This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
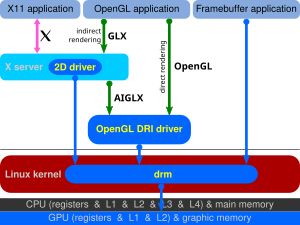
Accelerated Indirect GLX ("AIGLX") is an open source project founded by Red Hat and the Fedora community, led by Kristian Høgsberg, to allow accelerated indirect GLX rendering capabilities to the X.Org Server and DRI drivers. This allows remote X clients to get fully hardware accelerated rendering over the GLX protocol; coincidentally, this development was required for OpenGL compositing window managers to function with hardware acceleration.
Rationale
There are two ways in which a windowing system can allow an OpenGL implementation to talk to the graphics card.
The first is to specify the OpenGL command stream in a portable network-neutral manner using a client/server implementation similar to the X11 drawing routines. This method, used by AIGLX, is indirect in that the drawing commands are sent to the X server and then the X server sends them along to the graphics card.
The second way, which is at the base of Xgl, is to open a window and then allow the OpenGL library to send commands directly to the graphics card.
Accelerating the indirect OpenGL path is orthogonal to how the X server itself is implemented, but it has the side effect of allowing the OpenGL command stream to be more easily captured and redirected to a texture. This allows Compiz and other compositing window managers to be built on top of a traditional X server with a small extension rather than requiring a full Xgl server. This is also an advantage over DRI which bypasses the compositing engine even while providing hardware acceleration.
Deployment
The AIGLX project was merged into X.Org and has been available with X.Org 7.1.
AIGLX needed driver support to run. Specifically, it depended on the texture_from_pixmap OpenGL extension.
Relationship to Xgl
Although the AIGLX project has features similar to Xgl, it was not intended to be a competing product. According to the Fedora Project Wiki, the project was founded in part because Xgl was written during its final stages "behind closed doors." This lack of peer-review drew criticism claiming to be the root of flaws in the software. An agreement was reached to share the source code between the two projects under the premise that doing so would prevent compatibility conflicts. Xgl was removed from the X Server on June 12, 2008.
History
-
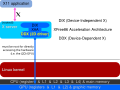 2D drivers inside of the X server
2D drivers inside of the X server
-
 Indirect rendering over GLX, using Utah GLX
Indirect rendering over GLX, using Utah GLX
-
 early Direct Rendering Infrastructure
early Direct Rendering Infrastructure
-
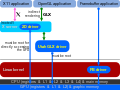
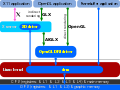 Finally all access goes through the Direct Rendering Manager
Finally all access goes through the Direct Rendering Manager
-
 In Linux kernel 3.12 render nodes were merged and the KMS was split off. Wayland implements direct rendering over EGL
In Linux kernel 3.12 render nodes were merged and the KMS was split off. Wayland implements direct rendering over EGL
See also
- CGL – the equivalent Mac OS X interface to OpenGL
- EGL – the equivalent Wayland interface to OpenGL ES and OpenVG (Wayland is also being mainly developed by Kristian Høgsberg)
- GLX – the equivalent X11 interface to OpenGL
References
- "Interview: Kristian Høgsberg". 2007-02-06.
Learn from AIGLX creator Kristian Høgsberg....
- XGL Version Info
External links
- Fedora Project Wiki AIGLX Article — contains early demonstration videos in the free Ogg Theora format.
| X Window System | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture |  | ||||||||||||||
| Extensions | |||||||||||||||
| Components and notable implementations |
| ||||||||||||||
| Standards | |||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||