This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
Ferrovie Nord Milano (FNM S.p.A.) is an Italian public transport company: the second largest railway company in Italy. It operates primarily in the northern Italian regions of Lombardy and Piedmont and in Canton Ticino in southern Switzerland. Listed on the Borsa Italiana, its main shareholders are the Lombardy Region (57.57%), Ferrovie dello Stato (14.5%) and Aurelia S.p.A. (3%).
History
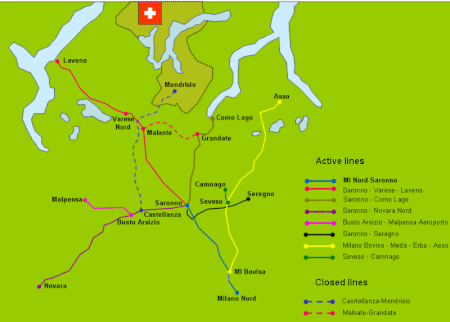
The company was founded as Società Anonima Ferrovie Milano-Saronno e Milano-Erba in 1877 by the Belgian Albert Vaucamps. The Milan-Saronno railroad was inaugurated on 22 March 1879, while the Milan-Erba was opened later in December the same year. In 1883, the company was rechristened Società Anonima per le Ferrovie Nord Milano (FNM). Five years later the consortium was joined by Società per le Ferrovie del Ticino, who held the Como-Malnate-Varese-Laveno and Saronno-Malnate lines. Until the end of the century FNM also acquired the lines Novara-Seregno and Saronno-Grandate, forming a large network in northern Lombardy in direct competition with the Società per le Strade Ferrate del Mediterraneo. When railways were nationalized in Italy in 1907, Mediterranea acquired the shares of the Belgian owners.
Electrification of most lines began in 1929, and was completed in 1953. In 1958, passenger service was discontinued on the Saronno-Seregno line, while the Malnate-Grandate line was closed in 1966. In 1974 FNM, a joint-stock company starting from 1943, was entirely acquired by the Lombardy regional government.
Two different companies, Ferrovie Nord Milano Esercizio and Ferrovie Nord Milano Autotrasporti, were created in 1985 with responsibilities for rail and road transport respectively. In 2004 the former was again split into two companies, Ferrovie Nord Cargo (for cargo services) and Ferrovie Nord Milano Trasporti (for passenger trains). In 2006 a new logo and new identities for three companies were adopted: Ferrovie Nord Milano Trasporti S.r.l. became LeNord S.r.l., Ferrovie Nord Milano Esercizio S.p.A. became FERROVIENORD S.p.A. and Ferrovie Nord Cargo S.r.l. became NordCargo S.r.l.. The whole group name became FNM S.p.A..
Since 1993, FERROVIENORD (through LeNord and NordCargo) is managing the Brescia-Iseo-Edolo railway branch, not connected to the main group of lines, centered in the Milan area.
Bus Services by Ferrovie Nord Milano Autoservizi
Province of Brescia
- F23a Saviore-Cedegolo
- F23b Valle-Cedegolo
- F27 Brescia-Iseo-Edolo
- F28 Iseo-Breno
- F29 Breno-Edolo
- L62 Iseo-Provaglio-Brescia
Province of Como
- C64 Olgiate Comasco-Appiano Gentile-Lomazzo
- C66 Appiano Gentile-Lurago Marinone-Lomazzo
- C67 Saronno-Fenegrò-Lomazzo
- C69 Lomazzo-Tradate
- C76 Tradate-Olgiate Comasco
- C77 Como-Varese
- C84 Cantù-Lomazzo
Province of Varese
- B48 Tradate-Castiglione Olona
- B50 Somma Lombardo-Varese
- C77 Como-Varese
- H203 Saronno-Turate-Saronno
- H204 Tradate-Saronno (Caronno Pertusella)
- H601 Tradate-Legnano-Busto Arsizio
- H632 Varese-Gallarate
Other Bus Services
- Asso-Saronno-Cesenatico-Rimini-Gabicce Mare (summer seasonal long-distance route)
- Asso-Saronno-Varazze-Alassio-Sanremo (summer seasonal long-distance route)
- Olgiate Comasco-Tradate-Origgio-Cervia-Rimini-Cattolica (summer seasonal long-distance route)
- Milan Cadorna-Campione d'Italia
Locomotives and rolling stock
Electric locomotives
Diesel locomotives
Electric multiple units (EMUs)
Diesel multiple units (DMUs)
Coaches
Subsidiaries
- Ferrovienord
- LeNord
- Ferrovie Nord Milano Autoservizi. It hols public road transport in the province of Como, Varese and Val Camonica.
- NordCargo
- Nord Ing S.r.l., engineering company
- NordCom S.p.A., provides informatics services for FNM companies and other public administrations
- Nordenergia S.p.A.. It produces electric energy.
- CargoClay, another rail cargo company (30% shared by Edicer)
- Sems S.r.l. Rents low environmental impact vehicles.
- VieNord S.r.l. Provides commercial and marketing services for the group's company.
In fiction
- In 2016, in the animated film, Thomas & Friends: The Great Race, one of the Ferrovie Nord Milano's locomotives is modeled for Gina, who also appears in Series 23.
See also
References
- Historical review at PLAIN (in Italian)