This article is about the early modern duchy. For the short-lived state founded during World War I, see Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (1918).
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Duchy of Courland and Semigallia" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Duchy of Courland and SemigalliaDucatus Curlandiæ et Semigalliæ (Latin) Kurzemes un Zemgales hercogiste (Latvian) Księstwo Kurlandii i Semigalii (Polish) Kuršo ir Žiemgalos kunigaikštystė (Lithuanian) Herzogtum Kurland und Semgallen (German) Hertigdömet Kurland och Semgallen (Swedish) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1561–1795 | |||||||||||
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||||
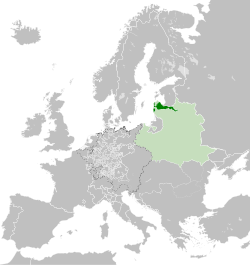 Duchy of Courland and Semigallia in 1714 Duchy of Courland and Semigallia in 1714
| |||||||||||
| Status | Vassal state of Grand Duchy of Lithuania (1561–1569) and Poland–Lithuania (1569–1795) | ||||||||||
| Capital | Mitau | ||||||||||
| Common languages | |||||||||||
| Religion | Lutheran, Roman Catholic | ||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Courlander, Couronian, Courish, Courlandish | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| Duke | |||||||||||
| • 1561–1587 | Gotthard Kettler (first) | ||||||||||
| • 1769–1795 | Peter von Biron (last) | ||||||||||
| Legislature | Landtag | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| • Treaty of Vilnius | 28 November 1561 | ||||||||||
| • Colonial acquisitions | 1637–1690 | ||||||||||
| • Third Partition of Poland | 28 March 1795 | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| • Total | 27,290 km (10,540 sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
| • Estimate | ~200,000 (1794) | ||||||||||
| • Density | 7.3/km (18.9/sq mi) | ||||||||||
| Currency | Thaler | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Latvia | ||||||||||
The Duchy of Courland and Semigallia was a duchy in the Baltic region, then known as Livonia, that existed from 1561 to 1569 as a nominal vassal state of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and subsequently made part of the Crown of the Polish Kingdom from 1569 to 1726 and incorporated into the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1726. On October 24, 1795, it was annexed by the Russian Empire in the Third Partition of Poland.
There was also a short-lived wartime state with the same name that existed from March 8 to September 22, 1918. Plans for it to become part of the United Baltic Duchy, subject to the German Empire, were thwarted by Germany's surrender of the Baltic region at the end of the First World War. The area became a part of Latvia at the end of World War I.
History
| Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Latvia |
 |
| Ancient Latvia |
| Middle Ages |
| Early modern period |
| National Awakening |
Modern Latvia
|
| Chronology |
|
|

In 1561, during the Livonian Wars, the Livonian Confederation was dismantled and the Livonian Order was disbanded. On the basis of the Treaty of Vilnius, the southern part of Estonia and the northern part of Latvia were ceded to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. On 25 December 1566, the Union of Grodno established a real union between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Duchy of Livonia. The part of Latvia between the west bank of the Daugava River and the Baltic Sea became the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia. It was ruled by the dukes from the House of Kettler with the exception of Ernst Johann Biron and his son Peter von Biron.
Gotthard Kettler, the last Master of the Livonian Order, became the first duke of Courland. Other members of the Order became the Couronian nobility, with the fiefdoms they had hitherto held becoming their estates. In all, Kettler received nearly one-third of the land in the new duchy. Mitau (Jelgava) was designated as the new capital and a Landtag was to meet there twice a year.
Several parts of the Courish area did not belong to the Duchy. The Order of Livonia had already loaned the Grobiņa district (on the coast of Baltic Sea) to the Duke of Prussia. Another district, the former Bishopric of Courland, belonged to Magnus, son of the king of Denmark. He promised to transfer it to the Duchy of Courland after his death, but this plan failed and only later did Wilhelm Kettler regain this district.
Like the other members of the Order, Kettler was German and set about establishing the Duchy along the lines of similar German states. In 1570, he issued the Privilegium Gotthardinum, which allowed the landholders to enserf the native peasantry on their lands.
When Gotthard Kettler died in 1587, his sons, Friedrich and Wilhelm, became the dukes of Courland. They divided the Duchy into two parts in 1596. Friedrich controlled the eastern part, Semigalia (Zemgale), with his residence in Mitau (Jelgava). Wilhelm owned the western part, Courland (Kurzeme), with his residence in Goldingen (Kuldīga). Wilhelm regained the Grobiņa district when he married the daughter of the Duke of Prussia. He also paid out and regained control over the District of Pilten, but eventually, it fell to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Here he developed metalworking and shipyards, and the new ships delivered the goods of Courland to other countries.
However, relations between the duke and the landowners were quite hostile. In addition, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which was the overlord of the Duchy of Courland, supported the landowners. Wilhelm expressed his disappointment with the landowners, but this ended with his removal from the duke's seat in 1616. Finally, Wilhelm left Courland and spent the rest of his life abroad. Thus, Friedrich became the only duke of Courland after 1616.
From 1600 to 1629, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden conducted a war with its main battlefields around Riga. As a result, Sweden gained control of what is today central and northern Latvia, which became Swedish Livonia. The Commonwealth retained the eastern part of the Duchy of Livonia, thereafter called Inflanty Voivodeship in Polish. Courland was also involved in this war, but did not suffer severe damage.
Under the next duke, Jacob Kettler, the Duchy reached the peak of its prosperity. During his travels in Western Europe, Jacob became a eager proponent of mercantilist ideas. Metalworking and shipbuilding became much more developed, and powder mills began producing gunpowder. Trading relations developed not only with nearby countries but also with Britain, France, the Netherlands and Portugal. Jacob established the merchant fleet of the Duchy of Courland, with its main harbours in Ventspils and Libau.
Colonization
See also: Curonian colonisation and Curonian colonization of the AmericasIn 1651 the Duchy established its first colony in Africa, St. Andrews Island at the Gambia River, and founded Jacob Fort there. The main export goods included ivory, gold, furs and spices. Soon afterwards, in 1652, Courlanders established another colony, in Tobago in the West Indies. There the main export goods included sugar, tobacco, coffee and spices.
However, during this time, the Duchy of Courland remained an object of interest for both Sweden and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In 1655 the Swedish army entered the territory of the Duchy, starting the Swedish–Polish war (1655–1660). The Swedish army captured Duke Jacob (1658–1660). During this period, the Dutch took over both of Courland's colonies that lacked supplies and manpower, and the merchant fleet and factories suffered destruction. This war ended with the peace Treaty of Oliwa (1660). Courland regained Tobago on the basis of the treaty and held it until 1689. Duke Jacob set about restoring the fleet and factories, but the Duchy of Courland never again reached its pre-war level of prosperity.
18th century

When Jacob died in 1682, his son, Friedrich Casimir, became the next duke. During his reign production continued to decrease. The duke himself was more interested in glamorous celebrations and spent more money than he had. This forced him to sell Tobago to the British. During this period, the Commonwealth increased its influence in the political and economic life of the Duchy. Additionally, Russia showed an interest in this area.
Friedrich Casimir died in 1698. His successor, Friedrich Wilhelm Kettler, was only six years old and was under the regency of his uncle Ferdinand – a Polish general. During this time the Great Northern War (1700–1721) began between Sweden and Russia with its allies – the Commonwealth, Saxony and Denmark. As a result of the war, Russia took control of Swedish Livonia starting in 1710. In Courland, Russia also had such a strong influence that its ambassador, Pyotr Bestuzhev, became the most powerful man in the duchy. The Tsar of Russia, Peter the Great, received a promise from Friedrich Wilhelm that he would marry one of the daughters of the tsar's brother. By having this promise, Peter the Great wished to increase the influence of Russia in Courland. In 1710, Friedrich Wilhelm married Anna Ioannovna (later Empress of Russia), but on his way back from St Petersburg, he took ill and died. Anna ruled as the duchess of Courland from 1711 to 1730.
After the death of Friedrich Wilhelm, the next candidate for the seat of duke was Ferdinand Kettler, who, at the time, lived in Danzig. Because the law required the duke to reside within the Duchy, the Diet did not recognize him. Because Ferdinand was the last representative of Kettler's family, a remarkable number of candidates tried to gain the dukedom during this period. One favorite was Maurice de Saxe, natural son of Augustus II the Strong, King of Poland. Saxe had managed to gain support and was even mentioned as marrying Anna Ioannovna, Duchess of Courland at that time.
He was elected duke in 1726, but only managed to maintain himself by force of arms till the next year. Russia disliked him and sent an army to western Courland to destroy Maurice's base. When Catherine was Empress Peter Lacy was given responsibility for removing Maurice de Saxe from Courland. As the result Maurice de Saxe had to leave Courland, and Russia increased its influence. This was achieved in good measure due to service of Peter Lacy who was governor of Livonia from 1727 until his death in 1751. Russian influence increased further when Frederick August III, the Elector of Saxony, in his successful bid to succeed his father on the Polish throne in the 1730s, agreed to grant Anna of Russia her choice of successor to the Courish duchy in exchange for Russian support in the War of the Polish Succession. (Because of the duchy's position as a vassal of the Commonwealth and Ferdinand Kettler's lack of issue, the duchy would otherwise formally have devolved onto the Polish throne.) Anna appointed Ernst Johann von Biron duke of Courland in 1737.

Von Biron received remarkable financial support from Russia and invested it in construction – for example, the Castle of Ruhenthal projected by the distinguished Italian architect Bartolomeo Rastrelli. Anna Ivanovna died in 1740, resulting in von Biron's exile to Siberia the following year. From there, through the Council of the Duke, he continued to control the Duchy, with the agreement of the king of Poland. However, the landowners of Courland disliked the agreement and even refused to follow the regulations of the Council of the Duke.
Duke Louis Ernest of Brunswick-Lüneburg was selected as Biron's successor on June 27, 1741, with the support of his cousin Maria Theresa of Austria, but while he was in St Petersburg to get this title ratified, Elizabeth of Russia carried out a coup on December 6, 1741, and he lost the title.
King Augustus III of Poland proclaimed his son, Carl Christian Joseph of Saxony, the next duke. Thus, the Duchy of Courland had two dukes simultaneously thereafter. The situation became extremely tense – one part of the Landtag of Courland accepted von Biron, the other, Carl of Saxony. The Empress Catherine II of Russia (reigned 1762–1796) solved this situation by recalling Ernst von Biron from exile in 1763. By doing this, she avoided the possible increase of influence of the Commonwealth in Courland. However, political fighting had exhausted Ernst Biron, and he turned the seat of duke over to his son, Peter von Biron, in 1769. But political tumult continued in Courland. Some landowners supported the Commonwealth, some Russia. Ultimately, Russia determined the further fate of Courland when with its allies it began the third division of Poland (1795). Given a "nice recommendation" by Russia, Duke Peter von Biron gave up his rights to Russia in 1795. With the signing of the final document on October 24, 1795, the Duchy of Courland was incorporated into the Russian Empire and title of Duke of Courland was added to the title of Russian emperors.
List of dukes
| Portrait | Name | Lifespan | Reign | Consorts | Succession |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Gotthard Kettler | February 2, 1517 – May 17, 1587 | November 28, 1561 – May 17, 1587 | Anna of Mecklenburg March 11, 1566 Königsberg 3 children |
First |

|
Friedrich Kettler | November 25, 1569 – August 17, 1642 | May 17, 1587 – August 17, 1642 | Elisabeth Magdalena of Pomerania March 14, 1600 no issue |
Son of Gotthard Kettler |

|
Jacob Kettler | October 28, 1610 – January 1, 1682 | August 17, 1642 – January 1, 1682 | Louise Charlotte of Brandenburg October 9, 1645 9 children |
Nephew of Friedrich Kettler |

|
Friedrich Casimir Kettler | July 6, 1650 – January 22, 1698 | January 1, 1682 – January 22, 1698 | (1) Sophie Amalie of Nassau-Siegen October 5, 1675 The Hague 5 children (2) Elisabeth Sophie of Brandenburg April 29, 1691 2 children |
Son of Jacob Kettler |

|
Friedrich Wilhelm Kettler | July 19, 1692 – January 21, 1711 | January 22, 1698 – January 21, 1711 | Anna of Russia November 11, 1710 St. Petersburg no issue |
Son of Frederick Casimir Kettler |

|
Ferdinand Kettler | November 1, 1655 – May 4, 1737 | January 21, 1711 – May 4, 1737 | Johanna Magdalene of Saxe-Weissenfels September 20, 1730 Danzig no issue |
Uncle of Frederick William Kettler |

|
Ernst Johann von Biron | November 23, 1690 – December 29, 1772 | June 1737 – 1740 | Benigna Gottlieb von Trotha gt Treyden 1723 3 children |
Elected |

|
Louis Ernest of Brunswick-Lüneburg | September 25, 1718 – May 12, 1788 | June 27, 1741 – December 6, 1741 | Never married | Elected |

|
Karl of Saxony | July 13, 1733 – June 16, 1796 | November 10, 1758 – 1763 | Franciszka Krasińska March 25, 1760 Warsaw 2 daughters |
Appointed by Augustus III, King of Poland |

|
Ernst Johann von Biron | November 23, 1690 – December 29, 1772 | 1763–1769 | Benigna Gottlieb von Trotha gt Treyden 1723 3 children |
Reappointed by Catherine the Great |

|
Peter von Biron | February 15, 1724 – January 13, 1800 | 1769 – March 28, 1795 | (1) Caroline of Waldeck and Pyrmont October 5, 1765 1 son (stillborn) (2) Yevdokiya Borisovna Yusupova March 6, 1774 Jelgava no issue (3) Dorothea von Medem November 6, 1779 6 children |
Son of Ernst Johann von Biron |
Gallery
-
 Greater coat of arms of the Dukes of Courland of the Kettler family
Greater coat of arms of the Dukes of Courland of the Kettler family
-
 Naval Flag of Courland and Semigallia
Naval Flag of Courland and Semigallia
-
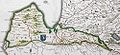 German map of Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (about 1600)
German map of Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (about 1600)
-
 Jelgava Palace, the main residence of the dukes
Jelgava Palace, the main residence of the dukes
-
 Sigismund Augustus King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania incorporates fiefdoms, Duchies of Courland and Semigalia into the Crown in 1569
Sigismund Augustus King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania incorporates fiefdoms, Duchies of Courland and Semigalia into the Crown in 1569
See also
- Coat of arms of Courland
- Duchess of Courland
- Courland
- Couronian colonisation
- Couronian colonisation of the Americas
- Ernst Friedrich von Ockel
- Livonia
- Semigallia
Notes
- Latin: Ducatus Curlandiæ et Semigalliæ; German: Herzogtum Kurland und Semgallen; Latvian: Kurzemes un Zemgales hercogiste; Lithuanian: Kuršo ir Žiemgalos kunigaikštystė; Polish: Księstwo Kurlandii i Semigalii.
References
- Volumina Legum, t. II, Petersburg 1859, p. 106
- Volumina Legum, t. VI, Petersburg 1860, p. 209.
- "How the Duchy of Courland was briefly resurrected in 1918". eng.lsm.lv. Retrieved February 8, 2023.
- "Duke Gotthard". archiv.org.lv.
- Palkans, p. 50.
- "The Fall of Curonian Colonization". History & Culture Academy of Latgale.
- ^ McGee, James E. (1873). Sketches of Irish soldiers in every land. New York: Lang, Little & Hillman. p. 106.
Bibliography
- Ceaser, Ray A., Duchy of Courland, University of Washington, June 2001.
- Plakans, Andrejs (1995) The Latvians: A Short History, Hoover Institution Press.
External links
- Courland
- Courland 1641–1795
- Flags of Courland
- Die Kurländische Ritterschaft
- Ritterschaften der Familie in Kurland
|
| Administrative division of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth | ||
|---|---|---|
| Province of Greater Poland |  | |
| Province of Lesser Poland | ||
| Grand Duchy of Lithuania | ||
| Polish Livonia | ||
| Fiefs | ||
| Fiefdoms of Poland | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medieval district principalities |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other medieval fiefs | |||||||||||||||
| Early modern fiefs of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland |
| ||||||||||||||
56°38′11″N 23°42′55″E / 56.63639°N 23.71528°E / 56.63639; 23.71528
Categories: