauss in the early 1800s.
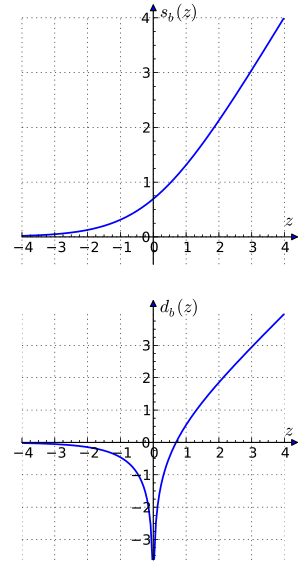
The operations of addition and subtraction can be calculated by the formulas
where , , the "sum" function is defined by , and the "difference" function by . The functions and are also known as Gaussian logarithms.
For natural logarithms with the following identities with hyperbolic functions exist:
This shows that has a Taylor expansion where all but the first term are rational and all odd terms except the linear term are zero.
The simplification of multiplication, division, roots, and powers is counterbalanced by the cost of evaluating these functions for addition and subtraction.
See also
- Softplus operation in neural networks
- Zech's logarithm
- Logarithm table
- Logarithmic number system (LNS)
References
- ^ "Logarithm: Addition and Subtraction, or Gaussian Logarithms". Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition.
- ^ Leonelli, Zecchini (1803) . Supplément logarithmique. Théorie des logarithmes additionels et diductifs (in French). Bordeaux: Brossier. (NB. 1802/1803 is the year XI. in the French Republican Calendar.)
- ^ Leonhardi, Gottfried Wilhelm (1806). LEONELLIs logarithmische Supplemente, als ein Beitrag, Mängel der gewöhnlichen Logarithmentafeln zu ersetzen. Aus dem Französischen nebst einigen Zusätzen von GOTTFRIED WILHELM LEONHARDI, Souslieutenant beim kurfürstlichen sächsischen Feldartilleriecorps (in German). Dresden: Walther'sche Hofbuchhandlung. (NB. An expanded translation of Zecchini Leonelli's Supplément logarithmique. Théorie des logarithmes additionels et diductifs.)
- ^ Gauß, Johann Carl Friedrich (1808-02-12). "LEONELLI, Logarithmische Supplemente". Allgemeine Literaturzeitung (in German) (45). Halle-Leipzig: 353–356.
- ^ Dunnington, Guy Waldo (2004) . Gray, Jeremy; Dohse, Fritz-Egbert (eds.). Carl Friedrich Gauss - Titan of Science. Spectrum series (revised ed.). Mathematical Association of America (MAA). ISBN 978-0-88385-547-8. ISBN 0-88385-547-X.
Further reading
- Stark, Bruce D. (1997) . Stark Tables for Clearing the Lunar Distance and Finding Universal Time by Sextant Observation Including a Convenient Way to Sharpen Celestial Navigation Skills While On Land (2 ed.). Starpath Publications. ISBN 978-0914025214. 091402521X. Retrieved 2015-12-02. (NB. Contains a table of Gaussian logarithms lg(1+10).)
- Kalivoda, Jan (2003-07-30). "Bruce Stark - Tables for Clearing the Lunar Distance and Finding G.M.T. by Sextant Observation (1995, 1997)" (Review). Prague, Czech Republic. Archived from the original on 2004-01-12. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
…] Bruce Stark uses the Gaussian logarithms that make possible to remain in world of logarithms all the time of calculation and transform an addition of natural numbers to the addition and subtraction of their common and special logarithmic values by use of a special table. It is much easier than to convert logs to their natural values, to add them and again to convert them to logs. Moreover, Gaussian logs yield greater accuracy of result than the traditional computing method and help 5-digit log values to be sufficiently accurate for this method. The use of "Gaussians" by Bruce is original in the field of navigation. I don't know another example of using them by seamen or aviators - with the exception of Soviet navigators, which had Gaussians in their standard table sets up to ca. 1960. haversine that was not allowed to the Soviet navigational practice. Gaussians coact peacefully with haversines in rationalizing the LD procedure
- Kremer, Hermann (2002-08-29). "Gauss'sche Additionslogarithmen feiern 200. Geburtstag". de.sci.mathematik (in German). Archived from the original on 2018-07-07. Retrieved 2018-07-07.
- Kühn, Klaus (2008). "C. F. Gauß und die Logarithmen" (PDF) (in German). Alling-Biburg, Germany. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-07-14. Retrieved 2018-07-14.
 and
and  functions for
functions for  .
.

 ,
,  , the "sum" function is defined by
, the "sum" function is defined by  , and the "difference" function by
, and the "difference" function by  . The functions
. The functions 

 has a
has a