| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Basic Interoperable Scrambling System" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (June 2007) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Basic Interoperable Scrambling System, usually known as BISS, is a satellite signal scrambling system developed by the European Broadcasting Union, Eurovision Media Services and a consortium of hardware manufacturers.

Prior to its development, "ad hoc" or "occasional use" satellite news feeds were transmitted either using proprietary encryption methods (e.g. RAS, or PowerVu), or without any encryption. Unencrypted satellite feeds allowed anyone with the correct equipment to view the program material.
Proprietary encryption methods were determined by encoder manufacturers, and placed major compatibility limitations on the type of satellite receiver (IRD) that could be used for each feed. BISS was an attempt to create an "open platform" encryption system, which could be used across a range of manufacturers equipment.
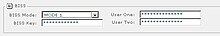
There are mainly two different types of BISS encryption used:
- BISS-1 transmissions are protected by a 12 digit hexadecimal "session key" that is agreed by the transmitting and receiving parties prior to transmission. The key is entered into both the encoder and decoder, this key then forms part of the encryption of the digital TV signal and any receiver with BISS-support with the correct key will decrypt the signal.
- BISS-E (E for encrypted) is a variation where the decoder has stored one secret BISS-key entered by for example a rights holder. This is unknown to the user of the decoder. The user is then sent a 16-digit hexadecimal code, which is entered as a "session key". This session key is then mathematically combined internally to calculate a BISS-1 key that can decrypt the signal.
Only a decoder with the correct secret BISS-key will be able to decrypt a BISS-E feed. This gives the rights holder control as to exactly which decoder can be used to decrypt/decode a specific feed. Any BISS-E encrypted feed will have a corresponding BISS-1 key that will unlock it.
BISS-E is amongst others used by EBU to protect UEFA Champions League, NBC in the United States for NBC O&O and Affiliated station and other high-profile satellite feeds.
External links
| Broadcast encryption and digital rights management | |
|---|---|
| Conditional access | |
| DVB | |
| Smart cards and encryption | |
| Digital video disc |
|
| DRM | |
| Data security | |
| Analogue broadcast encoding | |
| See also free-to-view and pay television | |