Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɛθklɔːrˈvaɪnɒl/ ETH-klor-VY-nol |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 35–50% |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.239.078 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
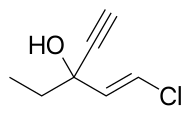
| Formula | C7H9ClO |
| Molar mass | 144.60 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (what is this?) (verify) | |
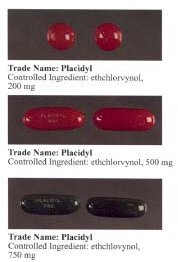
Ethchlorvynol is a GABA-ergic hypnotic sedative medication first developed by Pfizer in the 1950s. In the United States it was sold by Abbott Laboratories under the trade name Placidyl. Placidyl was available in 200 mg, 500 mg, and 750 mg strength gel filled capsules. While the 500 mg and 750 mg strength capsules were for use in reducing sleep latency, the 200 mg strength capsules were intended to be used to re-induce sleep in case of early awakening. Abbott discontinued production in 1999, due to it being replaced by the benzodiazepine family and its widespread abuse, after which Placidyl was available for about a year in the United States. Although, theoretically, ethchlorvynol could be manufactured for sale in the United States by another pharmaceutical company (subject to FDA approval of such manufacture), no pharmaceutical company has chosen to do so. Individuals with a valid prescription for the substance may legally transport a reasonable amount of ethclorvynol with them into the United States.
Use and effects
Ethchlorvynol was used to treat insomnia, but prescriptions for the drug had fallen significantly by 1990, as other hypnotics that were considered safer (i.e., less dangerous in overdose) became much more common. It is no longer prescribed in the United States due to unavailability, but it is still available in some countries and would still be considered legal to possess and use with a valid prescription.
Along with expected sedative effects of relaxation and drowsiness, adverse reactions to ethchlorvynol include skin rash, faintness, restlessness and euphoria. Early adjustment side effects may include nausea and vomiting, numbness, blurred vision, stomach pains and temporary dizziness. There are no specific antidotes available for ethchlorvynol, and treatment is supportive with protocols resembling those for the treatment of barbiturate overdose. Overdose may be marked by a variety of symptoms, including confusion, fever, peripheral numbness and weakness, reduced coordination and muscle control, slurred speech, reduced heartbeat, respiratory depression, and in extreme overdoses, coma and death.
As with all GABAA receptor agonists, Placidyl can be habit forming and extremely physically addictive (with potentially lethal withdrawal resembling delirium tremens and benzodiazepine withdrawal). After prolonged use, withdrawal symptoms may include convulsions, hallucinations, and amnesia. As with most hypnotics, Placidyl was indicated for use in the treatment of insomnia for a short period of time (a week or two). However, it was nonetheless not uncommon for doctors to prescribe Placidyl (and other hypnotics) for extended periods of time, as currently prescribed soporifics are today.
During the late 1970s, ethchlorvynol was sometimes over-prescribed causing a minor epidemic of persons who quickly became addicted to this powerful drug. Elvis Presley was quite fond of Placidyl, Supreme Court Justice William Rehnquist had to be hospitalized for detox of Placidyl, as was Steven Tyler of Aerosmith. Occasional deaths would occur when addicted persons would try to inject the drug directly into a vein or an artery. Ethchlorvynol is not compatible with intravenous injection and serious injury (including the loss of limbs due to vascular injury) or death can occur when it is used in this manner.
Chemistry
Ethchlorvynol is a member of the class of sedative-hypnotic carbinols, which includes methylparafynol and tert-amyl alcohol. It is not a benzodiazepine, carbamate, or barbituric acid derivative, and its molecular structure is considerably simpler. The systematic name of ethchlorvynol is usually given as ethyl 2-chlorovinyl ethynyl carbinol or 1-chloro-3-ethylpent-1-en-4-yn-3-ol. Its empirical formula is C7H9ClO.
Ethchlorvynol is synthesized by an ethynylation reaction using lithium acetylide and 1-chloro-1-penten-3-one in liquid ammonia, followed by acidic work-up.
The analogous compound consisting of a carbamate derived from the hydroxyl group was investigated and was shown to have a slower onset, longer duration, and increased potency, but was not developed commercially.
References
- Anvisa (31 March 2023). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 4 April 2023). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "Erowid Ethchlorvynol Vault". Erowid. 12 January 2007. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- "Annual Statistical Report on Substances Listed in the Convention on Psychotropic Substances of 1971 Form P" (PDF). International Narcotics Control Board (INCB). January 2014. p. 9. Archived from the original (PDF) on 10 September 2015. Retrieved 17 April 2014.
- ^ US 2746900, Bavley A, McLamore WM, "Hypnotic Agent and Method of Making the Same", issued 1956
- Glauser FL, Smith WR, Caldwell A, Hoshiko M, Dolan GS, Baer H, Olsher N (January 1976). "Ethchlorvynol (Placidyl)-induced pulmonary edema". Annals of Internal Medicine. 84 (1): 46–8. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-84-1-46. PMID 942681.
- McLamore WM, P'an SY, Bavley A (1955). "Hypnotics and Anticonvulsants. II. Halogenated Tertiary Acetylenic Carbinols". Journal of Organic Chemistry. 20: 109–117. doi:10.1021/jo01119a018.
External links
- "Electronic Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations". Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 12 December 2005.
| Hypnotics/sedatives (N05C) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GABAA |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GABAB | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2-Adrenergic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT2A |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melatonin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orexin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| α2δ VDCC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GABAA receptor positive modulators | |
|---|---|
| Alcohols | |
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
