For the river in Canterbury region of New Zealand, see Ashley River / Rakahuri. For other uses, see Ashley River (disambiguation).
| Ashley River | |
|---|---|
 Ashley River, as seen from Brittlebank Park Ashley River, as seen from Brittlebank Park | |
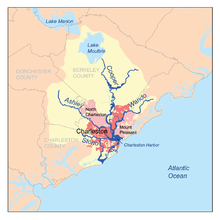 Map of the Charleston Harbor watershed showing Ashley River Map of the Charleston Harbor watershed showing Ashley River | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Dorchester County |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | |
| • location | Charleston Harbor, Atlantic Ocean |
| • coordinates | 32°45′46″N 79°55′44″W / 32.76278°N 79.92889°W / 32.76278; -79.92889 |
The Ashley River is a blackwater and tidal river in South Carolina, rising from the Wassamassaw and Great Cypress Swamps in western Berkeley County. It consolidates its main channel about five miles west of Summerville, widening into a tidal estuary just south of Fort Dorchester. The river then flows for approximately 17 mi (27 km) along the historical banks of the City of North Charleston before reaching peninsular Charleston. The much wider Ashley joins the Cooper River off the Battery in Charleston to form Charleston Harbor before discharging into the Atlantic Ocean. As of 2012 the land around the Ashley River (or in Ashley Barony, as the original land grant was called) is mostly undeveloped.
The river was named for Anthony Ashley Cooper, 1st Earl of Shaftesbury and chief Lord Proprietor of the Carolina Colony by explorer Robert Sandford. In 1675 Cooper was granted 12,000 acres (4,900 ha) of land along the river after a permanent settlement was made at Albemarle Point in 1670. This settlement was the “first permanent European settlement” in South Carolina and today Albemarle Point is known as Charles Towne Landing. The settlement would be moved to its current peninsular location across the river ten years later and is well known as Charleston.
The land closest to the river was developed by plantation owners throughout the eighteenth century. During the Revolutionary War the British occupied the plantations from 1780 to 1782. The major crops grown along the Ashley River included rice, indigo, and cotton. After the Civil War much of the region began to be used predominantly for hunting and tourism.
The Ashley River area contains 26 separate sites listed in the National Register of Historic Places with 22 mi (35 km) being designated a State Scenic River, extending from Sland's Bridge (US Highway 17-A) near Summerville to the Mark Clark expressway (I-526) bridge in Charleston. Within this segment, a visitor can experience a blackwater swamp, the tides of the Atlantic, and much of the history of South Carolina. Some of the sites include Drayton Hall, Middleton Place, Magnolia Plantation, and the Colonial Dorchester State Historic Site. The River ranges from 6 to 8 feet in depth.
References
- "South Carolina Department of Natural Resources - Ashley Scenic River". Archived from the original on April 19, 2012. Retrieved May 8, 2012.
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Ashley River
- Robert Sandford, “A Relation of a Voyage on the Coast of the Province of Carolina, 1666,” in Salley, AS, ed , 1967, “Narratives of Early Carolina, 1650-1708, Vol. 4 of “Original Narratives of Early American History,” Edited by J. Franklin Jameson (New York: Barnes and Noble) p. 108, found in Lockhart, Matthew A. “Quitting More Than Port Royal: A Political Interpretation of the Siting and Development of Charles Town, South Carolina, 1660-1680”, Southeastern Geographer, Vol 43, N 2, Nov 2003, UNC Press
- "The History of the Ashley River Corridor". Retrieved October 10, 2014.
- "Ashley Scenic River". Retrieved May 28, 2021.