| Graphite | |
|---|---|
 Graphite specimen Graphite specimen | |
| General | |
| Category | Native mineral |
| Formula (repeating unit) | C |
| IMA symbol | Gr |
| Strunz classification | 1.CB.05a |
| Crystal system | Hexagonal or Rhombohedral |
| Crystal class | Dihexagonal dipyramidal (6/mmm) Hermann–Mauguin notation: (6/m 2/m 2/m) |
| Space group | P63mc (buckled) P63/mmc (flat) |
| Unit cell | a = 2.461, c = 6.708 ; Z = 4 |
| Identification | |
| Color | Iron-black to steel-gray; deep blue in transmitted light |
| Crystal habit | Tabular, six-sided foliated masses, granular to compacted masses |
| Twinning | Present |
| Cleavage | Basal – perfect on {0001} |
| Fracture | Flaky, otherwise rough when not on cleavage |
| Tenacity | Flexible non-elastic, sectile |
| Mohs scale hardness | 1–2 |
| Luster | Metallic, earthy |
| Streak | Black |
| Diaphaneity | Opaque, transparent only in extremely thin flakes |
| Specific gravity | 1.9–2.3 |
| Density | 2.09–2.23 g/cm |
| Optical properties | Uniaxial (−) |
| Pleochroism | Strong |
| Solubility | Soluble in molten nickel, warm chlorosulfuric acid |
| Other characteristics | strongly anisotropic, conducts electricity, greasy feel, readily marks |
| References | |
Graphite (/ˈɡræfaɪt/) is a crystalline allotrope (form) of the element carbon. It consists of many stacked layers of graphene, typically in the excess of hundreds of layers. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on a large scale (1.3 million metric tons per year in 2022) for uses in many critical industries including refractories (50%), lithium-ion batteries (18%), foundries (10%), lubricants (5%), among others (17%). Under extremely high pressures and extremely high temperatures it converts to diamond. Graphite's low cost, thermal and chemical inertness and characteristic conductivity of heat and electricity finds numerous applications in high energy and high temperature processes.
Types and varieties
Natural graphite
Graphite occurs naturally in ores that can be classified into one of two categories either amorphous (microcrystalline) or crystalline (flake or lump/chip) which is determined by the ore morphology, crystallinity, and grain size. All naturally occurring graphite deposits are formed from the metamorphism of carbonaceous sedimentary rocks, and the ore type is due to its geologic setting. Coal that has been thermally metamorphosed is the typical source of amorphous graphite. Crystalline flake graphite is mined from carbonaceous metamorphic rocks, while lump or chip graphite is mined from veins which occur in high-grade metamorphic regions. There are serious negative environmental impacts to graphite mining.
Synthetic graphite
Synthetic graphite is graphite of high purity produced by thermal graphitization at temperatures in excess of 2,100 °C from hydrocarbon materials, most commonly through the Acheson process. The high temperatures are maintained for weeks, and are required not only to form the graphite from the precursor carbons but to also vaporize any impurities that may be present, including hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, organics, and metals. This is why synthetic graphite is highly pure in excess of 99.9% C purity, but typically has lower density, conductivity and a higher porosity than its natural equivalent. Synthetic graphite can also be formed into very large flakes (cm) while maintaining its high purity unlike almost all sources of natural graphite. Synthetic graphite has also been known to be formed by other methods including by chemical vapor deposition from hydrocarbons at temperatures above 2,500 K (2,230 °C), by decomposition of thermally unstable carbides or by crystallizing from metal melts supersaturated with carbon.
Biographite
Biographite is a commercial product proposal for reducing the carbon footprint of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. It is produced from forestry waste and similar byproducts by a company in New Zealand using a novel process called thermo-catalytic graphitisation which project is supported by grants from interested parties including a forestry company in Finland and a battery maker in Hong Kong
Natural graphite
Occurrence
Graphite occurs in metamorphic rocks as a result of the reduction of sedimentary carbon compounds during metamorphism. It also occurs in igneous rocks and in meteorites. Minerals associated with graphite include quartz, calcite, micas and tourmaline. The principal export sources of mined graphite are in order of tonnage: China, Mexico, Canada, Brazil, and Madagascar. Significant unexploited graphite resources also exists in Colombia's Cordillera Central in the form of graphite-bearing schists.
In meteorites, graphite occurs with troilite and silicate minerals. Small graphitic crystals in meteoritic iron are called cliftonite. Some microscopic grains have distinctive isotopic compositions, indicating that they were formed before the Solar System. They are one of about 12 known types of minerals that predate the Solar System and have also been detected in molecular clouds. These minerals were formed in the ejecta when supernovae exploded or low to intermediate-sized stars expelled their outer envelopes late in their lives. Graphite may be the second or third oldest mineral in the Universe.
Structure
Graphite consists of sheets of trigonal planar carbon. The individual layers are called graphene. In each layer, each carbon atom is bonded to three other atoms forming a continuous layer of sp bonded carbon hexagons, like a honeycomb lattice with a bond length of 0.142 nm, and the distance between planes is 0.335 nm. Bonding between layers is relatively weak van der Waals bonds, which allows the graphene-like layers to be easily separated and to glide past each other. Electrical conductivity perpendicular to the layers is consequently about 1000 times lower.
There are two allotropic forms called alpha (hexagonal) and beta (rhombohedral), differing in terms of the stacking of the graphene layers: stacking in alpha graphite is ABA, as opposed to ABC stacking in the energetically less stable beta graphite. Rhombohedral graphite cannot occur in pure form. Natural graphite, or commercial natural graphite, contains 5 to 15% rhombohedral graphite and this may be due to intensive milling. The alpha form can be converted to the beta form through shear forces, and the beta form reverts to the alpha form when it is heated to 1300 °C for four hours.
-
 Scanning tunneling microscope image of graphite surface
Scanning tunneling microscope image of graphite surface
-
 Side view of ABA layer stacking
Side view of ABA layer stacking
-
 Plane view of layer stacking
Plane view of layer stacking
-
 Alpha graphite's unit cell
Alpha graphite's unit cell
Thermodynamics

The equilibrium pressure and temperature conditions for a transition between graphite and diamond is well established theoretically and experimentally. The pressure changes linearly between 1.7 GPa at 0 K and 12 GPa at 5000 K (the diamond/graphite/liquid triple point). However, the phases have a wide region about this line where they can coexist. At normal temperature and pressure, 20 °C (293 K) and 1 standard atmosphere (0.10 MPa), the stable phase of carbon is graphite, but diamond is metastable and its rate of conversion to graphite is negligible. However, at temperatures above about 4500 K, diamond rapidly converts to graphite. Rapid conversion of graphite to diamond requires pressures well above the equilibrium line: at 2000 K, a pressure of 35 GPa is needed.
Other properties

The acoustic and thermal properties of graphite are highly anisotropic, since phonons propagate quickly along the tightly bound planes, but are slower to travel from one plane to another. Graphite's high thermal stability and electrical and thermal conductivity facilitate its widespread use as electrodes and refractories in high temperature material processing applications. However, in oxygen-containing atmospheres graphite readily oxidizes to form carbon dioxide at temperatures of 700 °C and above.
Graphite is an electrical conductor, hence useful in such applications as arc lamp electrodes. It can conduct electricity due to the vast electron delocalization within the carbon layers (a phenomenon called aromaticity). These valence electrons are free to move, so are able to conduct electricity. However, the electricity is primarily conducted within the plane of the layers. The conductive properties of powdered graphite allow its use as pressure sensor in carbon microphones.
Graphite and graphite powder are valued in industrial applications for their self-lubricating and dry lubricating properties. However, the use of graphite is limited by its tendency to facilitate pitting corrosion in some stainless steel, and to promote galvanic corrosion between dissimilar metals (due to its electrical conductivity). It is also corrosive to aluminium in the presence of moisture. For this reason, the US Air Force banned its use as a lubricant in aluminium aircraft, and discouraged its use in aluminium-containing automatic weapons. Even graphite pencil marks on aluminium parts may facilitate corrosion. Another high-temperature lubricant, hexagonal boron nitride, has the same molecular structure as graphite. It is sometimes called white graphite, due to its similar properties.
When a large number of crystallographic defects bind these planes together, graphite loses its lubrication properties and becomes what is known as pyrolytic graphite. It is also highly anisotropic, and diamagnetic, thus it will float in mid-air above a strong magnet. (If it is made in a fluidized bed at 1000–1300 °C then it is isotropic turbostratic, and is used in blood-contacting devices like mechanical heart valves and is called pyrolytic carbon, and is not diamagnetic. Pyrolytic graphite and pyrolytic carbon are often confused but are very different materials.)
For a long time graphite has been considered to be hydrophobic. However, recent studies using highly ordered pyrolytic graphite have shown that freshly clean graphite is hydrophilic (contact angle of 70° approximately), and it becomes hydrophobic (contact angle of 95° approximately) due to airborne pollutants (hydrocarbons) present in the atmosphere. Those contaminants also alter the electric equipotential surface of graphite by creating domains with potential differences of up to 200 mV as measured with kelvin probe force microscopy. Such contaminants can be desorbed by increasing the temperature of graphite to approximately 50 °C or higher.
Natural and crystalline graphites are not often used in pure form as structural materials, due to their shear-planes, brittleness, and inconsistent mechanical properties.
History of natural graphite use

In the 4th millennium BCE, during the Neolithic Age in southeastern Europe, the Marița culture used graphite in a ceramic paint for decorating pottery.
Sometime before 1565 (some sources say as early as 1500), an enormous deposit of graphite was discovered on the approach to Grey Knotts from the hamlet of Seathwaite in Borrowdale parish, Cumbria, England, which the locals found useful for marking sheep. During the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603), Borrowdale graphite was used as a refractory material to line molds for cannonballs, resulting in rounder, smoother balls that could be fired farther, contributing to the strength of the English navy. This particular deposit of graphite was extremely pure and soft, and could easily be cut into sticks. Because of its military importance, this unique mine and its production were strictly controlled by the Crown.
During the 19th century, graphite's uses greatly expanded to include stove polish, lubricants, paints, crucibles, foundry facings, and pencils, a major factor in the expansion of educational tools during the first great rise of education for the masses. The British Empire controlled most of the world's production (especially from Ceylon), but production from Austrian, German, and American deposits expanded by mid-century. For example, the Dixon Crucible Company of Jersey City, New Jersey, founded by Joseph Dixon and partner Orestes Cleveland in 1845, opened mines in the Lake Ticonderoga district of New York, built a processing plant there, and a factory to manufacture pencils, crucibles and other products in New Jersey, described in the Engineering & Mining Journal 21 December 1878. The Dixon pencil is still in production.

The beginnings of the revolutionary froth flotation process are associated with graphite mining. Included in the E&MJ article on the Dixon Crucible Company is a sketch of the "floating tanks" used in the age-old process of extracting graphite. Because graphite is so light, the mix of graphite and waste was sent through a final series of water tanks where a cleaner graphite "floated" off, which left waste to drop out. In an 1877 patent, the two brothers Bessel (Adolph and August) of Dresden, Germany, took this "floating" process a step further and added a small amount of oil to the tanks and boiled the mix – an agitation or frothing step – to collect the graphite, the first steps toward the future flotation process. Adolph Bessel received the Wohler Medal for the patented process that upgraded the recovery of graphite to 90% from the German deposit. In 1977, the German Society of Mining Engineers and Metallurgists organized a special symposium dedicated to their discovery and, thus, the 100th anniversary of flotation.
In the United States, in 1885, Hezekiah Bradford of Philadelphia patented a similar process, but it is uncertain if his process was used successfully in the nearby graphite deposits of Chester County, Pennsylvania, a major producer by the 1890s. The Bessel process was limited in use, primarily because of the abundant cleaner deposits found around the globe, which needed not much more than hand-sorting to gather the pure graphite. The state of the art, c. 1900, is described in the Canadian Department of Mines report on graphite mines and mining when Canadian deposits began to become important producers of graphite.
Other names

Historically, graphite was called black lead or plumbago. Plumbago was commonly used in its massive mineral form. Both of these names arise from confusion with the similar-appearing lead ores, particularly galena. The Latin word for lead, plumbum, gave its name to the English term for this grey metallic-sheened mineral and even to the leadworts or plumbagos, plants with flowers that resemble this colour.
The term black lead usually refers to a powdered or processed graphite, matte black in color.
Abraham Gottlob Werner coined the name graphite ("writing stone") in 1789. He attempted to clear up the confusion between molybdena, plumbago and black lead after Carl Wilhelm Scheele in 1778 proved that these were at least three different minerals. Scheele's analysis showed that the chemical compounds molybdenum sulfide (molybdenite), lead(II) sulfide (galena) and graphite were three different soft black minerals.
Uses of natural graphite
Natural graphite is mostly used for refractories, batteries, steelmaking, expanded graphite, brake linings, foundry facings, and lubricants.
Refractories
The use of graphite as a refractory (heat-resistant) material began before 1900 with graphite crucibles used to hold molten metal; this is now a minor part of refractories. In the mid-1980s, the carbon-magnesite brick became important, and a bit later the alumina-graphite shape. As of 2017 the order of importance is: alumina-graphite shapes, carbon-magnesite brick, Monolithics (gunning and ramming mixes), and then crucibles.
Crucibles began using very large flake graphite, and carbon-magnesite bricks requiring not quite so large flake graphite; for these and others there is now much more flexibility in the size of flake required, and amorphous graphite is no longer restricted to low-end refractories. Alumina-graphite shapes are used as continuous casting ware, such as nozzles and troughs, to convey the molten steel from ladle to mold, and carbon magnesite bricks line steel converters and electric-arc furnaces to withstand extreme temperatures. Graphite blocks are also used in parts of blast furnace linings where the high thermal conductivity of the graphite is critical to ensuring adequate cooling of the bottom and hearth of the furnace. High-purity monolithics are often used as a continuous furnace lining instead of carbon-magnesite bricks.
The US and European refractories industry had a crisis in 2000–2003, with an indifferent market for steel and a declining refractory consumption per tonne of steel underlying firm buyouts and many plant closures. Many of the plant closures resulted from the acquisition of Harbison-Walker Refractories by RHI AG and some plants had their equipment auctioned off. Since much of the lost capacity was for carbon-magnesite brick, graphite consumption within the refractories area moved towards alumina-graphite shapes and Monolithics, and away from the brick. The major source of carbon-magnesite brick is now China. Almost all of the above refractories are used to make steel and account for 75% of refractory consumption; the rest is used by a variety of industries, such as cement.
According to the USGS, US natural graphite consumption in refractories comprised 12,500 tonnes in 2010.
Batteries
The use of graphite in batteries has increased since the 1970s. Natural and synthetic graphite are used as an anode material to construct electrodes in major battery technologies.
The demand for batteries, primarily nickel–metal hydride and lithium-ion batteries, caused a growth in demand for graphite in the late 1980s and early 1990s – a growth driven by portable electronics, such as portable CD players and power tools. Laptops, mobile phones, tablets, and smartphone products have increased the demand for batteries. Electric-vehicle batteries are anticipated to increase graphite demand. As an example, a lithium-ion battery in a fully electric Nissan Leaf contains nearly 40 kg of graphite.
Radioactive graphite removed from nuclear reactors has been investigated as a source of electricity for low-power applications. This waste is rich in carbon-14, which emits electrons through beta decay, so it could potentially be used as the basis for a betavoltaic device. This concept is known as the diamond battery.
Graphite anode materials
Graphite is "predominant anode material used today in lithium-ion batteries". Electric-vehicle (EV) batteries contain four basic components: anode, cathode, electrolyte, and separator. While there is much focus on the cathode materials – lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese, etc. – the predominant anode material used in virtually all EV batteries is graphite.
Steelmaking
Natural graphite in steelmaking mostly goes into raising the carbon content in molten steel; it can also serve to lubricate the dies used to extrude hot steel. Carbon additives face competitive pricing from alternatives such as synthetic graphite powder, petroleum coke, and other forms of carbon. A carbon raiser is added to increase the carbon content of the steel to a specified level. An estimate based on USGS's graphite consumption statistics indicates that steelmakers in the US used 10,500 tonnes in this fashion in 2005.
Brake linings
Natural amorphous and fine flake graphite are used in brake linings or brake shoes for heavier (nonautomotive) vehicles, and became important with the need to substitute for asbestos. This use has been important for quite some time, but nonasbestos organic (NAO) compositions are beginning to reduce graphite's market share. A brake-lining industry shake-out with some plant closures has not been beneficial, nor has an indifferent automotive market. According to the USGS, US natural graphite consumption in brake linings was 6,510 tonnes in 2005.
Foundry facings and lubricants
A foundry-facing mold wash is a water-based paint of amorphous or fine flake graphite. Painting the inside of a mold with it and letting it dry leaves a fine graphite coat that will ease the separation of the object cast after the hot metal has cooled. Graphite lubricants are specialty items for use at very high or very low temperatures, as forging die lubricant, an antiseize agent, a gear lubricant for mining machinery, and to lubricate locks. Having low-grit graphite, or even better, no-grit graphite (ultra high purity), is highly desirable. It can be used as a dry powder, in water or oil, or as colloidal graphite (a permanent suspension in a liquid). An estimate based on USGS graphite consumption statistics indicates that 2,200 tonnes were used in this fashion in 2005. Metal can also be impregnated into graphite to create a self-lubricating alloy for application in extreme conditions, such as bearings for machines exposed to high or low temperatures.
Everyday use
Pencils

The ability to leave marks on paper and other objects gave graphite its name, given in 1789 by German mineralogist Abraham Gottlob Werner. It stems from γράφειν ("graphein"), meaning to write or draw in Ancient Greek.
From the 16th century, all pencils were made with leads of English natural graphite, but modern pencil lead is most commonly a mix of powdered graphite and clay; it was invented by Nicolas-Jacques Conté in 1795. It is chemically unrelated to the metal lead, whose ores had a similar appearance, hence the continuation of the name. Plumbago is another older term for natural graphite used for drawing, typically as a lump of the mineral without a wood casing. The term plumbago drawing is normally restricted to 17th and 18th-century works, mostly portraits.
Today, pencils are still a small but significant market for natural graphite. Around 7% of the 1.1 million tonnes produced in 2011 was used to make pencils. Low-quality amorphous graphite is used and sourced mainly from China.
In art, graphite is typically used to create detailed and precise drawings, as it allows for a wide range of values (light to dark) to be achieved. It can also be used to create softer, more subtle lines and shading. Graphite is popular among artists because it is easy to control, easy to erase, and produces a clean, professional look. It is also relatively inexpensive and widely available. Many artists use graphite in conjunction with other media, such as charcoal or ink, to create a range of effects and textures in their work. Graphite of various hardness or softness results in different qualities and tones when used as an artistic medium.
Pinewood derby
Graphite is probably the most-used lubricant in pinewood derbies.
Other uses
Natural graphite has found uses in zinc-carbon batteries, electric motor brushes, and various specialized applications. Railroads would often mix powdered graphite with waste oil or linseed oil to create a heat-resistant protective coating for the exposed portions of a steam locomotive's boiler, such as the smokebox or lower part of the firebox. The Scope soldering iron uses a graphite tip as its heating element.
Expanded graphite
Expanded graphite is made by immersing natural flake graphite in a bath of chromic acid, then concentrated sulfuric acid, which forces the crystal lattice planes apart, thus expanding the graphite. The expanded graphite can be used to make graphite foil or used directly as a "hot top" compound to insulate molten metal in a ladle or red-hot steel ingots and decrease heat loss, or as firestops fitted around a fire door or in sheet metal collars surrounding plastic pipe (during a fire, the graphite expands and chars to resist fire penetration and spread), or to make high-performance gasket material for high-temperature use. After being made into graphite foil, the foil is machined and assembled into the bipolar plates in fuel cells. The foil is made into heat sinks for laptop computers which keeps them cool while saving weight, and is made into a foil laminate that can be used in valve packings or made into gaskets. Old-style packings are now a minor member of this grouping: fine flake graphite in oils or greases for uses requiring heat resistance. A GAN estimate of current US natural graphite consumption in this end-use is 7,500 tonnes.
Intercalated graphite
Main article: Graphite intercalation compound
Graphite forms intercalation compounds with some metals and small molecules. In these compounds, the host molecule or atom gets "sandwiched" between the graphite layers, resulting in a type of compound with variable stoichiometry. A prominent example of an intercalation compound is potassium graphite, denoted by the formula KC8. Some graphite intercalation compounds are superconductors. The highest transition temperature (by June 2009) Tc = 11.5 K is achieved in CaC6, and it further increases under applied pressure (15.1 K at 8 GPa). Graphite's ability to intercalate lithium ions without significant damage from swelling is what makes it the dominant anode material in lithium-ion batteries.
History of synthetic graphite
Invention of a process to produce synthetic graphite
In 1893, Charles Street of Le Carbone discovered a process for making artificial graphite. In the mid-1890s, Edward Goodrich Acheson (1856–1931) accidentally invented another way to produce synthetic graphite after synthesizing carborundum (also called silicon carbide). He discovered that overheating carborundum, as opposed to pure carbon, produced almost pure graphite. While studying the effects of high temperature on carborundum, he had found that silicon vaporizes at about 4,150 °C (7,500 °F), leaving the carbon behind in graphitic carbon. This graphite became valuable as a lubricant.
Acheson's technique for producing silicon carbide and graphite is named the Acheson process. In 1896, Acheson received a patent for his method of synthesizing graphite, and in 1897 started commercial production. The Acheson Graphite Co. was formed in 1899.
Synthetic graphite can also be prepared from polyimide and then commercialized.
Scientific research
Highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) is the highest-quality synthetic form of graphite. It is used in scientific research, in particular, as a length standard for the calibration of scanning probe microscopes.
Electrodes
Graphite electrodes carry the electricity that melts scrap iron and steel, and sometimes direct-reduced iron (DRI), in electric arc furnaces, which are the vast majority of steel furnaces. They are made from petroleum coke after it is mixed with coal tar pitch. They are extruded and shaped, then baked to carbonize the binder (pitch). This is finally graphitized by heating it to temperatures approaching 3,000 °C (5,430 °F), at which the carbon atoms arrange into graphite. They can vary in size up to 3.5 m (11 ft) long and 75 cm (30 in) in diameter. An increasing proportion of global steel is made using electric arc furnaces, and the electric arc furnace itself is becoming more efficient, making more steel per tonne of electrode. An estimate based on USGS data indicates that graphite electrode consumption was 197,000 t (217,000 short tons) in 2005.
Electrolytic aluminium smelting also uses graphitic carbon electrodes. On a much smaller scale, synthetic graphite electrodes are used in electrical discharge machining (EDM), commonly to make injection molds for plastics.
Powder and scrap
The powder is made by heating powdered petroleum coke above the temperature of graphitization, sometimes with minor modifications. The graphite scrap comes from pieces of unusable electrode material (in the manufacturing stage or after use) and lathe turnings, usually after crushing and sizing. Most synthetic graphite powder goes to carbon raising in steel (competing with natural graphite), with some used in batteries and brake linings. According to the United States Geographical Survey, US synthetic graphite powder and scrap production were 95,000 t (93,000 long tons; 105,000 short tons) in 2001 (latest data).
Neutron moderator
Main article: Nuclear graphiteSpecial grades of synthetic graphite, such as Gilsocarbon, also find use as a matrix and neutron moderator within nuclear reactors. Its low neutron cross-section also recommends it for use in proposed fusion reactors. Care must be taken that reactor-grade graphite is free of neutron absorbing materials such as boron, widely used as the seed electrode in commercial graphite deposition systems – this caused the failure of the Germans' World War II graphite-based nuclear reactors. Since they could not isolate the difficulty they were forced to use far more expensive heavy water moderators. Graphite used for nuclear reactors is often referred to as nuclear graphite. Herbert G. McPherson, a Berkeley trained physicist at National Carbon, a division of Union Carbide, was key in confirming a conjecture of Leo Szilard that boron impurities even in "pure" graphite were responsible for a neutron absorption cross-section in graphite that compromised U-235 chain reactions. McPherson was aware of the presence of impurities in graphite because, with the use of Technicolor in cinematography, the spectra of graphite electrode arcs used in movie projectors required impurities to enhance emission of light in the red region to display warmer skin tones on the screen. Thus, had it not been for color movies, chances are that the first sustained natural U chain reaction would have required a heavy water moderated reactor.
Other uses
Graphite (carbon) fiber and carbon nanotubes are also used in carbon fiber reinforced plastics, and in heat-resistant composites such as reinforced carbon-carbon (RCC). Commercial structures made from carbon fiber graphite composites include fishing rods, golf club shafts, bicycle frames, sports car body panels, the fuselage of the Boeing 787 Dreamliner and pool cue sticks and have been successfully employed in reinforced concrete. The mechanical properties of carbon fiber graphite-reinforced plastic composites and grey cast iron are strongly influenced by the role of graphite in these materials. In this context, the term "(100%) graphite" is often loosely used to refer to a pure mixture of carbon reinforcement and resin, while the term "composite" is used for composite materials with additional ingredients.
Modern smokeless powder is coated in graphite to prevent the buildup of static charge.
Graphite has been used in at least three radar absorbent materials. It was mixed with rubber in Sumpf and Schornsteinfeger, which were used on U-boat snorkels to reduce their radar cross section. It was also used in tiles on early F-117 Nighthawk stealth strike fighters.
Graphite composites are used as absorber for high-energy particles, for example in the Large Hadron Collider beam dump.
Graphite rods when filed into shape are used as a tool in glassworking to manipulate hot molten glass.
Graphite mining, beneficiation, and milling



Graphite is mined by both open pit and underground methods. Graphite usually needs beneficiation. This may be carried out by hand-picking the pieces of gangue (rock) and hand-screening the product or by crushing the rock and floating out the graphite. Beneficiation by flotation encounters the difficulty that graphite is very soft and "marks" (coats) the particles of gangue. This makes the "marked" gangue particles float off with the graphite, yielding impure concentrate. There are two ways of obtaining a commercial concentrate or product: repeated regrinding and floating (up to seven times) to purify the concentrate, or by acid leaching (dissolving) the gangue with hydrofluoric acid (for a silicate gangue) or hydrochloric acid (for a carbonate gangue).
In milling, the incoming graphite products and concentrates can be ground before being classified (sized or screened), with the coarser flake size fractions (below 8 mesh, 8–20 mesh, 20–50 mesh) carefully preserved, and then the carbon contents are determined. Some standard blends can be prepared from the different fractions, each with a certain flake size distribution and carbon content. Custom blends can also be made for individual customers who want a certain flake size distribution and carbon content. If flake size is unimportant, the concentrate can be ground more freely. Typical end products include a fine powder for use as a slurry in oil drilling and coatings for foundry molds, carbon raiser in the steel industry (Synthetic graphite powder and powdered petroleum coke can also be used as carbon raiser). Environmental impacts from graphite mills consist of air pollution including fine particulate exposure of workers and also soil contamination from powder spillages leading to heavy metal contamination of soil.
According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), world production of natural graphite in 2016 was 1,200,000 tonnes, of which the following major exporters are: China (780,000 t), India (170,000 t), Brazil (80,000 t), Turkey (32,000 t) and North Korea (6,000 t). Graphite is not currently mined in the United States, but there are many historical mine sites including ones in Alabama, Montana, and in the Adirondacks of NY. Westwater Resources is in the development stages of creating a pilot plant for their Coosa Graphite Mine near Sylacauga, Alabama. U.S. production of synthetic graphite in 2010 was 134,000 t valued at $1.07 billion.
Occupational safety
Potential health effects include:
- Inhalation: No inhalation hazard in manufactured and shipped state. Dust and fumes generated from the material can enter the body by inhalation. High concentrations of dust and fumes may irritate the throat and respiratory system and cause coughing. Frequent inhalation of fume/dust over a long period of time increases the risk of developing lung diseases. Prolonged and repeated overexposure to dust can lead to pneumoconiosis. Pre-existing pulmonary disorders, such as emphysema, may possibly be aggravated by prolonged exposure to high concentrations of graphite dusts.
- Eye contact: Dust in the eyes will cause irritation. Exposed may experience eye tearing, redness, and discomfort.
- Skin contact: Under normal conditions of intended use, this material does not pose a risk to health. Dust may irritate skin.
- Ingestion: Not relevant, due to the form of the product in its manufactured and shipped state. However, ingestion of dusts generated during working operations may cause nausea and vomiting.
- Potential physical / chemical effects: Bulk material is non-combustible. The material may form dust and can accumulate electrostatic charges, which may cause an electrical spark (ignition source). High dust levels may create potential for explosion.
United States
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has set the legal limit (permissible exposure limit) for graphite exposure in the workplace as a time weighted average (TWA) of 15 million particles per cubic foot (1.5 mg/m) over an 8-hour workday. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of TWA 2.5 mg/m respirable dust over an 8-hour workday. At levels of 1250 mg/m, graphite is immediately dangerous to life and health.
Graphite recycling
The most common way of recycling graphite occurs when synthetic graphite electrodes are either manufactured and pieces are cut off or lathe turnings are discarded for reuse, or the electrode (or other materials) are used all the way down to the electrode holder. A new electrode replaces the old one, but a sizeable piece of the old electrode remains. This is crushed and sized, and the resulting graphite powder is mostly used to raise the carbon content of molten steel.
Graphite-containing refractories are sometimes also recycled, but often are not due to their low graphite content: the largest-volume items, such as carbon-magnesite bricks that contain only 15–25% graphite, usually contain too little graphite to be worthwhile to recycle. However, some recycled carbon–magnesite brick is used as the basis for furnace-repair materials, and also crushed carbon–magnesite brick is used in slag conditioners.
While crucibles have a high graphite content, the volume of crucibles used and then recycled is very small.
A high-quality flake graphite product that closely resembles natural flake graphite can be made from steelmaking kish. Kish is a large-volume near-molten waste skimmed from the molten iron feed to a basic oxygen furnace and consists of a mix of graphite (precipitated out of the supersaturated iron), lime-rich slag, and some iron. The iron is recycled on-site, leaving a mixture of graphite and slag. The best recovery process uses hydraulic classification (which utilizes a flow of water to separate minerals by specific gravity: graphite is light and settles nearly last) to get a 70% graphite rough concentrate. Leaching this concentrate with hydrochloric acid gives a 95% graphite product with a flake size ranging from 10 mesh (2 mm) down.
Research and innovation in graphite technologies
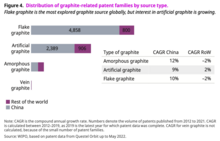

Globally, over 60,000 patent families in graphite technologies were filed from 2012 to 2021. Patents were filed by applicants from over 60 countries and regions. However, graphite-related patent families originated predominantly from just a few countries. China was the top contributor with more than 47,000 patent families, accounting for four in every five graphite patent families filed worldwide in the last decade. Among other leading countries were Japan, the Republic of Korea, the United States and the Russian Federation. Together, these top five countries of applicant origin accounted for 95 percent of global patenting output related to graphite.
Among the different graphite sources, flake graphite has the highest number of patent families, with more than 5,600 filed worldwide from 2012 to 2021. Supported by active research from its commercial entities and research institutions, China is the country most actively exploiting flake graphite and has contributed to 85 percent of global patent filings in this area.
At the same time, innovations exploring new synthesis methods and uses for artificial graphite are gaining interest worldwide, as countries seek to exploit the superior material qualities associated with this man-made substance and reduce reliance on the natural material. Patenting activity is strongly led by commercial entities, particularly world-renowned battery manufacturers and anode material suppliers, with patenting interest focused on battery anode applications.
The exfoliation process for bulk graphite, which involves separating the carbon layers within graphite, has been extensively studied between 2012 and 2021. Specifically, ultrasonic and thermal exfoliation have been the two most popular approaches worldwide, with 4,267 and 2,579 patent families, respectively, significantly more than for either the chemical or electrochemical alternatives.
Global patenting activity relating to ultrasonic exfoliation has decreased over the years, indicating that this low-cost technique has become well established. Thermal exfoliation is a more recent process. Compared to ultrasonic exfoliation, this fast and solvent-free thermal approach has attracted greater commercial interest.
As the most widespread anode material for lithium-ion batteries, graphite has drawn significant attention worldwide for use in battery applications. With over 8,000 patent families filed from 2012 to 2021, battery applications were a key driver of global graphite-related inventions. Innovations in this area are led by battery manufacturers or anode suppliers who have amassed sizable patent portfolios focused strongly on battery performance improvements based on graphite anode innovation. Besides industry players, academia and research institutions have been an essential source of innovation in graphite anode technologies.
Graphite for polymer applications was an innovation hot topic from 2012 to 2021, with over 8,000 patent families recorded worldwide. However, in recent years, in the top countries of applicant origin in this area, including China, Japan and the United States of America (US), patent filings have decreased.
Graphite for manufacturing ceramics represents another area of intensive research, with over 6,000 patent families registered in the last decade alone. Specifically, graphite for refractory accounted for over one-third of ceramics-related graphite patent families in China and about one-fifth in the rest of the world. Other important graphite applications include high-value ceramic materials such as carbides for specific industries, ranging from electrical and electronics, aerospace and precision engineering to military and nuclear applications.
Carbon brushes represent a long-explored graphite application area. There have been few inventions in this area over the last decade, with less than 300 patent families filed from 2012 to 2021, very significantly less than between 1992 and 2011.
Biomedical, sensor, and conductive ink are emerging application areas for graphite that have attracted interest from both academia and commercial entities, including renowned universities and multinational corporations. Typically for an emerging technology area, related patent families were filed by various organizations without any players dominating. As a result, the top applicants have a small number of inventions, unlike in well-explored areas, where they will have strong technology accumulation and large patent portfolios. The innovation focus of these three emerging areas is highly scattered and can be diverse, even for a single applicant. However, recent inventions are seen to leverage the development of graphite nanomaterials, particularly graphite nanocomposites and graphene.
See also
- Carbon fiber
- Carbon nanotube
- Exfoliated graphite nano-platelets
- Fullerene
- Graphene
- Graphitizing and non-graphitizing carbons
- Intumescent
- Lonsdaleite
- Passive fire protection
- Pyrolytic carbon
Sources
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC-BY. Text taken from Patent Landscape Report - Graphite and its applications, WIPO.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC-BY. Text taken from Patent Landscape Report - Graphite and its applications, WIPO.
References
- Warr, L.N. (2021). "IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols". Mineralogical Magazine. 85 (3): 291–320. Bibcode:2021MinM...85..291W. doi:10.1180/mgm.2021.43. S2CID 235729616.
- Liquid method: pure graphene production. Phys.org (May 30, 2010).
- Graphite. Mindat.org.
- Graphite. Webmineral.com.
- ^ Anthony, John W.; Bideaux, Richard A.; Bladh, Kenneth W.; Nichols, Monte C., eds. (1990). "Graphite" (PDF). Handbook of Mineralogy. Vol. I (Elements, Sulfides, Sulfosalts). Chantilly, VA: Mineralogical Society of America. ISBN 978-0962209703. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2013-10-04.
- "Graphite global consumption share by end use and type".
- ^ Robinson, Gilpin R.; Hammarstrom, Jane M.; Olson, Donald W. (2017). Schulz, Klaus J.; Deyoung, John H.; Seal, Robert R.; Bradley, Dwight C. (eds.). "Graphite". doi:10.3133/pp1802J.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- US 836355, Acheson, E. G., "Production of Graphite", published 1906-11-20
- Marsh, Harry; Rodríguez-Reinoso, Francisco (2006). "Production and Reference Material". Activated Carbon. pp. 454–508. doi:10.1016/B978-008044463-5/50023-6. ISBN 978-0-08-044463-5.
- "Batteries made from woodchips could clean up the EV industry". euronews. February 26, 2024.
- "CarbonScape Renewable Biographite Anode Material Ready to Scale".
- "Graphite". Minerals Database. Minerals Education Coalition. 2018. Retrieved 9 December 2018.
- Bustamante, C.; Cardona, A. (2024). "Is the Central Cordillera of Colombia a potential source of graphite?: Implications for the energy transition in Colombia". Andean Geology. 51 (2): 413–420. doi:10.5027/andgeoV51n2-3728.
- ^ graphite. Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
- Lugaro, Maria (2005). Stardust From Meteorites: An Introduction To Presolar Grains. World Scientific. pp. 14, 154–157. ISBN 9789814481373.
- Hazen, R. M.; Downs, R. T.; Kah, L.; Sverjensky, D. (13 February 2013). "Carbon Mineral Evolution". Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. 75 (1): 79–107. Bibcode:2013RvMG...75...79H. doi:10.2138/rmg.2013.75.4.
- McCoy, T. J. (22 February 2010). "Mineralogical Evolution of Meteorites". Elements. 6 (1): 19–23. Bibcode:2010Eleme...6...19M. doi:10.2113/gselements.6.1.19.
- Delhaes, Pierre (2000). "Polymorphism of carbon". In Delhaes, Pierre (ed.). Graphite and precursors. Gordon & Breach. pp. 1–24. ISBN 9789056992286.
- Pierson, Hugh O. (2012). Handbook of carbon, graphite, diamond, and fullerenes : properties, processing, and applications. Noyes Publications. pp. 40–41. ISBN 9780815517399.
- Delhaes, P. (2001). Graphite and Precursors. CRC Press. ISBN 978-90-5699-228-6.
- Chung, D. D. L. (2002). "Review Graphite". Journal of Materials Science. 37 (8): 1475–1489. doi:10.1023/A:1014915307738. S2CID 189839788.
- Pierson, Hugh O. (1993). Handbook of carbon, graphite, diamond, and fullerenes : properties, processing, and applications. Park Ridge, N.J.: Noyes Publications. ISBN 0-8155-1739-4. OCLC 49708274.
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Rhombohedral graphite". doi:10.1351/goldbook.R05385
- ^ Latychevskaia, Tataiana; Son, Seok-Kyun; Yang, Yaping; Chancellor, Dale; Brown, Michael; Ozdemir, Servet; Madan, Ivan; Berruto, Gabriele; Carbone, Fabrizio; Mishchenko, Artem; Novoselov, Kostya (2019-08-17). "Stacking transition in rhombohedral graphite". Frontiers of Physics. 14 (1). 13608. arXiv:1908.06284. Bibcode:2019FrPhy..1413608L. doi:10.1007/s11467-018-0867-y. S2CID 125322808.
- E. Fitzer; et al. (1995). "Recommended terminology for the description of carbon as a solid (IUPAC Recommendations 1995)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 67 (3): 473–506. doi:10.1351/pac199567030473.
- ^ Bundy, P.; Bassett, W. A.; Weathers, M. S.; Hemley, R. J.; Mao, H. K.; Goncharov, A. F. (1996). "The pressure-temperature phase and transformation diagram for carbon; updated through 1994". Carbon. 34 (2): 141–153. Bibcode:1996Carbo..34..141B. doi:10.1016/0008-6223(96)00170-4.
- Wang, C. X.; Yang, G. W. (2012). "Thermodynamic and kinetic approaches of diamond and related nanomaterials formed by laser ablation in liquid". In Yang, Guowei (ed.). Laser ablation in liquids : principles and applications in the preparation of nanomaterials. Pan Stanford Pub. pp. 164–165. ISBN 9789814241526.
- Rock, Peter A. (1983). Chemical Thermodynamics. University Science Books. pp. 257–260. ISBN 9781891389320.
- Hanaor, Dorian; Michelazzi, Marco; Chenu, Jeremy; Leonelli, Cristina; Sorrell, Charles C. (December 2011). "The effects of firing conditions on the properties of electrophoretically deposited titanium dioxide films on graphite substrates". Journal of the European Ceramic Society. 31 (15): 2877–2885. arXiv:1303.2757. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.07.007.
- Deprez, N.; McLachlan, D. S. (1988). "The analysis of the electrical conductivity of graphite conductivity of graphite powders during compaction". Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 21 (1): 101–107. Bibcode:1988JPhD...21..101D. doi:10.1088/0022-3727/21/1/015. S2CID 250886376.
- Galvanic Corrosion Archived 2009-03-10 at the Wayback Machine. keytometals.com
- "ASM Tech Notes – TN7-0506 – Galvanic Corrosion" (PDF). Atlas Specialty Metals. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-02-27.
- Jones, Rick (USAF-Retired) Better Lubricants than Graphite. graflex.org
- "Weapons Lubricant in the Desert". September 16, 2005. Archived from the original on 2007-10-15. Retrieved 2009-06-06.
- "Good Engineering Practice/Corrosion". Lotus Seven Club. 9 April 2003. Archived from the original on 16 September 2009.
- Marsh, Harry; Reinoso, Francisco Rodríguez (2007). Activated carbon (1st ed.). Elsevier. pp. 497–498. ISBN 9780080455969.
- ^ Martinez-Martin, David; Longuinhos, Raphael; Izquierdo, Jesus G.; Marele, Antonela; Alexandre, Simone S.; Jaafar, Miriam; Gómez-Rodríguez, Jose M.; Bañares, Luis; Soler, Jose M.; Gomez-Herrero, Julio (September 2013). "Atmospheric contaminants on graphitic surfaces". Carbon. 61: 33–39. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.056.
- Li, Zhiting; Wang, Yongjin; Kozbial, Andrew; Shenoy, Ganesh; Zhou, Feng; McGinley, Rebecca; Ireland, Patrick; Morganstein, Brittni; Kunkel, Alyssa; Surwade, Sumedh P.; Li, Lei; Liu, Haitao (October 2013). "Effect of airborne contaminants on the wettability of supported graphene and graphite". Nature Materials. 12 (10): 925–931. doi:10.1038/nmat3709. PMID 23872731.
- Boardman, John. "The Neolithic-Eneolithic Period" (PDF). The Cambridge ancient history, Volume 3, Part 1. pp. 31–32. ISBN 978-0521224963. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 February 2013.
- Norgate, Martin; Norgate, Jean (2008). "Old Cumbria Gazetteer, black lead mine, Seathwaite". Geography Department, Portsmouth University. Retrieved 2008-05-19.
- Wainwright, Alfred (2005). A Pictorial Guide to the Lakeland Fells, Western Fells. London: Frances Lincoln. ISBN 978-0-7112-2460-5.
- The Statutes at Large: From the ... Year of the Reign of ... to the ... Year of the Reign of . 1764. p. 415.
- "History". Dixon Ticonderoga Company. Archived from the original on 7 April 2018.
- ^ Nguyen, Ahn (2003). Colloidal Science of Flotation. CRC Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0824747824.
- Cirkel, Fritz (1907). Graphite its Properties, Occurrence, Refining and Uses. Ottawa: Canadian Department of Mines. p. passim. Retrieved 6 April 2018.
- Electro-Plating on Non-Metallic Substances. Spons' Workshop Receipts Vol. II: Dyeing to Japanning. Spon. 1921. p. 132.
- Evans, John W. (1908). "V.— the Meanings and Synonyms of Plumbago". Transactions of the Philological Society. 26 (2): 133–179. doi:10.1111/j.1467-968X.1908.tb00513.x.
- Widenmann, Johann Friedrich Wilhelm (1794). Handbuch des oryktognostischen Theils der Mineralogie: Mit einer Farbentabelle und einer Kupfertafel. Crusius. p. 653.
- Scheele, C. W. K. (1779). "Versuche mit Wasserbley; Molybdaena". Svenska Vetensk. Academ. Handlingar. 40: 238.
- ^ "Graphite Statistics and Information". USGS. Retrieved 2009-09-09.
- Almeida, Bruno Vidal de; Neves, Elton Silva; Silva, Sidiney Nascimento; Vernilli Junior, Fernando (15 May 2017). "Blast Furnace Hearth Lining: Post Mortem Analysis". Materials Research. 20 (3): 814–818. doi:10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0875.
- Li, Yiwei; Li, Yawei; Sang, Shaobai; Chen, Xilai; Zhao, Lei; Li, Yuanbing; Li, Shujing (January 2014). "Preparation of Ceramic-Bonded Carbon Block for Blast Furnace". Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A. 45 (1): 477–481. Bibcode:2014MMTA...45..477L. doi:10.1007/s11661-013-1976-4. S2CID 137571156.
- Targray (August 27, 2020). "Graphite Anode Materials". Targray.
- Zhang, Hao; Yang, Yang; Ren, Dongsheng; Wang, Li; He, Xiangming (April 2021). "Graphite as anode materials: Fundamental mechanism, recent progress and advances". Energy Storage Materials. 36: 147–170. doi:10.1016/j.ensm.2020.12.027.
- "EV batteries need graphite – here's what's forecast for supply". Electrek.
- "Graphite/Metal Alloy Extends Material Life in High-Temperature Processes". Foundry Management & Technology. 2004-06-04. Retrieved 2019-06-20.
- Harper, Douglas. "graphite". Online Etymology Dictionary.
- Ritter, Steve (October 15, 2001). "Pencils & Pencil Lead". American Chemical Society.
- "The History of the Pencil". University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. Archived from the original on 2015-03-17. Retrieved 2013-02-15.
- "Electric Graphite Growing Demand From Electric Vehicles & Mobile Electronics" (PDF). galaxycapitalcorp.com. July 20, 2011. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2013. Retrieved February 15, 2013.
- Not known (January 29, 2018). "ART TECHNIQUE-GRAPHITE AS A MEDIUM". Sybaris.
- "Module 6: Media for 2-D Art" (PDF). Saylor.org. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-08-09. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- "Top 5 Speed Tips for Your Pinewood Derby Car". S&W Crafts Mfg. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- True color/appearance of the "Graphite, or Smokebox colors. List.nwhs.org. Retrieved on 2013-04-15.
- Emery, Nicolas; Hérold, Claire; Marêché, Jean-François; Lagrange, Philippe (2008). "Synthesis and superconducting properties of CaC6". Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 9 (4): 044102. Bibcode:2008STAdM...9d4102E. doi:10.1088/1468-6996/9/4/044102. PMC 5099629. PMID 27878015.
- Acheson, E. G. "Manufacture of Graphite", U.S. patent 568,323, issued September 29, 1896.
- Kato, Tomofumi; Yamada, Yasuhiro; Nishikawa, Yasushi; Ishikawa, Hiroki; Sato, Satoshi (June 2021). "Carbonization mechanisms of polyimide: Methodology to analyze carbon materials with nitrogen, oxygen, pentagons, and heptagons". Carbon. 178: 58–80. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.090.
- Kato, Tomofumi; Yamada, Yasuhiro; Nishikawa, Yasushi; Otomo, Toshiya; Sato, Hayato; Sato, Satoshi (October 2021). "Origins of peaks of graphitic and pyrrolic nitrogen in N1s X-ray photoelectron spectra of carbon materials: quaternary nitrogen, tertiary amine, or secondary amine?". Journal of Materials Science. 56 (28): 15798–15811. doi:10.1007/s10853-021-06283-5.
- Lapshin, Rostislav V. (1 September 1998). "Automatic lateral calibration of tunneling microscope scanners". Review of Scientific Instruments. 69 (9): 3268–3276. doi:10.1063/1.1149091.
- Lapshin, Rostislav V. (March 2019). "Drift-insensitive distributed calibration of probe microscope scanner in nanometer range: Real mode". Applied Surface Science. 470: 1122–1129. arXiv:1501.06679. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.149.
- Pierson, Hugh O. (1993). Handbook of Carbon, Graphite, Diamonds and Fullerenes: Properties, Processing and Applications. Noyes Publications. ISBN 0-8155-1339-9. OL 8048799M.
- Arregui-Mena, José David; Bodel, William; Worth, Robert N.; Margetts, Lee; Mummery, Paul M. (December 2016). "Spatial variability in the mechanical properties of Gilsocarbon" (PDF). Carbon. 110: 497–517. doi:10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.051.
- Arregui-Mena, José David; Edmondson, Philip D.; Margetts, Lee; Griffiths, D.V.; Windes, William E.; Carroll, Mark; Mummery, Paul M. (December 2018). "Characterisation of the spatial variability of material properties of Gilsocarbon and NBG-18 using random fields". Journal of Nuclear Materials. 511: 91–108. doi:10.1016/j.jnucmat.2018.09.008.
- Weinberg, Alvin M. (1994). The First Nuclear Era. New York, N.Y.: American Institute of Physics. Figure 11. ISBN 978-1563963582.
- Cooper, Jeff. What is the best material for a tennis racquet? Archived 2011-07-07 at the Wayback Machine. tennis.about.com
- Yurkewicz, Katie. "Protecting the LHC from itself" (PDF). Symmetry Magazine. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2015-09-10.
- Olmec Advanced Materials (2019). "How graphite is used in the glass and fibreglass industries". Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- "Mineral Commodity Summaries 2020" (PDF). National Minerals Information Center. USGS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-02-09.
- "Wonder 5: Graphite Mines – Boom Town". 24 March 2015.
- Jeremy Law (2018-05-16). "Westwater Resources acquires Alabama Graphite". Retrieved 2020-02-22.
- "CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Graphite (natural)". www.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2015-11-03.
- ^ World Intellectual Property Organization. (2023). "Patent Landscape Report - Graphite and its applications". www.wipo.int. Patent Landscape Reports. WIPO. doi:10.34667/tind.47589. Retrieved 2023-11-13.
Further reading
- Lipson, H.; Stokes, A. R. (1942). "A New Structure of Carbon". Nature. 149 (3777): 328. Bibcode:1942Natur.149Q.328L. doi:10.1038/149328a0. S2CID 36502694.
- C.Michael Hogan; Marc Papineau; et al. (December 18, 1989). Phase I Environmental Site Assessment, Asbury Graphite Mill, 2426–2500 Kirkham Street, Oakland, California, Earth Metrics report 10292.001 (Report).
- Klein, Cornelis; Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr. (1985). Manual of Mineralogy: after Dana (20th ed.). Wiley. ISBN 978-0-471-80580-9.
- Taylor, Harold A. (2000). Graphite. Financial Times Executive Commodity Reports. London: Mining Journal Books. ISBN 978-1-84083-332-4.
- Taylor, Harold A. (2005). Graphite. Industrial Minerals and Rocks (7th ed.). Littleton, CO: AIME-Society of Mining Engineers. ISBN 978-0-87335-233-8.
External links
- Battery Grade Graphite
- Graphite at Minerals.net
- Mineral galleries
- Mineral & Exploration – Map of World Graphite Mines and Producers 2012
- Mindat w/ locations
- giant covalent structures
- The Graphite Page
- Video lecture on the properties of graphite by M. Heggie, University of Sussex
- CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
| Allotropes of carbon | |
|---|---|
| sp forms | |
| sp forms | |
| sp forms | |
| mixed sp/sp forms | |
| other forms | |
| hypothetical forms | |
| related | |
| Coal | ||
|---|---|---|
| Coal types by grade (lowest to highest) |  | |
| Coal combustion | ||
| Coal mining |
| |
| Note: Peat is considered a precursor to coal. Graphite is only technically considered a coal type. | ||