| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Convolutional neural network" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Part of a series on |
| Machine learning and data mining |
|---|
| Paradigms |
Problems
|
|
Supervised learning (classification • regression) |
| Clustering |
| Dimensionality reduction |
| Structured prediction |
| Anomaly detection |
| Artificial neural network |
| Reinforcement learning |
| Learning with humans |
| Model diagnostics |
| Mathematical foundations |
| Journals and conferences |
| Related articles |
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a regularized type of feed-forward neural network that learns features by itself via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced -- in some cases -- by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections. For example, for each neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded convolution (or cross-correlation) kernels, only 25 neurons are required to process 5x5-sized tiles. Higher-layer features are extracted from wider context windows, compared to lower-layer features.
Some applications of CNNs include:
- image and video recognition,
- recommender systems,
- image classification,
- image segmentation,
- medical image analysis,
- natural language processing,
- brain–computer interfaces, and
- financial time series.
CNNs are also known as shift invariant or space invariant artificial neural networks, based on the shared-weight architecture of the convolution kernels or filters that slide along input features and provide translation-equivariant responses known as feature maps. Counter-intuitively, most convolutional neural networks are not invariant to translation, due to the downsampling operation they apply to the input.
Feed-forward neural networks are usually fully connected networks, that is, each neuron in one layer is connected to all neurons in the next layer. The "full connectivity" of these networks makes them prone to overfitting data. Typical ways of regularization, or preventing overfitting, include: penalizing parameters during training (such as weight decay) or trimming connectivity (skipped connections, dropout, etc.) Robust datasets also increase the probability that CNNs will learn the generalized principles that characterize a given dataset rather than the biases of a poorly-populated set.
Convolutional networks were inspired by biological processes in that the connectivity pattern between neurons resembles the organization of the animal visual cortex. Individual cortical neurons respond to stimuli only in a restricted region of the visual field known as the receptive field. The receptive fields of different neurons partially overlap such that they cover the entire visual field.
CNNs use relatively little pre-processing compared to other image classification algorithms. This means that the network learns to optimize the filters (or kernels) through automated learning, whereas in traditional algorithms these filters are hand-engineered. This independence from prior knowledge and human intervention in feature extraction is a major advantage.
Architecture
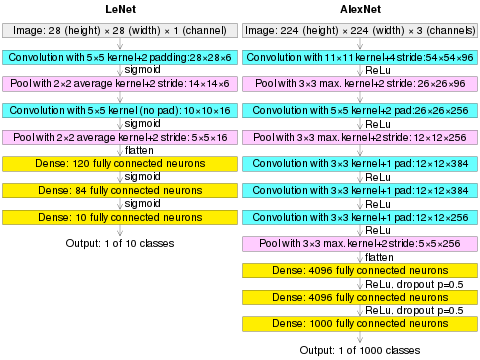
(AlexNet image size should be 227×227×3, instead of 224×224×3, so the math will come out right. The original paper said different numbers, but Andrej Karpathy, the head of computer vision at Tesla, said it should be 227×227×3 (he said Alex did not describe why he put 224×224×3). The next convolution should be 11×11 with stride 4: 55×55×96 (instead of 54×54×96). It would be calculated, for example, as: + 1 = + 1 = 55. Since the kernel output is the same length as width, its area is 55×55.)
A convolutional neural network consists of an input layer, hidden layers and an output layer. In a convolutional neural network, the hidden layers include one or more layers that perform convolutions. Typically this includes a layer that performs a dot product of the convolution kernel with the layer's input matrix. This product is usually the Frobenius inner product, and its activation function is commonly ReLU. As the convolution kernel slides along the input matrix for the layer, the convolution operation generates a feature map, which in turn contributes to the input of the next layer. This is followed by other layers such as pooling layers, fully connected layers, and normalization layers. Here it should be noted how close a convolutional neural network is to a matched filter.
Convolutional layers
In a CNN, the input is a tensor with shape:
(number of inputs) × (input height) × (input width) × (input channels)
After passing through a convolutional layer, the image becomes abstracted to a feature map, also called an activation map, with shape:
(number of inputs) × (feature map height) × (feature map width) × (feature map channels).
Convolutional layers convolve the input and pass its result to the next layer. This is similar to the response of a neuron in the visual cortex to a specific stimulus. Each convolutional neuron processes data only for its receptive field.
Although fully connected feedforward neural networks can be used to learn features and classify data, this architecture is generally impractical for larger inputs (e.g., high-resolution images), which would require massive numbers of neurons because each pixel is a relevant input feature. A fully connected layer for an image of size 100 × 100 has 10,000 weights for each neuron in the second layer. Convolution reduces the number of free parameters, allowing the network to be deeper. For example, using a 5 × 5 tiling region, each with the same shared weights, requires only 25 neurons. Using regularized weights over fewer parameters avoids the vanishing gradients and exploding gradients problems seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks.
To speed processing, standard convolutional layers can be replaced by depthwise separable convolutional layers, which are based on a depthwise convolution followed by a pointwise convolution. The depthwise convolution is a spatial convolution applied independently over each channel of the input tensor, while the pointwise convolution is a standard convolution restricted to the use of kernels.
Pooling layers
Convolutional networks may include local and/or global pooling layers along with traditional convolutional layers. Pooling layers reduce the dimensions of data by combining the outputs of neuron clusters at one layer into a single neuron in the next layer. Local pooling combines small clusters, tiling sizes such as 2 × 2 are commonly used. Global pooling acts on all the neurons of the feature map. There are two common types of pooling in popular use: max and average. Max pooling uses the maximum value of each local cluster of neurons in the feature map, while average pooling takes the average value.
Fully connected layers
Fully connected layers connect every neuron in one layer to every neuron in another layer. It is the same as a traditional multilayer perceptron neural network (MLP). The flattened matrix goes through a fully connected layer to classify the images.
Receptive field
In neural networks, each neuron receives input from some number of locations in the previous layer. In a convolutional layer, each neuron receives input from only a restricted area of the previous layer called the neuron's receptive field. Typically the area is a square (e.g. 5 by 5 neurons). Whereas, in a fully connected layer, the receptive field is the entire previous layer. Thus, in each convolutional layer, each neuron takes input from a larger area in the input than previous layers. This is due to applying the convolution over and over, which takes the value of a pixel into account, as well as its surrounding pixels. When using dilated layers, the number of pixels in the receptive field remains constant, but the field is more sparsely populated as its dimensions grow when combining the effect of several layers.
To manipulate the receptive field size as desired, there are some alternatives to the standard convolutional layer. For example, atrous or dilated convolution expands the receptive field size without increasing the number of parameters by interleaving visible and blind regions. Moreover, a single dilated convolutional layer can comprise filters with multiple dilation ratios, thus having a variable receptive field size.
Weights
Each neuron in a neural network computes an output value by applying a specific function to the input values received from the receptive field in the previous layer. The function that is applied to the input values is determined by a vector of weights and a bias (typically real numbers). Learning consists of iteratively adjusting these biases and weights.
The vectors of weights and biases are called filters and represent particular features of the input (e.g., a particular shape). A distinguishing feature of CNNs is that many neurons can share the same filter. This reduces the memory footprint because a single bias and a single vector of weights are used across all receptive fields that share that filter, as opposed to each receptive field having its own bias and vector weighting.
Deconvolutional
A deconvolutional neural network is essentially the reverse of a CNN. It consists of deconvolutional layers and unpooling layers.
A deconvolutional layer is the transpose of a convolutional layer. Specifically, a convolutional layer can be written as a multiplication with a matrix, and a deconvolutional layer is multiplication with the transpose of that matrix.
An unpooling layer expands the layer. The max-unpooling layer is the simplest, as it simply copies each entry multiple times. For example, a 2-by-2 max-unpooling layer is .
Deconvolution layers are used in image generators. By default, it creates periodic checkerboard artifact, which can be fixed by upscale-then-convolve.
History
CNN are often compared to the way the brain achieves vision processing in living organisms.
Receptive fields in the visual cortex
Work by Hubel and Wiesel in the 1950s and 1960s showed that cat visual cortices contain neurons that individually respond to small regions of the visual field. Provided the eyes are not moving, the region of visual space within which visual stimuli affect the firing of a single neuron is known as its receptive field. Neighboring cells have similar and overlapping receptive fields. Receptive field size and location varies systematically across the cortex to form a complete map of visual space. The cortex in each hemisphere represents the contralateral visual field.
Their 1968 paper identified two basic visual cell types in the brain:
- simple cells, whose output is maximized by straight edges having particular orientations within their receptive field
- complex cells, which have larger receptive fields, whose output is insensitive to the exact position of the edges in the field.
Hubel and Wiesel also proposed a cascading model of these two types of cells for use in pattern recognition tasks.
Neocognitron, origin of the CNN architecture
Inspired by Hubel and Wiesel's work, in 1969, Kunihiko Fukushima published a deep CNN that uses ReLU activation function. Unlike most modern networks, this network used hand-designed kernels. It was not used in his neocognitron, since all the weights were nonnegative; lateral inhibition was used instead. The rectifier has become the most popular activation function for CNNs and deep neural networks in general.
The "neocognitron" was introduced by Kunihiko Fukushima in 1979. The kernels were trained by unsupervised learning. It was inspired by the above-mentioned work of Hubel and Wiesel. The neocognitron introduced the two basic types of layers:
- "S-layer": a shared-weights receptive-field layer, later known as a convolutional layer, which contains units whose receptive fields cover a patch of the previous layer. A shared-weights receptive-field group (a "plane" in neocognitron terminology) is often called a filter, and a layer typically has several such filters.
- "C-layer": a downsampling layer that contain units whose receptive fields cover patches of previous convolutional layers. Such a unit typically computes a weighted average of the activations of the units in its patch, and applies inhibition (divisive normalization) pooled from a somewhat larger patch and across different filters in a layer, and applies a saturating activation function. The patch weights are nonnegative and are not trainable in the original neocognitron. The downsampling and competitive inhibition help to classify features and objects in visual scenes even when the objects are shifted.
In a variant of the neocognitron called the cresceptron, instead of using Fukushima's spatial averaging with inhibition and saturation, J. Weng et al. in 1993 introduced a method called max-pooling where a downsampling unit computes the maximum of the activations of the units in its patch. Max-pooling is often used in modern CNNs.
Several supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms have been proposed over the decades to train the weights of a neocognitron. Today, however, the CNN architecture is usually trained through backpropagation.
Convolution in time
The term "convolution" first appears in neural networks in a paper by Toshiteru Homma, Les Atlas, and Robert Marks II at the first Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems in 1987. Their paper replaced multiplication with convolution in time, inherently providing shift invariance, motivated by and connecting more directly to the signal-processing concept of a filter, and demonstrated it on a speech recognition task. They also pointed out that as a data-trainable system, convolution is essentially equivalent to correlation since reversal of the weights does not affect the final learned function ("For convenience, we denote * as correlation instead of convolution. Note that convolving a(t) with b(t) is equivalent to correlating a(-t) with b(t)."). Modern CNN implementations typically do correlation and call it convolution, for convenience, as they did here.
Time delay neural networks
The time delay neural network (TDNN) was introduced in 1987 by Alex Waibel et al. for phoneme recognition and was one of the first convolutional networks, as it achieved shift-invariance. A TDNN is a 1-D convolutional neural net where the convolution is performed along the time axis of the data. It is the first CNN utilizing weight sharing in combination with a training by gradient descent, using backpropagation. Thus, while also using a pyramidal structure as in the neocognitron, it performed a global optimization of the weights instead of a local one.
TDNNs are convolutional networks that share weights along the temporal dimension. They allow speech signals to be processed time-invariantly. In 1990 Hampshire and Waibel introduced a variant that performs a two-dimensional convolution. Since these TDNNs operated on spectrograms, the resulting phoneme recognition system was invariant to both time and frequency shifts, as with images processed by a neocognitron.
TDNNs improved the performance of far-distance speech recognition.
Image recognition with CNNs trained by gradient descent
Denker et al. (1989) designed a 2-D CNN system to recognize hand-written ZIP Code numbers. However, the lack of an efficient training method to determine the kernel coefficients of the involved convolutions meant that all the coefficients had to be laboriously hand-designed.
Following the advances in the training of 1-D CNNs by Waibel et al. (1987), Yann LeCun et al. (1989) used back-propagation to learn the convolution kernel coefficients directly from images of hand-written numbers. Learning was thus fully automatic, performed better than manual coefficient design, and was suited to a broader range of image recognition problems and image types. Wei Zhang et al. (1988) used back-propagation to train the convolution kernels of a CNN for alphabets recognition. The model was called shift-invariant pattern recognition neural network before the name CNN was coined later in the early 1990s. Wei Zhang et al. also applied the same CNN without the last fully connected layer for medical image object segmentation (1991) and breast cancer detection in mammograms (1994).
This approach became a foundation of modern computer vision.
Max pooling
In 1990 Yamaguchi et al. introduced the concept of max pooling, a fixed filtering operation that calculates and propagates the maximum value of a given region. They did so by combining TDNNs with max pooling to realize a speaker-independent isolated word recognition system. In their system they used several TDNNs per word, one for each syllable. The results of each TDNN over the input signal were combined using max pooling and the outputs of the pooling layers were then passed on to networks performing the actual word classification.
LeNet-5
Main article: LeNetLeNet-5, a pioneering 7-level convolutional network by LeCun et al. in 1995, classifies hand-written numbers on checks (British English: cheques) digitized in 32x32 pixel images. The ability to process higher-resolution images requires larger and more layers of convolutional neural networks, so this technique is constrained by the availability of computing resources.
It was superior than other commercial courtesy amount reading systems (as of 1995). The system was integrated in NCR's check reading systems, and fielded in several American banks since June 1996, reading millions of checks per day.
Shift-invariant neural network
A shift-invariant neural network was proposed by Wei Zhang et al. for image character recognition in 1988. It is a modified Neocognitron by keeping only the convolutional interconnections between the image feature layers and the last fully connected layer. The model was trained with back-propagation. The training algorithm was further improved in 1991 to improve its generalization ability. The model architecture was modified by removing the last fully connected layer and applied for medical image segmentation (1991) and automatic detection of breast cancer in mammograms (1994).
A different convolution-based design was proposed in 1988 for application to decomposition of one-dimensional electromyography convolved signals via de-convolution. This design was modified in 1989 to other de-convolution-based designs.
Topological deep learning
Topological deep learning was first introduced in 2017. It integrates topological data analysis and convolutional neural networks for intricately complex data. Topological deep learning has become a new frontier in deep learning.
GPU implementations
Although CNNs were invented in the 1980s, their breakthrough in the 2000s required fast implementations on graphics processing units (GPUs).
In 2004, it was shown by K. S. Oh and K. Jung that standard neural networks can be greatly accelerated on GPUs. Their implementation was 20 times faster than an equivalent implementation on CPU. In 2005, another paper also emphasised the value of GPGPU for machine learning.
The first GPU-implementation of a CNN was described in 2006 by K. Chellapilla et al. Their implementation was 4 times faster than an equivalent implementation on CPU. In the same period, GPUs were also used for unsupervised training of deep belief networks.
In 2010, Dan Ciresan et al. at IDSIA trained deep feedforward networks on GPUs. In 2011, they extended this to CNNs, accelerating by 60 compared to training CPU. In 2011, the network win an image recognition contest where they achieved superhuman performance for the first time. Then they won more competitions and achieved state of the art on several benchmarks.
Subsequently, AlexNet, a similar GPU-based CNN by Alex Krizhevsky et al. won the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2012. It was an early catalytic event for the AI boom.
Compared to the training of CNNs using GPUs, not much attention was given to CPU. (Viebke et al 2019) parallelizes CNN by thread- and SIMD-level parallelism that is available on the Intel Xeon Phi.
Distinguishing features
In the past, traditional multilayer perceptron (MLP) models were used for image recognition. However, the full connectivity between nodes caused the curse of dimensionality, and was computationally intractable with higher-resolution images. A 1000×1000-pixel image with RGB color channels has 3 million weights per fully-connected neuron, which is too high to feasibly process efficiently at scale.

For example, in CIFAR-10, images are only of size 32×32×3 (32 wide, 32 high, 3 color channels), so a single fully connected neuron in the first hidden layer of a regular neural network would have 32*32*3 = 3,072 weights. A 200×200 image, however, would lead to neurons that have 200*200*3 = 120,000 weights.
Also, such network architecture does not take into account the spatial structure of data, treating input pixels which are far apart in the same way as pixels that are close together. This ignores locality of reference in data with a grid-topology (such as images), both computationally and semantically. Thus, full connectivity of neurons is wasteful for purposes such as image recognition that are dominated by spatially local input patterns.
Convolutional neural networks are variants of multilayer perceptrons, designed to emulate the behavior of a visual cortex. These models mitigate the challenges posed by the MLP architecture by exploiting the strong spatially local correlation present in natural images. As opposed to MLPs, CNNs have the following distinguishing features:
- 3D volumes of neurons. The layers of a CNN have neurons arranged in 3 dimensions: width, height and depth. Where each neuron inside a convolutional layer is connected to only a small region of the layer before it, called a receptive field. Distinct types of layers, both locally and completely connected, are stacked to form a CNN architecture.
- Local connectivity: following the concept of receptive fields, CNNs exploit spatial locality by enforcing a local connectivity pattern between neurons of adjacent layers. The architecture thus ensures that the learned "filters" produce the strongest response to a spatially local input pattern. Stacking many such layers leads to nonlinear filters that become increasingly global (i.e. responsive to a larger region of pixel space) so that the network first creates representations of small parts of the input, then from them assembles representations of larger areas.
- Shared weights: In CNNs, each filter is replicated across the entire visual field. These replicated units share the same parameterization (weight vector and bias) and form a feature map. This means that all the neurons in a given convolutional layer respond to the same feature within their specific response field. Replicating units in this way allows for the resulting activation map to be equivariant under shifts of the locations of input features in the visual field, i.e. they grant translational equivariance—given that the layer has a stride of one.
- Pooling: In a CNN's pooling layers, feature maps are divided into rectangular sub-regions, and the features in each rectangle are independently down-sampled to a single value, commonly by taking their average or maximum value. In addition to reducing the sizes of feature maps, the pooling operation grants a degree of local translational invariance to the features contained therein, allowing the CNN to be more robust to variations in their positions.
Together, these properties allow CNNs to achieve better generalization on vision problems. Weight sharing dramatically reduces the number of free parameters learned, thus lowering the memory requirements for running the network and allowing the training of larger, more powerful networks.
Building blocks
A CNN architecture is formed by a stack of distinct layers that transform the input volume into an output volume (e.g. holding the class scores) through a differentiable function. A few distinct types of layers are commonly used. These are further discussed below.

Convolutional layer

The convolutional layer is the core building block of a CNN. The layer's parameters consist of a set of learnable filters (or kernels), which have a small receptive field, but extend through the full depth of the input volume. During the forward pass, each filter is convolved across the width and height of the input volume, computing the dot product between the filter entries and the input, producing a 2-dimensional activation map of that filter. As a result, the network learns filters that activate when it detects some specific type of feature at some spatial position in the input.
Stacking the activation maps for all filters along the depth dimension forms the full output volume of the convolution layer. Every entry in the output volume can thus also be interpreted as an output of a neuron that looks at a small region in the input. Each entry in an activation map use the same set of parameters that define the filter.
Self-supervised learning has been adapted for use in convolutional layers by using sparse patches with a high-mask ratio and a global response normalization layer.
Local connectivity
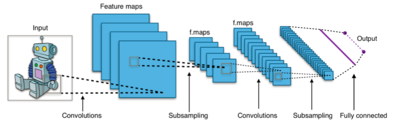
When dealing with high-dimensional inputs such as images, it is impractical to connect neurons to all neurons in the previous volume because such a network architecture does not take the spatial structure of the data into account. Convolutional networks exploit spatially local correlation by enforcing a sparse local connectivity pattern between neurons of adjacent layers: each neuron is connected to only a small region of the input volume.
The extent of this connectivity is a hyperparameter called the receptive field of the neuron. The connections are local in space (along width and height), but always extend along the entire depth of the input volume. Such an architecture ensures that the learned (British English: learnt) filters produce the strongest response to a spatially local input pattern.
Spatial arrangement
Three hyperparameters control the size of the output volume of the convolutional layer: the depth, stride, and padding size:
- The depth of the output volume controls the number of neurons in a layer that connect to the same region of the input volume. These neurons learn to activate for different features in the input. For example, if the first convolutional layer takes the raw image as input, then different neurons along the depth dimension may activate in the presence of various oriented edges, or blobs of color.
- Stride controls how depth columns around the width and height are allocated. If the stride is 1, then we move the filters one pixel at a time. This leads to heavily overlapping receptive fields between the columns, and to large output volumes. For any integer a stride S means that the filter is translated S units at a time per output. In practice, is rare. A greater stride means smaller overlap of receptive fields and smaller spatial dimensions of the output volume.
- Sometimes, it is convenient to pad the input with zeros (or other values, such as the average of the region) on the border of the input volume. The size of this padding is a third hyperparameter. Padding provides control of the output volume's spatial size. In particular, sometimes it is desirable to exactly preserve the spatial size of the input volume, this is commonly referred to as "same" padding.

The spatial size of the output volume is a function of the input volume size , the kernel field size of the convolutional layer neurons, the stride , and the amount of zero padding on the border. The number of neurons that "fit" in a given volume is then:
If this number is not an integer, then the strides are incorrect and the neurons cannot be tiled to fit across the input volume in a symmetric way. In general, setting zero padding to be when the stride is ensures that the input volume and output volume will have the same size spatially. However, it is not always completely necessary to use all of the neurons of the previous layer. For example, a neural network designer may decide to use just a portion of padding.
Parameter sharing
A parameter sharing scheme is used in convolutional layers to control the number of free parameters. It relies on the assumption that if a patch feature is useful to compute at some spatial position, then it should also be useful to compute at other positions. Denoting a single 2-dimensional slice of depth as a depth slice, the neurons in each depth slice are constrained to use the same weights and bias.
Since all neurons in a single depth slice share the same parameters, the forward pass in each depth slice of the convolutional layer can be computed as a convolution of the neuron's weights with the input volume. Therefore, it is common to refer to the sets of weights as a filter (or a kernel), which is convolved with the input. The result of this convolution is an activation map, and the set of activation maps for each different filter are stacked together along the depth dimension to produce the output volume. Parameter sharing contributes to the translation invariance of the CNN architecture.
Sometimes, the parameter sharing assumption may not make sense. This is especially the case when the input images to a CNN have some specific centered structure; for which we expect completely different features to be learned on different spatial locations. One practical example is when the inputs are faces that have been centered in the image: we might expect different eye-specific or hair-specific features to be learned in different parts of the image. In that case it is common to relax the parameter sharing scheme, and instead simply call the layer a "locally connected layer".
Pooling layer
Main article: Pooling layer

Another important concept of CNNs is pooling, which is used as a form of non-linear down-sampling. Pooling provides downsampling because it reduces the spatial dimensions (height and width) of the input feature maps while retaining the most important information. There are several non-linear functions to implement pooling, where max pooling and average pooling are the most common. Pooling aggregates information from small regions of the input creating partitions of the input feature map, typically using a fixed-size window (like 2x2) and applying a stride (often 2) to move the window across the input. Note that without using a stride greater than 1, pooling would not perform downsampling, as it would simply move the pooling window across the input one step at a time, without reducing the size of the feature map. In other words, the stride is what actually causes the downsampling by determining how much the pooling window moves over the input.
Intuitively, the exact location of a feature is less important than its rough location relative to other features. This is the idea behind the use of pooling in convolutional neural networks. The pooling layer serves to progressively reduce the spatial size of the representation, to reduce the number of parameters, memory footprint and amount of computation in the network, and hence to also control overfitting. This is known as down-sampling. It is common to periodically insert a pooling layer between successive convolutional layers (each one typically followed by an activation function, such as a ReLU layer) in a CNN architecture. While pooling layers contribute to local translation invariance, they do not provide global translation invariance in a CNN, unless a form of global pooling is used. The pooling layer commonly operates independently on every depth, or slice, of the input and resizes it spatially. A very common form of max pooling is a layer with filters of size 2×2, applied with a stride of 2, which subsamples every depth slice in the input by 2 along both width and height, discarding 75% of the activations: In this case, every max operation is over 4 numbers. The depth dimension remains unchanged (this is true for other forms of pooling as well).
In addition to max pooling, pooling units can use other functions, such as average pooling or ℓ2-norm pooling. Average pooling was often used historically but has recently fallen out of favor compared to max pooling, which generally performs better in practice.
Due to the effects of fast spatial reduction of the size of the representation, there is a recent trend towards using smaller filters or discarding pooling layers altogether.

Channel max pooling
A channel max pooling (CMP) operation layer conducts the MP operation along the channel side among the corresponding positions of the consecutive feature maps for the purpose of redundant information elimination. The CMP makes the significant features gather together within fewer channels, which is important for fine-grained image classification that needs more discriminating features. Meanwhile, another advantage of the CMP operation is to make the channel number of feature maps smaller before it connects to the first fully connected (FC) layer. Similar to the MP operation, we denote the input feature maps and output feature maps of a CMP layer as F ∈ R(C×M×N) and C ∈ R(c×M×N), respectively, where C and c are the channel numbers of the input and output feature maps, M and N are the widths and the height of the feature maps, respectively. Note that the CMP operation only changes the channel number of the feature maps. The width and the height of the feature maps are not changed, which is different from the MP operation.
See for reviews for pooling methods.
ReLU layer
ReLU is the abbreviation of rectified linear unit. It was proposed by Alston Householder in 1941, and used in CNN by Kunihiko Fukushima in 1969. ReLU applies the non-saturating activation function . It effectively removes negative values from an activation map by setting them to zero. It introduces nonlinearity to the decision function and in the overall network without affecting the receptive fields of the convolution layers. In 2011, Xavier Glorot, Antoine Bordes and Yoshua Bengio found that ReLU enables better training of deeper networks, compared to widely used activation functions prior to 2011.
Other functions can also be used to increase nonlinearity, for example the saturating hyperbolic tangent , , and the sigmoid function . ReLU is often preferred to other functions because it trains the neural network several times faster without a significant penalty to generalization accuracy.
Fully connected layer
After several convolutional and max pooling layers, the final classification is done via fully connected layers. Neurons in a fully connected layer have connections to all activations in the previous layer, as seen in regular (non-convolutional) artificial neural networks. Their activations can thus be computed as an affine transformation, with matrix multiplication followed by a bias offset (vector addition of a learned or fixed bias term).
Loss layer
Main articles: Loss function and Loss functions for classificationThe "loss layer", or "loss function", specifies how training penalizes the deviation between the predicted output of the network, and the true data labels (during supervised learning). Various loss functions can be used, depending on the specific task.
The Softmax loss function is used for predicting a single class of K mutually exclusive classes. Sigmoid cross-entropy loss is used for predicting K independent probability values in . Euclidean loss is used for regressing to real-valued labels .
Hyperparameters
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (June 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Hyperparameters are various settings that are used to control the learning process. CNNs use more hyperparameters than a standard multilayer perceptron (MLP).
Kernel size
The kernel is the number of pixels processed together. It is typically expressed as the kernel's dimensions, e.g., 2x2, or 3x3.
Padding
Padding is the addition of (typically) 0-valued pixels on the borders of an image. This is done so that the border pixels are not undervalued (lost) from the output because they would ordinarily participate in only a single receptive field instance. The padding applied is typically one less than the corresponding kernel dimension. For example, a convolutional layer using 3x3 kernels would receive a 2-pixel pad, that is 1 pixel on each side of the image.
Stride
The stride is the number of pixels that the analysis window moves on each iteration. A stride of 2 means that each kernel is offset by 2 pixels from its predecessor.
Number of filters
Since feature map size decreases with depth, layers near the input layer tend to have fewer filters while higher layers can have more. To equalize computation at each layer, the product of feature values va with pixel position is kept roughly constant across layers. Preserving more information about the input would require keeping the total number of activations (number of feature maps times number of pixel positions) non-decreasing from one layer to the next.
The number of feature maps directly controls the capacity and depends on the number of available examples and task complexity.
Filter size
Common filter sizes found in the literature vary greatly, and are usually chosen based on the data set. Typical filter sizes range from 1x1 to 7x7. As two famous examples, AlexNet used 3x3, 5x5, and 11x11. Inceptionv3 used 1x1, 3x3, and 5x5.
The challenge is to find the right level of granularity so as to create abstractions at the proper scale, given a particular data set, and without overfitting.
Pooling type and size
Max pooling is typically used, often with a 2x2 dimension. This implies that the input is drastically downsampled, reducing processing cost.
Greater pooling reduces the dimension of the signal, and may result in unacceptable information loss. Often, non-overlapping pooling windows perform best.
Dilation
Dilation involves ignoring pixels within a kernel. This reduces processing memory potentially without significant signal loss. A dilation of 2 on a 3x3 kernel expands the kernel to 5x5, while still processing 9 (evenly spaced) pixels. Specifically, the processed pixels after the dilation are the cells (1,1), (1,3), (1,5), (3,1), (3,3), (3,5), (5,1), (5,3), (5,5), where (i,j) denotes the cell of the i-th row and j-th column in the expanded 5x5 kernel. Accordingly, dilation of 4 expands the kernel to 7x7.
Translation equivariance and aliasing
It is commonly assumed that CNNs are invariant to shifts of the input. Convolution or pooling layers within a CNN that do not have a stride greater than one are indeed equivariant to translations of the input. However, layers with a stride greater than one ignore the Nyquist-Shannon sampling theorem and might lead to aliasing of the input signal While, in principle, CNNs are capable of implementing anti-aliasing filters, it has been observed that this does not happen in practice and yield models that are not equivariant to translations. Furthermore, if a CNN makes use of fully connected layers, translation equivariance does not imply translation invariance, as the fully connected layers are not invariant to shifts of the input. One solution for complete translation invariance is avoiding any down-sampling throughout the network and applying global average pooling at the last layer. Additionally, several other partial solutions have been proposed, such as anti-aliasing before downsampling operations, spatial transformer networks, data augmentation, subsampling combined with pooling, and capsule neural networks.
Evaluation
The accuracy of the final model is based on a sub-part of the dataset set apart at the start, often called a test-set. Other times methods such as k-fold cross-validation are applied. Other strategies include using conformal prediction.
Regularization methods
Main article: Regularization (mathematics)| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (June 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Regularization is a process of introducing additional information to solve an ill-posed problem or to prevent overfitting. CNNs use various types of regularization.
Empirical
Dropout
Because a fully connected layer occupies most of the parameters, it is prone to overfitting. One method to reduce overfitting is dropout, introduced in 2014. At each training stage, individual nodes are either "dropped out" of the net (ignored) with probability or kept with probability , so that a reduced network is left; incoming and outgoing edges to a dropped-out node are also removed. Only the reduced network is trained on the data in that stage. The removed nodes are then reinserted into the network with their original weights.
In the training stages, is usually 0.5; for input nodes, it is typically much higher because information is directly lost when input nodes are ignored.
At testing time after training has finished, we would ideally like to find a sample average of all possible dropped-out networks; unfortunately this is unfeasible for large values of . However, we can find an approximation by using the full network with each node's output weighted by a factor of , so the expected value of the output of any node is the same as in the training stages. This is the biggest contribution of the dropout method: although it effectively generates neural nets, and as such allows for model combination, at test time only a single network needs to be tested.
By avoiding training all nodes on all training data, dropout decreases overfitting. The method also significantly improves training speed. This makes the model combination practical, even for deep neural networks. The technique seems to reduce node interactions, leading them to learn more robust features that better generalize to new data.
DropConnect
DropConnect is the generalization of dropout in which each connection, rather than each output unit, can be dropped with probability . Each unit thus receives input from a random subset of units in the previous layer.
DropConnect is similar to dropout as it introduces dynamic sparsity within the model, but differs in that the sparsity is on the weights, rather than the output vectors of a layer. In other words, the fully connected layer with DropConnect becomes a sparsely connected layer in which the connections are chosen at random during the training stage.
Stochastic pooling
A major drawback to Dropout is that it does not have the same benefits for convolutional layers, where the neurons are not fully connected.
Even before Dropout, in 2013 a technique called stochastic pooling, the conventional deterministic pooling operations were replaced with a stochastic procedure, where the activation within each pooling region is picked randomly according to a multinomial distribution, given by the activities within the pooling region. This approach is free of hyperparameters and can be combined with other regularization approaches, such as dropout and data augmentation.
An alternate view of stochastic pooling is that it is equivalent to standard max pooling but with many copies of an input image, each having small local deformations. This is similar to explicit elastic deformations of the input images, which delivers excellent performance on the MNIST data set. Using stochastic pooling in a multilayer model gives an exponential number of deformations since the selections in higher layers are independent of those below.
Artificial data
Main article: Data augmentationBecause the degree of model overfitting is determined by both its power and the amount of training it receives, providing a convolutional network with more training examples can reduce overfitting. Because there is often not enough available data to train, especially considering that some part should be spared for later testing, two approaches are to either generate new data from scratch (if possible) or perturb existing data to create new ones. The latter one is used since mid-1990s. For example, input images can be cropped, rotated, or rescaled to create new examples with the same labels as the original training set.
Explicit
Early stopping
Main article: Early stoppingOne of the simplest methods to prevent overfitting of a network is to simply stop the training before overfitting has had a chance to occur. It comes with the disadvantage that the learning process is halted.
Number of parameters
Another simple way to prevent overfitting is to limit the number of parameters, typically by limiting the number of hidden units in each layer or limiting network depth. For convolutional networks, the filter size also affects the number of parameters. Limiting the number of parameters restricts the predictive power of the network directly, reducing the complexity of the function that it can perform on the data, and thus limits the amount of overfitting. This is equivalent to a "zero norm".
Weight decay
A simple form of added regularizer is weight decay, which simply adds an additional error, proportional to the sum of weights (L1 norm) or squared magnitude (L2 norm) of the weight vector, to the error at each node. The level of acceptable model complexity can be reduced by increasing the proportionality constant('alpha' hyperparameter), thus increasing the penalty for large weight vectors.
L2 regularization is the most common form of regularization. It can be implemented by penalizing the squared magnitude of all parameters directly in the objective. The L2 regularization has the intuitive interpretation of heavily penalizing peaky weight vectors and preferring diffuse weight vectors. Due to multiplicative interactions between weights and inputs this has the useful property of encouraging the network to use all of its inputs a little rather than some of its inputs a lot.
L1 regularization is also common. It makes the weight vectors sparse during optimization. In other words, neurons with L1 regularization end up using only a sparse subset of their most important inputs and become nearly invariant to the noisy inputs. L1 with L2 regularization can be combined; this is called elastic net regularization.
Max norm constraints
Another form of regularization is to enforce an absolute upper bound on the magnitude of the weight vector for every neuron and use projected gradient descent to enforce the constraint. In practice, this corresponds to performing the parameter update as normal, and then enforcing the constraint by clamping the weight vector of every neuron to satisfy . Typical values of are order of 3–4. Some papers report improvements when using this form of regularization.
Hierarchical coordinate frames
Pooling loses the precise spatial relationships between high-level parts (such as nose and mouth in a face image). These relationships are needed for identity recognition. Overlapping the pools so that each feature occurs in multiple pools, helps retain the information. Translation alone cannot extrapolate the understanding of geometric relationships to a radically new viewpoint, such as a different orientation or scale. On the other hand, people are very good at extrapolating; after seeing a new shape once they can recognize it from a different viewpoint.
An earlier common way to deal with this problem is to train the network on transformed data in different orientations, scales, lighting, etc. so that the network can cope with these variations. This is computationally intensive for large data-sets. The alternative is to use a hierarchy of coordinate frames and use a group of neurons to represent a conjunction of the shape of the feature and its pose relative to the retina. The pose relative to the retina is the relationship between the coordinate frame of the retina and the intrinsic features' coordinate frame.
Thus, one way to represent something is to embed the coordinate frame within it. This allows large features to be recognized by using the consistency of the poses of their parts (e.g. nose and mouth poses make a consistent prediction of the pose of the whole face). This approach ensures that the higher-level entity (e.g. face) is present when the lower-level (e.g. nose and mouth) agree on its prediction of the pose. The vectors of neuronal activity that represent pose ("pose vectors") allow spatial transformations modeled as linear operations that make it easier for the network to learn the hierarchy of visual entities and generalize across viewpoints. This is similar to the way the human visual system imposes coordinate frames in order to represent shapes.
Applications
Image recognition
CNNs are often used in image recognition systems. In 2012, an error rate of 0.23% on the MNIST database was reported. Another paper on using CNN for image classification reported that the learning process was "surprisingly fast"; in the same paper, the best published results as of 2011 were achieved in the MNIST database and the NORB database. Subsequently, a similar CNN called AlexNet won the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2012.
When applied to facial recognition, CNNs achieved a large decrease in error rate. Another paper reported a 97.6% recognition rate on "5,600 still images of more than 10 subjects". CNNs were used to assess video quality in an objective way after manual training; the resulting system had a very low root mean square error.
The ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge is a benchmark in object classification and detection, with millions of images and hundreds of object classes. In the ILSVRC 2014, a large-scale visual recognition challenge, almost every highly ranked team used CNN as their basic framework. The winner GoogLeNet (the foundation of DeepDream) increased the mean average precision of object detection to 0.439329, and reduced classification error to 0.06656, the best result to date. Its network applied more than 30 layers. That performance of convolutional neural networks on the ImageNet tests was close to that of humans. The best algorithms still struggle with objects that are small or thin, such as a small ant on a stem of a flower or a person holding a quill in their hand. They also have trouble with images that have been distorted with filters, an increasingly common phenomenon with modern digital cameras. By contrast, those kinds of images rarely trouble humans. Humans, however, tend to have trouble with other issues. For example, they are not good at classifying objects into fine-grained categories such as the particular breed of dog or species of bird, whereas convolutional neural networks handle this.
In 2015, a many-layered CNN demonstrated the ability to spot faces from a wide range of angles, including upside down, even when partially occluded, with competitive performance. The network was trained on a database of 200,000 images that included faces at various angles and orientations and a further 20 million images without faces. They used batches of 128 images over 50,000 iterations.
Video analysis
Compared to image data domains, there is relatively little work on applying CNNs to video classification. Video is more complex than images since it has another (temporal) dimension. However, some extensions of CNNs into the video domain have been explored. One approach is to treat space and time as equivalent dimensions of the input and perform convolutions in both time and space. Another way is to fuse the features of two convolutional neural networks, one for the spatial and one for the temporal stream. Long short-term memory (LSTM) recurrent units are typically incorporated after the CNN to account for inter-frame or inter-clip dependencies. Unsupervised learning schemes for training spatio-temporal features have been introduced, based on Convolutional Gated Restricted Boltzmann Machines and Independent Subspace Analysis. Its application can be seen in text-to-video model.
Natural language processing
CNNs have also been explored for natural language processing. CNN models are effective for various NLP problems and achieved excellent results in semantic parsing, search query retrieval, sentence modeling, classification, prediction and other traditional NLP tasks. Compared to traditional language processing methods such as recurrent neural networks, CNNs can represent different contextual realities of language that do not rely on a series-sequence assumption, while RNNs are better suitable when classical time series modeling is required.
Anomaly detection
A CNN with 1-D convolutions was used on time series in the frequency domain (spectral residual) by an unsupervised model to detect anomalies in the time domain.
Drug discovery
CNNs have been used in drug discovery. Predicting the interaction between molecules and biological proteins can identify potential treatments. In 2015, Atomwise introduced AtomNet, the first deep learning neural network for structure-based drug design. The system trains directly on 3-dimensional representations of chemical interactions. Similar to how image recognition networks learn to compose smaller, spatially proximate features into larger, complex structures, AtomNet discovers chemical features, such as aromaticity, sp carbons, and hydrogen bonding. Subsequently, AtomNet was used to predict novel candidate biomolecules for multiple disease targets, most notably treatments for the Ebola virus and multiple sclerosis.
In 2016-2019, topologyNet and mathematical deep learning achieved first place in multiple categories of the D3R Grand Challenges, a worldwide annual competition series focused on computer-aided drug design.
Checkers game
CNNs have been used in the game of checkers. From 1999 to 2001, Fogel and Chellapilla published papers showing how a convolutional neural network could learn to play checker using co-evolution. The learning process did not use prior human professional games, but rather focused on a minimal set of information contained in the checkerboard: the location and type of pieces, and the difference in number of pieces between the two sides. Ultimately, the program (Blondie24) was tested on 165 games against players and ranked in the highest 0.4%. It also earned a win against the program Chinook at its "expert" level of play.
Go
CNNs have been used in computer Go. In December 2014, Clark and Storkey published a paper showing that a CNN trained by supervised learning from a database of human professional games could outperform GNU Go and win some games against Monte Carlo tree search Fuego 1.1 in a fraction of the time it took Fuego to play. Later it was announced that a large 12-layer convolutional neural network had correctly predicted the professional move in 55% of positions, equalling the accuracy of a 6 dan human player. When the trained convolutional network was used directly to play games of Go, without any search, it beat the traditional search program GNU Go in 97% of games, and matched the performance of the Monte Carlo tree search program Fuego simulating ten thousand playouts (about a million positions) per move.
A couple of CNNs for choosing moves to try ("policy network") and evaluating positions ("value network") driving MCTS were used by AlphaGo, the first to beat the best human player at the time.
Time series forecasting
Recurrent neural networks are generally considered the best neural network architectures for time series forecasting (and sequence modeling in general), but recent studies show that convolutional networks can perform comparably or even better. Dilated convolutions might enable one-dimensional convolutional neural networks to effectively learn time series dependences. Convolutions can be implemented more efficiently than RNN-based solutions, and they do not suffer from vanishing (or exploding) gradients. Convolutional networks can provide an improved forecasting performance when there are multiple similar time series to learn from. CNNs can also be applied to further tasks in time series analysis (e.g., time series classification or quantile forecasting).
Cultural heritage and 3D-datasets
As archaeological findings such as clay tablets with cuneiform writing are increasingly acquired using 3D scanners, benchmark datasets are becoming available, including HeiCuBeDa providing almost 2000 normalized 2-D and 3-D datasets prepared with the GigaMesh Software Framework. So curvature-based measures are used in conjunction with geometric neural networks (GNNs), e.g. for period classification of those clay tablets being among the oldest documents of human history.
Fine-tuning
For many applications, training data is not very available. Convolutional neural networks usually require a large amount of training data in order to avoid overfitting. A common technique is to train the network on a larger data set from a related domain. Once the network parameters have converged an additional training step is performed using the in-domain data to fine-tune the network weights, this is known as transfer learning. Furthermore, this technique allows convolutional network architectures to successfully be applied to problems with tiny training sets.
Human interpretable explanations
End-to-end training and prediction are common practice in computer vision. However, human interpretable explanations are required for critical systems such as a self-driving cars. With recent advances in visual salience, spatial attention, and temporal attention, the most critical spatial regions/temporal instants could be visualized to justify the CNN predictions.
Related architectures
Deep Q-networks
A deep Q-network (DQN) is a type of deep learning model that combines a deep neural network with Q-learning, a form of reinforcement learning. Unlike earlier reinforcement learning agents, DQNs that utilize CNNs can learn directly from high-dimensional sensory inputs via reinforcement learning.
Preliminary results were presented in 2014, with an accompanying paper in February 2015. The research described an application to Atari 2600 gaming. Other deep reinforcement learning models preceded it.
Deep belief networks
Main article: Deep belief networkConvolutional deep belief networks (CDBN) have structure very similar to convolutional neural networks and are trained similarly to deep belief networks. Therefore, they exploit the 2D structure of images, like CNNs do, and make use of pre-training like deep belief networks. They provide a generic structure that can be used in many image and signal processing tasks. Benchmark results on standard image datasets like CIFAR have been obtained using CDBNs.

Neural abstraction pyramid
The feed-forward architecture of convolutional neural networks was extended in the neural abstraction pyramid by lateral and feedback connections. The resulting recurrent convolutional network allows for the flexible incorporation of contextual information to iteratively resolve local ambiguities. In contrast to previous models, image-like outputs at the highest resolution were generated, e.g., for semantic segmentation, image reconstruction, and object localization tasks.
Notable libraries
- Caffe: A library for convolutional neural networks. Created by the Berkeley Vision and Learning Center (BVLC). It supports both CPU and GPU. Developed in C++, and has Python and MATLAB wrappers.
- Deeplearning4j: Deep learning in Java and Scala on multi-GPU-enabled Spark. A general-purpose deep learning library for the JVM production stack running on a C++ scientific computing engine. Allows the creation of custom layers. Integrates with Hadoop and Kafka.
- Dlib: A toolkit for making real world machine learning and data analysis applications in C++.
- Microsoft Cognitive Toolkit: A deep learning toolkit written by Microsoft with several unique features enhancing scalability over multiple nodes. It supports full-fledged interfaces for training in C++ and Python and with additional support for model inference in C# and Java.
- TensorFlow: Apache 2.0-licensed Theano-like library with support for CPU, GPU, Google's proprietary tensor processing unit (TPU), and mobile devices.
- Theano: The reference deep-learning library for Python with an API largely compatible with the popular NumPy library. Allows user to write symbolic mathematical expressions, then automatically generates their derivatives, saving the user from having to code gradients or backpropagation. These symbolic expressions are automatically compiled to CUDA code for a fast, on-the-GPU implementation.
- Torch: A scientific computing framework with wide support for machine learning algorithms, written in C and Lua.
See also
- Attention (machine learning)
- Convolution
- Deep learning
- Natural-language processing
- Neocognitron
- Scale-invariant feature transform
- Time delay neural network
- Vision processing unit
- Topological deep learning
Notes
- When applied to other types of data than image data, such as sound data, "spatial position" may variously correspond to different points in the time domain, frequency domain, or other mathematical spaces.
- hence the name "convolutional layer"
- So-called categorical data.
References
- LeCun, Yann; Bengio, Yoshua; Hinton, Geoffrey (2015-05-28). "Deep learning". Nature. 521 (7553): 436–444. Bibcode:2015Natur.521..436L. doi:10.1038/nature14539. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 26017442.
- ^ Venkatesan, Ragav; Li, Baoxin (2017-10-23). Convolutional Neural Networks in Visual Computing: A Concise Guide. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-351-65032-8. Archived from the original on 2023-10-16. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- ^ Balas, Valentina E.; Kumar, Raghvendra; Srivastava, Rajshree (2019-11-19). Recent Trends and Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-030-32644-9. Archived from the original on 2023-10-16. Retrieved 2020-12-13.
- Zhang, Yingjie; Soon, Hong Geok; Ye, Dongsen; Fuh, Jerry Ying Hsi; Zhu, Kunpeng (September 2020). "Powder-Bed Fusion Process Monitoring by Machine Vision With Hybrid Convolutional Neural Networks". IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. 16 (9): 5769–5779. doi:10.1109/TII.2019.2956078. ISSN 1941-0050. S2CID 213010088. Archived from the original on 2023-07-31. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
- Chervyakov, N.I.; Lyakhov, P.A.; Deryabin, M.A.; Nagornov, N.N.; Valueva, M.V.; Valuev, G.V. (September 2020). "Residue Number System-Based Solution for Reducing the Hardware Cost of a Convolutional Neural Network". Neurocomputing. 407: 439–453. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.018. S2CID 219470398. Archived from the original on 2023-06-29. Retrieved 2023-08-12.
Convolutional neural networks represent deep learning architectures that are currently used in a wide range of applications, including computer vision, speech recognition, malware dedection, time series analysis in finance, and many others.
- ^ Habibi, Aghdam, Hamed (2017-05-30). Guide to convolutional neural networks : a practical application to traffic-sign detection and classification. Heravi, Elnaz Jahani. Cham, Switzerland. ISBN 9783319575490. OCLC 987790957.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Homma, Toshiteru; Les Atlas; Robert Marks II (1987). "An Artificial Neural Network for Spatio-Temporal Bipolar Patterns: Application to Phoneme Classification" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 1: 31–40. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
The notion of convolution or correlation used in the models presented is popular in engineering disciplines and has been applied extensively to designing filters, control systems, etc.
- Valueva, M.V.; Nagornov, N.N.; Lyakhov, P.A.; Valuev, G.V.; Chervyakov, N.I. (2020). "Application of the residue number system to reduce hardware costs of the convolutional neural network implementation". Mathematics and Computers in Simulation. 177. Elsevier BV: 232–243. doi:10.1016/j.matcom.2020.04.031. ISSN 0378-4754. S2CID 218955622.
Convolutional neural networks are a promising tool for solving the problem of pattern recognition.
- van den Oord, Aaron; Dieleman, Sander; Schrauwen, Benjamin (2013-01-01). Burges, C. J. C.; Bottou, L.; Welling, M.; Ghahramani, Z.; Weinberger, K. Q. (eds.). Deep content-based music recommendation (PDF). Curran Associates, Inc. pp. 2643–2651. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-03-07. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Collobert, Ronan; Weston, Jason (2008-01-01). "A unified architecture for natural language processing". Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning - ICML '08. New York, NY, US: ACM. pp. 160–167. doi:10.1145/1390156.1390177. ISBN 978-1-60558-205-4. S2CID 2617020.
- Avilov, Oleksii; Rimbert, Sebastien; Popov, Anton; Bougrain, Laurent (July 2020). "Deep Learning Techniques to Improve Intraoperative Awareness Detection from Electroencephalographic Signals". 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) (PDF). Vol. 2020. Montreal, QC, Canada: IEEE. pp. 142–145. doi:10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176228. ISBN 978-1-7281-1990-8. PMID 33017950. S2CID 221386616. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-05-19. Retrieved 2023-07-21.
- ^ Tsantekidis, Avraam; Passalis, Nikolaos; Tefas, Anastasios; Kanniainen, Juho; Gabbouj, Moncef; Iosifidis, Alexandros (July 2017). "Forecasting Stock Prices from the Limit Order Book Using Convolutional Neural Networks". 2017 IEEE 19th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI). Thessaloniki, Greece: IEEE. pp. 7–12. doi:10.1109/CBI.2017.23. ISBN 978-1-5386-3035-8. S2CID 4950757.
- ^ Zhang, Wei (1988). "Shift-invariant pattern recognition neural network and its optical architecture". Proceedings of Annual Conference of the Japan Society of Applied Physics. Archived from the original on 2020-06-23. Retrieved 2020-06-22.
- ^ Zhang, Wei (1990). "Parallel distributed processing model with local space-invariant interconnections and its optical architecture". Applied Optics. 29 (32): 4790–7. Bibcode:1990ApOpt..29.4790Z. doi:10.1364/AO.29.004790. PMID 20577468. Archived from the original on 2017-02-06. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- ^ Mouton, Coenraad; Myburgh, Johannes C.; Davel, Marelie H. (2020). "Stride and Translation Invariance in CNNs". In Gerber, Aurona (ed.). Artificial Intelligence Research. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Vol. 1342. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 267–281. arXiv:2103.10097. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-66151-9_17. ISBN 978-3-030-66151-9. S2CID 232269854. Archived from the original on 2021-06-27. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- Kurtzman, Thomas (August 20, 2019). "Hidden bias in the DUD-E dataset leads to misleading performance of deep learning in structure-based virtual screening". PLOS ONE. 14 (8): e0220113. Bibcode:2019PLoSO..1420113C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220113. PMC 6701836. PMID 31430292.
- ^ Fukushima, K. (2007). "Neocognitron". Scholarpedia. 2 (1): 1717. Bibcode:2007SchpJ...2.1717F. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.1717.
- ^ Hubel, D. H.; Wiesel, T. N. (1968-03-01). "Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex". The Journal of Physiology. 195 (1): 215–243. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008455. ISSN 0022-3751. PMC 1557912. PMID 4966457.
- ^ Fukushima, Kunihiko (1980). "Neocognitron: A Self-organizing Neural Network Model for a Mechanism of Pattern Recognition Unaffected by Shift in Position" (PDF). Biological Cybernetics. 36 (4): 193–202. doi:10.1007/BF00344251. PMID 7370364. S2CID 206775608. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 June 2014. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- ^ Matusugu, Masakazu; Katsuhiko Mori; Yusuke Mitari; Yuji Kaneda (2003). "Subject independent facial expression recognition with robust face detection using a convolutional neural network" (PDF). Neural Networks. 16 (5): 555–559. doi:10.1016/S0893-6080(03)00115-1. PMID 12850007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2013. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- Convolutional Neural Networks Demystified: A Matched Filtering Perspective Based Tutorial https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.11663v3
- "Convolutional Neural Networks (LeNet) – DeepLearning 0.1 documentation". DeepLearning 0.1. LISA Lab. Archived from the original on 28 December 2017. Retrieved 31 August 2013.
- Chollet, François (2017-04-04). "Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions". arXiv:1610.02357 .
- ^ Ciresan, Dan; Ueli Meier; Jonathan Masci; Luca M. Gambardella; Jurgen Schmidhuber (2011). "Flexible, High Performance Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification" (PDF). Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence-Volume Volume Two. 2: 1237–1242. Archived (PDF) from the original on 5 April 2022. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- Krizhevsky, Alex. "ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 April 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- ^ Yamaguchi, Kouichi; Sakamoto, Kenji; Akabane, Toshio; Fujimoto, Yoshiji (November 1990). A Neural Network for Speaker-Independent Isolated Word Recognition. First International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP 90). Kobe, Japan. Archived from the original on 2021-03-07. Retrieved 2019-09-04.
- ^ Ciresan, Dan; Meier, Ueli; Schmidhuber, Jürgen (June 2012). "Multi-column deep neural networks for image classification". 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, NY: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). pp. 3642–3649. arXiv:1202.2745. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.300.3283. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2012.6248110. ISBN 978-1-4673-1226-4. OCLC 812295155. S2CID 2161592.
- Yu, Fisher; Koltun, Vladlen (2016-04-30). "Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions". arXiv:1511.07122 .
- Chen, Liang-Chieh; Papandreou, George; Schroff, Florian; Adam, Hartwig (2017-12-05). "Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation". arXiv:1706.05587 .
- Duta, Ionut Cosmin; Georgescu, Mariana Iuliana; Ionescu, Radu Tudor (2021-08-16). "Contextual Convolutional Neural Networks". arXiv:2108.07387 .
- LeCun, Yann. "LeNet-5, convolutional neural networks". Archived from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2013.
- Zeiler, Matthew D.; Taylor, Graham W.; Fergus, Rob (November 2011). "Adaptive deconvolutional networks for mid and high level feature learning". 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE. pp. 2018–2025. doi:10.1109/iccv.2011.6126474. ISBN 978-1-4577-1102-2.
- Dumoulin, Vincent; Visin, Francesco (2018-01-11), A guide to convolution arithmetic for deep learning, arXiv:1603.07285
- Odena, Augustus; Dumoulin, Vincent; Olah, Chris (2016-10-17). "Deconvolution and Checkerboard Artifacts". Distill. 1 (10): e3. doi:10.23915/distill.00003. ISSN 2476-0757.
- van Dyck, Leonard Elia; Kwitt, Roland; Denzler, Sebastian Jochen; Gruber, Walter Roland (2021). "Comparing Object Recognition in Humans and Deep Convolutional Neural Networks—An Eye Tracking Study". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 15: 750639. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.750639. ISSN 1662-453X. PMC 8526843. PMID 34690686.
- ^ Hubel, DH; Wiesel, TN (October 1959). "Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat's striate cortex". J. Physiol. 148 (3): 574–91. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308. PMC 1363130. PMID 14403679.
- David H. Hubel and Torsten N. Wiesel (2005). Brain and visual perception: the story of a 25-year collaboration. Oxford University Press US. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-19-517618-6. Archived from the original on 2023-10-16. Retrieved 2019-01-18.
- ^ Fukushima, K. (1969). "Visual feature extraction by a multilayered network of analog threshold elements". IEEE Transactions on Systems Science and Cybernetics. 5 (4): 322–333. doi:10.1109/TSSC.1969.300225.
- Ramachandran, Prajit; Barret, Zoph; Quoc, V. Le (October 16, 2017). "Searching for Activation Functions". arXiv:1710.05941 .
- Fukushima, Kunihiko (October 1979). "位置ずれに影響されないパターン認識機構の神経回路のモデル --- ネオコグニトロン ---" [Neural network model for a mechanism of pattern recognition unaffected by shift in position — Neocognitron —]. Trans. IECE (in Japanese). J62-A (10): 658–665.
- Weng, J; Ahuja, N; Huang, TS (1993). "Learning recognition and segmentation of 3-D objects from 2-D images". 1993 (4th) International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE. pp. 121–128. doi:10.1109/ICCV.1993.378228. ISBN 0-8186-3870-2. S2CID 8619176.
- ^ Schmidhuber, Jürgen (2015). "Deep Learning". Scholarpedia. 10 (11): 1527–54. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.76.1541. doi:10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527. PMID 16764513. S2CID 2309950. Archived from the original on 2016-04-19. Retrieved 2019-01-20.
- ^ Waibel, Alex (December 1987). Phoneme Recognition Using Time-Delay Neural Networks (PDF). Meeting of the Institute of Electrical, Information and Communication Engineers (IEICE). Tokyo, Japan.
- Alexander Waibel et al., Phoneme Recognition Using Time-Delay Neural Networks Archived 2021-02-25 at the Wayback Machine IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Volume 37, No. 3, pp. 328. - 339 March 1989.
- LeCun, Yann; Bengio, Yoshua (1995). "Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series". In Arbib, Michael A. (ed.). The handbook of brain theory and neural networks (Second ed.). The MIT press. pp. 276–278. Archived from the original on 2020-07-28. Retrieved 2019-12-03.
- John B. Hampshire and Alexander Waibel, Connectionist Architectures for Multi-Speaker Phoneme Recognition Archived 2022-03-31 at the Wayback Machine, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1990, Morgan Kaufmann.
- Ko, Tom; Peddinti, Vijayaditya; Povey, Daniel; Seltzer, Michael L.; Khudanpur, Sanjeev (March 2018). A Study on Data Augmentation of Reverberant Speech for Robust Speech Recognition (PDF). The 42nd IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP 2017). New Orleans, LA, US. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-07-08. Retrieved 2019-09-04.
- Denker, J S, Gardner, W R, Graf, H. P, Henderson, D, Howard, R E, Hubbard, W, Jackel, L D, BaIrd, H S, and Guyon (1989) Neural network recognizer for hand-written zip code digits Archived 2018-08-04 at the Wayback Machine, AT&T Bell Laboratories
- ^ Y. LeCun, B. Boser, J. S. Denker, D. Henderson, R. E. Howard, W. Hubbard, L. D. Jackel, Backpropagation Applied to Handwritten Zip Code Recognition Archived 2020-01-10 at the Wayback Machine; AT&T Bell Laboratories
- ^ Zhang, Wei (1991). "Image processing of human corneal endothelium based on a learning network". Applied Optics. 30 (29): 4211–7. Bibcode:1991ApOpt..30.4211Z. doi:10.1364/AO.30.004211. PMID 20706526. Archived from the original on 2017-02-06. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- ^ Zhang, Wei (1994). "Computerized detection of clustered microcalcifications in digital mammograms using a shift-invariant artificial neural network". Medical Physics. 21 (4): 517–24. Bibcode:1994MedPh..21..517Z. doi:10.1118/1.597177. PMID 8058017. Archived from the original on 2017-02-06. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- ^ Lecun, Y.; Jackel, L. D.; Bottou, L.; Cortes, C.; Denker, J. S.; Drucker, H.; Guyon, I.; Muller, U. A.; Sackinger, E.; Simard, P.; Vapnik, V. (August 1995). Learning algorithms for classification: A comparison on handwritten digit recognition (PDF). World Scientific. pp. 261–276. doi:10.1142/2808. ISBN 978-981-02-2324-3. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 May 2023.
- Lecun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. (November 1998). "Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition". Proceedings of the IEEE. 86 (11): 2278–2324. doi:10.1109/5.726791.
- Zhang, Wei (1991). "Error Back Propagation with Minimum-Entropy Weights: A Technique for Better Generalization of 2-D Shift-Invariant NNs". Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Archived from the original on 2017-02-06. Retrieved 2016-09-22.
- Daniel Graupe, Ruey Wen Liu, George S Moschytz."Applications of neural networks to medical signal processing Archived 2020-07-28 at the Wayback Machine". In Proc. 27th IEEE Decision and Control Conf., pp. 343–347, 1988.
- Daniel Graupe, Boris Vern, G. Gruener, Aaron Field, and Qiu Huang. "Decomposition of surface EMG signals into single fiber action potentials by means of neural network Archived 2019-09-04 at the Wayback Machine". Proc. IEEE International Symp. on Circuits and Systems, pp. 1008–1011, 1989.
- Qiu Huang, Daniel Graupe, Yi Fang Huang, Ruey Wen Liu."Identification of firing patterns of neuronal signals." In Proc. 28th IEEE Decision and Control Conf., pp. 266–271, 1989. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/70115 Archived 2022-03-31 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Cang, Zixuan; Wei, Guo-Wei (2017-03-31). "TopologyNet: Topology based deep convolutional and multi-task neural networks for biomolecular property predictions". PLOS Computational Biology. 13 (7): e1005690. arXiv:1704.00063. Bibcode:2017PLSCB..13E5690C. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005690. PMID 28749969.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Papamarkou, Theodore; Birdal, Tolga; Bronstein, Michael M; Carlsson, Gunnar E; Curry, Justin; Gao, Yue; Hajij, Mustafa; Kwitt, Roland; Lio, Pietro; Di Lorenzo, Paolo; Maroulas, Vasileios; Miolane, Nina; Nasrin, Farzana; Ramamurthy, Karthikeyan Natesan; Rieck, Bastian; Scardapane, Simone; Schaub, Michael T; Veličković, Petar; Wang, Bei; Wang, Yusu; Wei, Guo-Wei; Zamzmi, Ghada (2024-05-01). Position: Topological Deep Learning is the New Frontier for Relational Learning. Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning. arXiv:2402.08871.
{{cite conference}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Oh, KS; Jung, K (2004). "GPU implementation of neural networks". Pattern Recognition. 37 (6): 1311–1314. Bibcode:2004PatRe..37.1311O. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2004.01.013.
- Dave Steinkraus; Patrice Simard; Ian Buck (2005). "Using GPUs for Machine Learning Algorithms". 12th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR 2005). pp. 1115–1119. doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2005.251. Archived from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Kumar Chellapilla; Sid Puri; Patrice Simard (2006). "High Performance Convolutional Neural Networks for Document Processing". In Lorette, Guy (ed.). Tenth International Workshop on Frontiers in Handwriting Recognition. Suvisoft. Archived from the original on 2020-05-18. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- Hinton, GE; Osindero, S; Teh, YW (Jul 2006). "A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets". Neural Computation. 18 (7): 1527–54. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.76.1541. doi:10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527. PMID 16764513. S2CID 2309950.
- Bengio, Yoshua; Lamblin, Pascal; Popovici, Dan; Larochelle, Hugo (2007). "Greedy Layer-Wise Training of Deep Networks" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems: 153–160. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-06-02. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Ranzato, MarcAurelio; Poultney, Christopher; Chopra, Sumit; LeCun, Yann (2007). "Efficient Learning of Sparse Representations with an Energy-Based Model" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-03-22. Retrieved 2014-06-26.
- Raina, R; Madhavan, A; Ng, Andrew (14 June 2009). "Large-scale deep unsupervised learning using graphics processors" (PDF). Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. ICML '09: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 873–880. doi:10.1145/1553374.1553486. ISBN 9781605585161. S2CID 392458. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 December 2020. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- Ciresan, Dan; Meier, Ueli; Gambardella, Luca; Schmidhuber, Jürgen (2010). "Deep big simple neural nets for handwritten digit recognition". Neural Computation. 22 (12): 3207–3220. arXiv:1003.0358. doi:10.1162/NECO_a_00052. PMID 20858131. S2CID 1918673.
- "IJCNN 2011 Competition result table". OFFICIAL IJCNN2011 COMPETITION. 2010. Archived from the original on 2021-01-17. Retrieved 2019-01-14.
- Schmidhuber, Jürgen (17 March 2017). "History of computer vision contests won by deep CNNs on GPU". Archived from the original on 19 December 2018. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ Krizhevsky, Alex; Sutskever, Ilya; Hinton, Geoffrey E. (2017-05-24). "ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks" (PDF). Communications of the ACM. 60 (6): 84–90. doi:10.1145/3065386. ISSN 0001-0782. S2CID 195908774. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-05-16. Retrieved 2018-12-04.
- Viebke, Andre; Memeti, Suejb; Pllana, Sabri; Abraham, Ajith (2019). "CHAOS: a parallelization scheme for training convolutional neural networks on Intel Xeon Phi". The Journal of Supercomputing. 75 (1): 197–227. arXiv:1702.07908. doi:10.1007/s11227-017-1994-x. S2CID 14135321.
- Viebke, Andre; Pllana, Sabri (2015). "The Potential of the Intel (R) Xeon Phi for Supervised Deep Learning". 2015 IEEE 17th International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications, 2015 IEEE 7th International Symposium on Cyberspace Safety and Security, and 2015 IEEE 12th International Conference on Embedded Software and Systems. IEEE Xplore. IEEE 2015. pp. 758–765. doi:10.1109/HPCC-CSS-ICESS.2015.45. ISBN 978-1-4799-8937-9. S2CID 15411954. Archived from the original on 2023-03-06. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Hinton, Geoffrey (2012). "ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks". NIPS'12: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1. 1: 1097–1105. Archived from the original on 2019-12-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26 – via ACM.
- ^ Azulay, Aharon; Weiss, Yair (2019). "Why do deep convolutional networks generalize so poorly to small image transformations?". Journal of Machine Learning Research. 20 (184): 1–25. ISSN 1533-7928. Archived from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- ^ Géron, Aurélien (2019). Hands-on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow. Sebastopol, CA: O'Reilly Media. ISBN 978-1-492-03264-9., pp. 448
- "CS231n Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition". cs231n.github.io. Archived from the original on 2019-10-23. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- Nirthika, Rajendran; Manivannan, Siyamalan; Ramanan, Amirthalingam; Wang, Ruixuan (2022-04-01). "Pooling in convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: a survey and an empirical study". Neural Computing and Applications. 34 (7): 5321–5347. doi:10.1007/s00521-022-06953-8. ISSN 1433-3058. PMC 8804673. PMID 35125669.
- ^ Scherer, Dominik; Müller, Andreas C.; Behnke, Sven (2010). "Evaluation of Pooling Operations in Convolutional Architectures for Object Recognition" (PDF). Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN), 20th International Conference on. Thessaloniki, Greece: Springer. pp. 92–101. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-04-03. Retrieved 2016-12-28.
- Graham, Benjamin (2014-12-18). "Fractional Max-Pooling". arXiv:1412.6071 .
- Springenberg, Jost Tobias; Dosovitskiy, Alexey; Brox, Thomas; Riedmiller, Martin (2014-12-21). "Striving for Simplicity: The All Convolutional Net". arXiv:1412.6806 .
- Ma, Zhanyu; Chang, Dongliang; Xie, Jiyang; Ding, Yifeng; Wen, Shaoguo; Li, Xiaoxu; Si, Zhongwei; Guo, Jun (2019). "Fine-Grained Vehicle Classification With Channel Max Pooling Modified CNNs". IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology. 68 (4). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE): 3224–3233. doi:10.1109/tvt.2019.2899972. ISSN 0018-9545. S2CID 86674074.
- Zafar, Afia; Aamir, Muhammad; Mohd Nawi, Nazri; Arshad, Ali; Riaz, Saman; Alruban, Abdulrahman; Dutta, Ashit Kumar; Almotairi, Sultan (2022-08-29). "A Comparison of Pooling Methods for Convolutional Neural Networks". Applied Sciences. 12 (17): 8643. doi:10.3390/app12178643. ISSN 2076-3417.
- Gholamalinezhad, Hossein; Khosravi, Hossein (2020-09-16), Pooling Methods in Deep Neural Networks, a Review, arXiv:2009.07485
- Householder, Alston S. (June 1941). "A theory of steady-state activity in nerve-fiber networks: I. Definitions and preliminary lemmas". The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics. 3 (2): 63–69. doi:10.1007/BF02478220. ISSN 0007-4985.
- Romanuke, Vadim (2017). "Appropriate number and allocation of ReLUs in convolutional neural networks". Research Bulletin of NTUU "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute". 1 (1): 69–78. doi:10.20535/1810-0546.2017.1.88156.
- Xavier Glorot; Antoine Bordes; Yoshua Bengio (2011). Deep sparse rectifier neural networks (PDF). AISTATS. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-12-13. Retrieved 2023-04-10.
Rectifier and softplus activation functions. The second one is a smooth version of the first.
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. E. (2012). "Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 1: 1097–1105. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Ribeiro, Antonio H.; Schön, Thomas B. (2021). "How Convolutional Neural Networks Deal with Aliasing". ICASSP 2021 - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). pp. 2755–2759. arXiv:2102.07757. doi:10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414627. ISBN 978-1-7281-7605-5. S2CID 231925012.
- Myburgh, Johannes C.; Mouton, Coenraad; Davel, Marelie H. (2020). "Tracking Translation Invariance in CNNS". In Gerber, Aurona (ed.). Artificial Intelligence Research. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Vol. 1342. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 282–295. arXiv:2104.05997. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-66151-9_18. ISBN 978-3-030-66151-9. S2CID 233219976. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- Richard, Zhang (2019-04-25). Making Convolutional Networks Shift-Invariant Again. OCLC 1106340711.
- Jadeberg, Simonyan, Zisserman, Kavukcuoglu, Max, Karen, Andrew, Koray (2015). "Spatial Transformer Networks" (PDF). Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 28. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-07-25. Retrieved 2021-03-26 – via NIPS.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - E, Sabour, Sara Frosst, Nicholas Hinton, Geoffrey (2017-10-26). Dynamic Routing Between Capsules. OCLC 1106278545.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Matiz, Sergio; Barner, Kenneth E. (2019-06-01). "Inductive conformal predictor for convolutional neural networks: Applications to active learning for image classification". Pattern Recognition. 90: 172–182. Bibcode:2019PatRe..90..172M. doi:10.1016/j.patcog.2019.01.035. ISSN 0031-3203. S2CID 127253432. Archived from the original on 2021-09-29. Retrieved 2021-09-29.
- Wieslander, Håkan; Harrison, Philip J.; Skogberg, Gabriel; Jackson, Sonya; Fridén, Markus; Karlsson, Johan; Spjuth, Ola; Wählby, Carolina (February 2021). "Deep Learning With Conformal Prediction for Hierarchical Analysis of Large-Scale Whole-Slide Tissue Images". IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics. 25 (2): 371–380. doi:10.1109/JBHI.2020.2996300. ISSN 2168-2208. PMID 32750907. S2CID 219885788.
- Srivastava, Nitish; C. Geoffrey Hinton; Alex Krizhevsky; Ilya Sutskever; Ruslan Salakhutdinov (2014). "Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from overfitting" (PDF). Journal of Machine Learning Research. 15 (1): 1929–1958. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-01-19. Retrieved 2015-01-03.
- "Regularization of Neural Networks using DropConnect | ICML 2013 | JMLR W&CP". jmlr.org: 1058–1066. 2013-02-13. Archived from the original on 2017-08-12. Retrieved 2015-12-17.
- Zeiler, Matthew D.; Fergus, Rob (2013-01-15). "Stochastic Pooling for Regularization of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks". arXiv:1301.3557 .
- ^ Platt, John; Steinkraus, Dave; Simard, Patrice Y. (August 2003). "Best Practices for Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to Visual Document Analysis – Microsoft Research". Microsoft Research. Archived from the original on 2017-11-07. Retrieved 2015-12-17.
- Hinton, Geoffrey E.; Srivastava, Nitish; Krizhevsky, Alex; Sutskever, Ilya; Salakhutdinov, Ruslan R. (2012). "Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors". arXiv:1207.0580 .
- "Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting". jmlr.org. Archived from the original on 2016-03-05. Retrieved 2015-12-17.
- Hinton, Geoffrey (1979). "Some demonstrations of the effects of structural descriptions in mental imagery". Cognitive Science. 3 (3): 231–250. doi:10.1016/s0364-0213(79)80008-7.
- Rock, Irvin. "The frame of reference." The legacy of Solomon Asch: Essays in cognition and social psychology (1990): 243–268.
- J. Hinton, Coursera lectures on Neural Networks, 2012, Url: https://www.coursera.org/learn/neural-networks Archived 2016-12-31 at the Wayback Machine
- Dave Gershgorn (18 June 2018). "The inside story of how AI got good enough to dominate Silicon Valley". Quartz. Archived from the original on 12 December 2019. Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- Lawrence, Steve; C. Lee Giles; Ah Chung Tsoi; Andrew D. Back (1997). "Face Recognition: A Convolutional Neural Network Approach". IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks. 8 (1): 98–113. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.92.5813. doi:10.1109/72.554195. PMID 18255614. S2CID 2883848.
- Le Callet, Patrick; Christian Viard-Gaudin; Dominique Barba (2006). "A Convolutional Neural Network Approach for Objective Video Quality Assessment" (PDF). IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks. 17 (5): 1316–1327. doi:10.1109/TNN.2006.879766. PMID 17001990. S2CID 221185563. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 February 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- "ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Competition 2014 (ILSVRC2014)". Archived from the original on 5 February 2016. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- Szegedy, Christian; Liu, Wei; Jia, Yangqing; Sermanet, Pierre; Reed, Scott E.; Anguelov, Dragomir; Erhan, Dumitru; Vanhoucke, Vincent; Rabinovich, Andrew (2015). "Going deeper with convolutions". IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2015, Boston, MA, USA, June 7–12, 2015. IEEE Computer Society. pp. 1–9. arXiv:1409.4842. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594. ISBN 978-1-4673-6964-0.
- Russakovsky, Olga; Deng, Jia; Su, Hao; Krause, Jonathan; Satheesh, Sanjeev; Ma, Sean; Huang, Zhiheng; Karpathy, Andrej; Khosla, Aditya; Bernstein, Michael; Berg, Alexander C.; Fei-Fei, Li (2014). "Image Net Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge". arXiv:1409.0575 .
- "The Face Detection Algorithm Set To Revolutionize Image Search". Technology Review. February 16, 2015. Archived from the original on 20 September 2020. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- Baccouche, Moez; Mamalet, Franck; Wolf, Christian; Garcia, Christophe; Baskurt, Atilla (2011-11-16). "Sequential Deep Learning for Human Action Recognition". In Salah, Albert Ali; Lepri, Bruno (eds.). Human Behavior Unterstanding. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 7065. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. pp. 29–39. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.385.4740. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-25446-8_4. ISBN 978-3-642-25445-1.
- Ji, Shuiwang; Xu, Wei; Yang, Ming; Yu, Kai (2013-01-01). "3D Convolutional Neural Networks for Human Action Recognition". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 35 (1): 221–231. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.169.4046. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59. ISSN 0162-8828. PMID 22392705. S2CID 1923924.
- Huang, Jie; Zhou, Wengang; Zhang, Qilin; Li, Houqiang; Li, Weiping (2018). "Video-based Sign Language Recognition without Temporal Segmentation". arXiv:1801.10111 .
- Karpathy, Andrej, et al. "Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks Archived 2019-08-06 at the Wayback Machine." IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). 2014.
- Simonyan, Karen; Zisserman, Andrew (2014). "Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos". arXiv:1406.2199 . (2014).
- Wang, Le; Duan, Xuhuan; Zhang, Qilin; Niu, Zhenxing; Hua, Gang; Zheng, Nanning (2018-05-22). "Segment-Tube: Spatio-Temporal Action Localization in Untrimmed Videos with Per-Frame Segmentation" (PDF). Sensors. 18 (5): 1657. Bibcode:2018Senso..18.1657W. doi:10.3390/s18051657. ISSN 1424-8220. PMC 5982167. PMID 29789447. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-03-01. Retrieved 2018-09-14.
- Duan, Xuhuan; Wang, Le; Zhai, Changbo; Zheng, Nanning; Zhang, Qilin; Niu, Zhenxing; Hua, Gang (2018). "Joint Spatio-Temporal Action Localization in Untrimmed Videos with Per-Frame Segmentation". 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). pp. 918–922. doi:10.1109/icip.2018.8451692. ISBN 978-1-4799-7061-2.
- Taylor, Graham W.; Fergus, Rob; LeCun, Yann; Bregler, Christoph (2010-01-01). Convolutional Learning of Spatio-temporal Features. Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision: Part VI. ECCV'10. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag. pp. 140–153. ISBN 978-3-642-15566-6. Archived from the original on 2022-03-31. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- Le, Q. V.; Zou, W. Y.; Yeung, S. Y.; Ng, A. Y. (2011-01-01). "Learning hierarchical invariant spatio-temporal features for action recognition with independent subspace analysis". CVPR 2011. CVPR '11. Washington, DC, US: IEEE Computer Society. pp. 3361–3368. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.294.5948. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995496. ISBN 978-1-4577-0394-2. S2CID 6006618.
- Grefenstette, Edward; Blunsom, Phil; de Freitas, Nando; Hermann, Karl Moritz (2014-04-29). "A Deep Architecture for Semantic Parsing". arXiv:1404.7296 .
- Mesnil, Gregoire; Deng, Li; Gao, Jianfeng; He, Xiaodong; Shen, Yelong (April 2014). "Learning Semantic Representations Using Convolutional Neural Networks for Web Search – Microsoft Research". Microsoft Research. Archived from the original on 2017-09-15. Retrieved 2015-12-17.
- Kalchbrenner, Nal; Grefenstette, Edward; Blunsom, Phil (2014-04-08). "A Convolutional Neural Network for Modelling Sentences". arXiv:1404.2188 .
- Kim, Yoon (2014-08-25). "Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification". arXiv:1408.5882 .
- Collobert, Ronan, and Jason Weston. "A unified architecture for natural language processing: Deep neural networks with multitask learning Archived 2019-09-04 at the Wayback Machine."Proceedings of the 25th international conference on Machine learning. ACM, 2008.
- Collobert, Ronan; Weston, Jason; Bottou, Leon; Karlen, Michael; Kavukcuoglu, Koray; Kuksa, Pavel (2011-03-02). "Natural Language Processing (almost) from Scratch". arXiv:1103.0398 .
- Yin, W; Kann, K; Yu, M; Schütze, H (2017-03-02). "Comparative study of CNN and RNN for natural language processing". arXiv:1702.01923 .
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.S.; Koltun, V. (2018). "An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling". arXiv:1803.01271 .
- Gruber, N. (2021). "Detecting dynamics of action in text with a recurrent neural network". Neural Computing and Applications. 33 (12): 15709–15718. doi:10.1007/S00521-021-06190-5. S2CID 236307579.
- Haotian, J.; Zhong, Li; Qianxiao, Li (2021). "Approximation Theory of Convolutional Architectures for Time Series Modelling". International Conference on Machine Learning. arXiv:2107.09355.
- Ren, Hansheng; Xu, Bixiong; Wang, Yujing; Yi, Chao; Huang, Congrui; Kou, Xiaoyu; Xing, Tony; Yang, Mao; Tong, Jie; Zhang, Qi (2019). Time-Series Anomaly Detection Service at Microsoft | Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. arXiv:1906.03821. doi:10.1145/3292500.3330680. S2CID 182952311.
- Wallach, Izhar; Dzamba, Michael; Heifets, Abraham (2015-10-09). "AtomNet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Bioactivity Prediction in Structure-based Drug Discovery". arXiv:1510.02855 .
- Yosinski, Jason; Clune, Jeff; Nguyen, Anh; Fuchs, Thomas; Lipson, Hod (2015-06-22). "Understanding Neural Networks Through Deep Visualization". arXiv:1506.06579 .
- "Toronto startup has a faster way to discover effective medicines". The Globe and Mail. Archived from the original on 2015-10-20. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- "Startup Harnesses Supercomputers to Seek Cures". KQED Future of You. 2015-05-27. Archived from the original on 2018-12-06. Retrieved 2015-11-09.
- Nguyen, Duc; Cang, Zixuan; Wu, Kedi; Wang, Menglun; Cao, Yin; Wei, Guo-Wei (2019-01-15). "Mathematical deep learning for pose and binding affinity prediction and ranking in D3R Grand Challenges". Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design. 33: 71–82. arXiv:1804.10647. doi:10.1007/s10822-018-0146-6. PMID 30116918.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Nguyen, Duc; Gao, Kaifu; Wang, Menglun; Wei, Guo-Wei (2020). "MathDL: mathematical deep learning for D3R Grand Challenge 4". Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design. 34: 131–147. arXiv:1909.07784. doi:10.1007/s10822-019-00237-5. PMID 31734815.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - Chellapilla, K; Fogel, DB (1999). "Evolving neural networks to play checkers without relying on expert knowledge". IEEE Trans Neural Netw. 10 (6): 1382–91. doi:10.1109/72.809083. PMID 18252639.
- Chellapilla, K.; Fogel, D.B. (2001). "Evolving an expert checkers playing program without using human expertise". IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation. 5 (4): 422–428. doi:10.1109/4235.942536.
- Fogel, David (2001). Blondie24: Playing at the Edge of AI. San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN 978-1558607835.
- Clark, Christopher; Storkey, Amos (2014). "Teaching Deep Convolutional Neural Networks to Play Go". arXiv:1412.3409 .
- Maddison, Chris J.; Huang, Aja; Sutskever, Ilya; Silver, David (2014). "Move Evaluation in Go Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks". arXiv:1412.6564 .
- "AlphaGo – Google DeepMind". Archived from the original on 30 January 2016. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- Bai, Shaojie; Kolter, J. Zico; Koltun, Vladlen (2018-04-19). "An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling". arXiv:1803.01271 .
- Yu, Fisher; Koltun, Vladlen (2016-04-30). "Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions". arXiv:1511.07122 .
- Borovykh, Anastasia; Bohte, Sander; Oosterlee, Cornelis W. (2018-09-17). "Conditional Time Series Forecasting with Convolutional Neural Networks". arXiv:1703.04691 .
- Mittelman, Roni (2015-08-03). "Time-series modeling with undecimated fully convolutional neural networks". arXiv:1508.00317 .
- Chen, Yitian; Kang, Yanfei; Chen, Yixiong; Wang, Zizhuo (2019-06-11). "Probabilistic Forecasting with Temporal Convolutional Neural Network". arXiv:1906.04397 .
- Zhao, Bendong; Lu, Huanzhang; Chen, Shangfeng; Liu, Junliang; Wu, Dongya (2017-02-01). "Convolutional neural networks for time series classi". Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics. 28 (1): 162–169. doi:10.21629/JSEE.2017.01.18.
- Petneházi, Gábor (2019-08-21). "QCNN: Quantile Convolutional Neural Network". arXiv:1908.07978 .
- Hubert Mara (2019-06-07), HeiCuBeDa Hilprecht – Heidelberg Cuneiform Benchmark Dataset for the Hilprecht Collection (in German), heiDATA – institutional repository for research data of Heidelberg University, doi:10.11588/data/IE8CCN
- Hubert Mara and Bartosz Bogacz (2019), "Breaking the Code on Broken Tablets: The Learning Challenge for Annotated Cuneiform Script in Normalized 2D and 3D Datasets", Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR) (in German), Sydney, Australien, pp. 148–153, doi:10.1109/ICDAR.2019.00032, ISBN 978-1-7281-3014-9, S2CID 211026941
- Bogacz, Bartosz; Mara, Hubert (2020), "Period Classification of 3D Cuneiform Tablets with Geometric Neural Networks", Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Frontiers of Handwriting Recognition (ICFHR), Dortmund, Germany
- Presentation of the ICFHR paper on Period Classification of 3D Cuneiform Tablets with Geometric Neural Networks on YouTube
- Durjoy Sen Maitra; Ujjwal Bhattacharya; S.K. Parui, "CNN based common approach to handwritten character recognition of multiple scripts" Archived 2023-10-16 at the Wayback Machine, in Document Analysis and Recognition (ICDAR), 2015 13th International Conference on, vol., no., pp.1021–1025, 23–26 Aug. 2015
- "NIPS 2017". Interpretable ML Symposium. 2017-10-20. Archived from the original on 2019-09-07. Retrieved 2018-09-12.
- Zang, Jinliang; Wang, Le; Liu, Ziyi; Zhang, Qilin; Hua, Gang; Zheng, Nanning (2018). "Attention-Based Temporal Weighted Convolutional Neural Network for Action Recognition". Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology. Vol. 519. Cham: Springer International Publishing. pp. 97–108. arXiv:1803.07179. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-92007-8_9. ISBN 978-3-319-92006-1. ISSN 1868-4238. S2CID 4058889.
- Wang, Le; Zang, Jinliang; Zhang, Qilin; Niu, Zhenxing; Hua, Gang; Zheng, Nanning (2018-06-21). "Action Recognition by an Attention-Aware Temporal Weighted Convolutional Neural Network" (PDF). Sensors. 18 (7): 1979. Bibcode:2018Senso..18.1979W. doi:10.3390/s18071979. ISSN 1424-8220. PMC 6069475. PMID 29933555. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-09-13. Retrieved 2018-09-14.
- Ong, Hao Yi; Chavez, Kevin; Hong, Augustus (2015-08-18). "Distributed Deep Q-Learning". arXiv:1508.04186v2 .
- Mnih, Volodymyr; et al. (2015). "Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning". Nature. 518 (7540): 529–533. Bibcode:2015Natur.518..529M. doi:10.1038/nature14236. PMID 25719670. S2CID 205242740.
- Sun, R.; Sessions, C. (June 2000). "Self-segmentation of sequences: automatic formation of hierarchies of sequential behaviors". IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part B: Cybernetics. 30 (3): 403–418. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.11.226. doi:10.1109/3477.846230. ISSN 1083-4419. PMID 18252373.
- "Convolutional Deep Belief Networks on CIFAR-10" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-30. Retrieved 2017-08-18.
- Lee, Honglak; Grosse, Roger; Ranganath, Rajesh; Ng, Andrew Y. (1 January 2009). "Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations". Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning. ACM. pp. 609–616. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.149.6800. doi:10.1145/1553374.1553453. ISBN 9781605585161. S2CID 12008458.
- Behnke, Sven (2003). Hierarchical Neural Networks for Image Interpretation (PDF). Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 2766. Springer. doi:10.1007/b11963. ISBN 978-3-540-40722-5. S2CID 1304548. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-10. Retrieved 2016-12-28.
- Cade Metz (May 18, 2016). "Google Built Its Very Own Chips to Power Its AI Bots". Wired. Archived from the original on January 13, 2018. Retrieved March 6, 2017.
External links
- CS231n: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition — Andrej Karpathy's Stanford computer science course on CNNs in computer vision
- vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic: A technical report on convolution arithmetic in the context of deep learning. Animations of convolutions.
 kernels.
kernels.
 .
.
 a stride S means that the filter is translated S units at a time per output. In practice,
a stride S means that the filter is translated S units at a time per output. In practice,  is rare. A greater stride means smaller overlap of receptive fields and smaller spatial dimensions of the output volume.
is rare. A greater stride means smaller overlap of receptive fields and smaller spatial dimensions of the output volume. , the kernel field size
, the kernel field size  of the convolutional layer neurons, the stride
of the convolutional layer neurons, the stride  , and the amount of zero padding
, and the amount of zero padding  on the border. The number of neurons that "fit" in a given volume is then:
on the border. The number of neurons that "fit" in a given volume is then:

 when the stride is
when the stride is  ensures that the input volume and output volume will have the same size spatially. However, it is not always completely necessary to use all of the neurons of the previous layer. For example, a neural network designer may decide to use just a portion of padding.
ensures that the input volume and output volume will have the same size spatially. However, it is not always completely necessary to use all of the neurons of the previous layer. For example, a neural network designer may decide to use just a portion of padding.
 In this case, every
In this case, every  . It effectively removes negative values from an activation map by setting them to zero. It introduces
. It effectively removes negative values from an activation map by setting them to zero. It introduces  ,
,  , and the
, and the  . ReLU is often preferred to other functions because it trains the neural network several times faster without a significant penalty to
. ReLU is often preferred to other functions because it trains the neural network several times faster without a significant penalty to  .
.  .
.
 or kept with probability
or kept with probability  , so that a reduced network is left; incoming and outgoing edges to a dropped-out node are also removed. Only the reduced network is trained on the data in that stage. The removed nodes are then reinserted into the network with their original weights.
, so that a reduced network is left; incoming and outgoing edges to a dropped-out node are also removed. Only the reduced network is trained on the data in that stage. The removed nodes are then reinserted into the network with their original weights.
 dropped-out networks; unfortunately this is unfeasible for large values of
dropped-out networks; unfortunately this is unfeasible for large values of  . However, we can find an approximation by using the full network with each node's output weighted by a factor of
. However, we can find an approximation by using the full network with each node's output weighted by a factor of  of every neuron to satisfy
of every neuron to satisfy  . Typical values of
. Typical values of  are order of 3–4. Some papers report improvements when using this form of regularization.
are order of 3–4. Some papers report improvements when using this form of regularization.