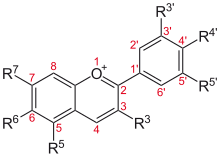

The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides (3-deoxyanthocyanins or 3-DA) are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol.
3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are yellow anthocyanidins that can be found primarily in ferns and mosses (Timberlake and Bridle, 1975, 1980), in Sorghum bicolor and in purple corn (Nakatani et al., 1979) (maíz morado).
3-Deoxyanthocyanidins are reported to be stable to color loss due to change in pH. Synthetic 3-deoxyanthocyanidins with a carboxylate group at carbon 4 show unusually stable colorant properties at pH 7.
In Sorghum, the SbF3'H2 gene, encoding a flavonoid 3'-hydroxylase, seems to be expressed in pathogen-specific 3-deoxyanthocyanidin phytoalexins synthesis, for example in Sorghum-Colletotrichum interactions.
This category include:
References
- ^ Sweeny, James G.; Iacobucci, Guillermo A. (May 1, 1983). "Effect of substitution on the stability of 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in aqueous solutions". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 31 (3): 531–533. doi:10.1021/jf00117a017.
- "Inclusions of flavonoid 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in Sorghum bicolor self-organize into spherical structures". Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology. 65 (4). Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved June 25, 2017.
- Awika, Joseph M. (January 1, 2008). "Behavior of 3-deoxyanthocyanidins in the presence of phenolic copigments". Food Research International. 41 (5): 532–538. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2008.03.002.
- Shih, Chun-Hat; Chu, Ivan K.; Yip, Wing Kin; Lo, Clive (October 1, 2006). "Differential Expression of Two Flavonoid 3′-Hydroxylase cDNAs Involved in Biosynthesis of Anthocyanin Pigments and 3-Deoxyanthocyanidin Phytoalexins in Sorghum". Plant and Cell Physiology. 47 (10): 1412–1419. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcl003. PMID 16943219.
- "Biosynthesis and regulation of 3-deoxyanthocyanidin phytoalexins induced during Sorghum-Colletotrichum interaction: Heterologous expression in maize. Chopra, Surinder Gaffoor, Iffa Ibraheem, Farag". aspb.org. Archived from the original on July 25, 2011. Retrieved June 25, 2017.