In mathematics, a monogenic semigroup is a semigroup generated by a single element. Monogenic semigroups are also called cyclic semigroups.
Structure
The monogenic semigroup generated by the singleton set {a} is denoted by . The set of elements of is {a, a, a, ...}. There are two possibilities for the monogenic semigroup :
- a = a ⇒ m = n.
- There exist m ≠ n such that a = a.
In the former case is isomorphic to the semigroup ({1, 2, ...}, +) of natural numbers under addition. In such a case, is an infinite monogenic semigroup and the element a is said to have infinite order. It is sometimes called the free monogenic semigroup because it is also a free semigroup with one generator.
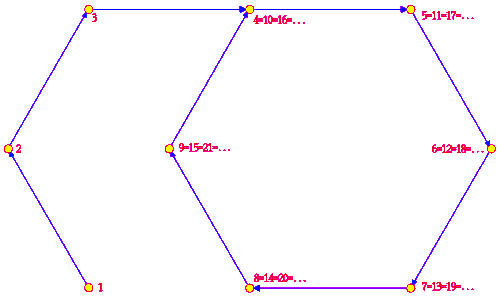
In the latter case let m be the smallest positive integer such that a = a for some positive integer x ≠ m, and let r be smallest positive integer such that a = a. The positive integer m is referred to as the index and the positive integer r as the period of the monogenic semigroup . The order of a is defined as m+r−1. The period and the index satisfy the following properties:
- a = a
- a = a if and only if m + x ≡ m + y (mod r)
- = {a, a, ... , a}
- Ka = {a, a, ... , a} is a cyclic subgroup and also an ideal of . It is called the kernel of a and it is the minimal ideal of the monogenic semigroup .
The pair (m, r) of positive integers determine the structure of monogenic semigroups. For every pair (m, r) of positive integers, there exists a monogenic semigroup having index m and period r. The monogenic semigroup having index m and period r is denoted by M(m, r). The monogenic semigroup M(1, r) is the cyclic group of order r.
The results in this section actually hold for any element a of an arbitrary semigroup and the monogenic subsemigroup it generates.
Related notions
A related notion is that of periodic semigroup (also called torsion semigroup), in which every element has finite order (or, equivalently, in which every monogenic subsemigroup is finite). A more general class is that of quasi-periodic semigroups (aka group-bound semigroups or epigroups) in which every element of the semigroup has a power that lies in a subgroup.
An aperiodic semigroup is one in which every monogenic subsemigroup has a period of 1.
See also
- Cycle detection, the problem of finding the parameters of a finite monogenic semigroup using a bounded amount of storage space
- Special classes of semigroups
References
- Howie, J M (1976). An Introduction to Semigroup Theory. L.M.S. Monographs. Vol. 7. Academic Press. pp. 7–11. ISBN 0-12-356950-8.
- A H Clifford; G B Preston (1961). The Algebraic Theory of Semigroups Vol.I. Mathematical Surveys. Vol. 7. American Mathematical Society. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-0821802724.
- "Kernel of a semi-group - Encyclopedia of Mathematics".
- "Minimal ideal - Encyclopedia of Mathematics".
- "Periodic semi-group - Encyclopedia of Mathematics".
- Peter M. Higgins (1992). Techniques of semigroup theory. Oxford University Press. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-19-853577-5.
 . The set of elements of
. The set of elements of