This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Lfstevens (talk | contribs) at 02:42, 9 August 2015 (→Sunspots: slight reorg). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 02:42, 9 August 2015 by Lfstevens (talk | contribs) (→Sunspots: slight reorg)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff)
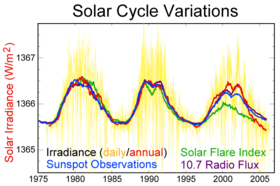
Solar variation is the change in the amount of radiation emitted by the Sun and in its spectral distribution over years to millennia. These variations have periodic components, the main one being the approximately 11-year solar cycle (or sunspot cycle). The changes also have aperiodic fluctuations. In recent decades, solar activity has been measured by satellites, while before it was estimated using sunspot counts, and prior to that using 'proxy' variables. Scientists studying climate change are interested in understanding the effects of variations in the total and spectral solar irradiance on Earth and its climate.
The amount of total solar irradiance received at the outer limits of Earth's atmosphere averages 1366 W/m. Variations in total solar irradiance were too small to detect with technology available before the satellite era, although the small fraction in ultra-violet light has recently been found to vary significantly over the course of a solar cycle. Total solar output is now measured to vary (over the last three 11-year sunspot cycles) by approximately 0.1%, or about 1.3 Watts per square meter (W/m) peak-to-trough from solar maximum to solar minimum during the 11-year sunspot cycle. No direct measurements of the longer-term variation are available, while proxy measure interpretations of variations differ. The intensity of solar radiation reaching Earth has been relatively constant through the last 2000 years, with variations estimated at around 0.1–0.2%. Solar variation, together with volcanic activity have been hypothesized to have contributed to climate change, for example during the Maunder Minimum. Changes in solar brightness are considered to be too weak to explain recent climate change.
History of study into solar variations
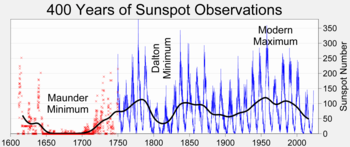
The longest recorded aspect of solar variations are changes in sunspots. The first record of sunspots dates to around 800 BC in China and the oldest surviving drawing of a sunspot dates to 1128. In 1610, astronomers began using telescopes to observe sunspots. Initial study focused on their nature and behavior. Although the physical aspects of sunspots were not identified until the 20th century, observations continued. Study was hampered during the 17th century due to the low number of sunspots during what is now recognized as an extended period of low solar activity, known as the Maunder Minimum. By the 19th century, then-sufficient sunspot records allowed researchers to infer periodic cycles in sunspot activity. In 1845, Henry and Alexander observed the Sun with a thermopile and determined that sunspots emitted less radiation than surrounding areas. The emission of higher than average amounts of radiation later were observed from the solar faculae.
Around 1900, researchers began to explore connections between solar variations and Earth's weather. Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) assigned Abbot and his team to detect changes in the radiation of the Sun. They began by inventing instruments to measure solar radiation. Later, when Abbot was SAO head, they established a solar station at Calama, Chile to complement its data from Mount Wilson Observatory. He detected 27 harmonic periods within the 273-month Hale cycles, including 7, 13, and 39-month patterns. He looked for connections to weather by means such as matching opposing solar trends during a month to opposing urban temperature and precipitation trends. With the advent of dendrochronology, scientists such as Glock attempted to connect variation in tree growth to periodic solar variations and infer long-term secular variability in the solar constant from similar variations in millennial-scale chronologies.
Statistical studies that correlate weather and climate with solar activity date back at least to 1801, when Herschel noted an apparent connection between wheat prices and sunspot records. They now often involve high-density global datasets compiled from surface networks and weather satellite observations and/or the forcing of climate models with synthetic or observed solar variability to investigate the detailed processes by which the effects of solar variations propagate through the Earth's climate system.
Irradiance measurement
Direct irradiance measurements have been available during the last three cycles and are a composite of multiple observing satellites. However, the correlation between irradiance measurements and other proxies of solar activity make it reasonable to estimate solar activity. Most important among these proxies is the record of sunspot observations that has been recorded since ~1610. Solar radio emissions at 10.7 cm wavelength provide another proxy that can be measured from the ground, since the atmosphere is transparent to such radiation.
Total solar irradiance has been claimed to vary in ways that are not predicted by sunspot changes or radio emissions. These shifts may be the result of satellite calibration problems. A long-term trend may exist in solar irradiance.
Sunspots
Main article: Sunspot
Sunspots are relatively dark areas on the radiating 'surface' (photosphere) of the Sun where intense magnetic activity inhibits convection and cools the photosphere. Faculae are slightly brighter areas that form around sunspot groups as the flow of energy to the photosphere is re-established and both the normal flow and the sunspot-blocked energy elevate the radiating 'surface' temperature. Scientists have speculated on possible relationships between sunspots and solar luminosity since the historical sunspot area record began in the 17th century. Decreases in luminosity caused by sunspots (generally < - 0.3%) is correlated with increases (generally < + 0.05%) caused both by faculae that are associated with active regions as well as the magnetically active 'bright network'.
Modulation of the solar luminosity by magnetically active regions was confirmed by satellite measurements of total solar irradiance (TSI) by the ACRIM1 experiment on the Solar Maximum Mission (launched in 1980). The modulations were later confirmed in the results of the ERB experiment launched on the Nimbus 7 satellite in 1978. Satellite observation was continued by ACRIM-3 and other satellites. Sunspots in magnetically active regions are cooler and 'darker' than the average photosphere and cause temporary decreases in TSI of as much as 0.3%. Faculae in magnetically active regions are hotter and 'brighter' than the average photosphere and cause temporary increases in TSI.
The net effect during periods of enhanced solar magnetic activity is increased radiant solar output because faculae are larger and persist longer than sunspots. Conversely, periods of lower solar magnetic activity and fewer sunspots (such as the Maunder Minimum) may correlate with times of lower terrestrial irradiance from the sun.
Data mostly from the Michelson Doppler Imager instrument on SOHO, show changes in solar diameter to be about 0.001%, much less than the effect of magnetic activity changes.
Various studies used sunspot number to estimate solar output and calibrated ground instruments by comparison with high-altitude and orbital instruments. Others combined later readings and factors to adjust historical data. Other proxy data – such as the abundance of cosmogenic isotopes – have been used to infer solar magnetic activity and thus likely brightness. Sunspot activity has been measured using the Wolf number for about 300 years. This index (also known as the Zürich number) uses both the number of sunspots and the number of groups of sunspots to compensate for variations in measurement. A 2003 study found that sunspots had been more frequent since the 1940s than in the previous 1150 years.
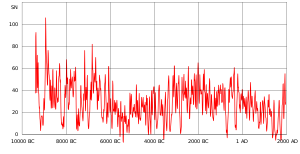
Solar cycles
Main article: Solar cycleThe sun undergoes various quasi-periodic changes. Only the 11 and closely related 22-year cycles are clear in the observations.
- 11 years: Most obvious is a gradual increase and more rapid decrease of the number of sunspots over a period ranging from 9 to 12 years, called the Schwabe cycle, named after Heinrich Schwabe. Differential rotation of the sun's convection zone (as a function of latitude) consolidates magnetic flux tubes, increases their magnetic field strength and makes them buoyant (see Babcock Model). As they rise through the solar atmosphere they partially block the convective flow of energy, cooling their region of the photosphere, causing 'sunspots'. The Sun's apparent surface, the photosphere, radiates more actively when there are more sunspots. Satellite monitoring of solar luminosity since 1980 has shown there is a direct relationship between the Schwabe cycle and luminosity with a solar cycle peak-to-peak amplitude of about 0.1%. Luminosity has also been found to decrease by as much as 0.3% on a 10-day timescale when large groups of sunspots rotate across the Earth's view and increase by as much as 0.05% for up to 6 months due to faculae associated with the large sunspot groups.
- 22 years: During the Hale cycle, named after George Ellery Hale, the magnetic field of the Sun reverses during each Schwabe cycle, so the magnetic poles return to the same state after two reversals. The two halves of the 22-year cycle are not identical, typically with alternating cycle showing higher sunspot counts (the "Gnevyshev–Ohl Rule.")
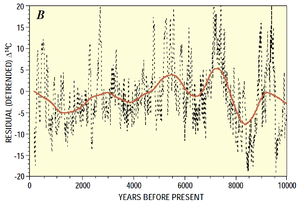
Hypothesized cycles
Periodicity of solar activity with periods longer than the sunspot cycle has been proposed, including:
- 87 years (70–100 years): Gleissberg cycle, named after Wolfgang Gleißberg, is thought to be an amplitude modulation of the Schwabe Cycle,
- 210 years: Suess cycle (a.k.a. "de Vries cycle"). Braun, et al., (2005). (Hathaway points out that while the proposed Seuss cycle is recorded from radiocarbon studies, there is "little evidence of the Suess Cycle" in the 400-year sunspot record.)
- 2,300 years: Hallstatt cycle
- 6000 years
Other patterns have been detected:
- In carbon-14: 105, 131, 232, 385, 504, 805, 2,241 years.
- During the Upper Permian 240 million years ago, mineral layers created in the Castile Formation show cycles of 2,500 years.
Predictions based on patterns
- Perry and Hsu (2000) proposed a simple model based on emulating harmonics by multiplying the basic 11-year cycle by powers of 2, which produced results similar to Holocene behavior. Extrapolation suggests a gradual cooling during the next few centuries with intermittent minor warmups and a return to near Little Ice Age conditions within the next 500 years. This cool period then may be followed approximately 1,500 years from now by a return to altithermal conditions similar to the previous Holocene Maximum.
- The Gleisberg cycle's characteristics indicate that the next solar cycle should have a maximum smoothed sunspot number of about 145±30 in 2010 while the following cycle should have a maximum of about 70±30 in 2023.

This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (July 2015) - Based on carbon-14 data, Damon and Sonett suggest variations are quasi periodic, and propose medium and short-term variations of periods 208 and 88 years; as well as suggesting a 2300-yr period in radiocarbon modulates the 208-year period. They also propose that these cycles modulate climate.
Solar irradiance of Earth and its surface

Solar irradiance and insolation are measures of the amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth. The equipment used might measure optical brightness, total radiation, or radiation in various frequencies. Historical estimates use various measurements and proxies.
There are two common meanings for solar irradiance:
- the radiation reaching the upper atmosphere
- the radiation reaching some point within the atmosphere, including the surface.
Various gases within the atmosphere absorb some solar radiation at different wavelengths, and clouds and dust also affect it. Measurements above the atmosphere are needed to determine variations in solar output, to avoid the confounding effects of changes within the atmosphere. There is some evidence that sunshine at the Earth's surface has been decreasing in the last 50 years (see global dimming) possibly caused by increased atmospheric pollution, whilst over roughly the same timespan solar output has been nearly constant.
Milankovitch cycle variations

Some variations in insolation are not due to solar changes but rather due to the Earth moving closer or further from the Sun, or changes in the latitudinal distribution of radiation. These orbital changes or Milankovitch cycles have caused variations of as much as 25% (locally; global average changes are much smaller) in solar insolation over long periods. The most recent significant event was an axial tilt of 24° during boreal summer at near the time of the Holocene climatic optimum.
Changes in solar interactions with Earth
 1979–2009: Over the past 3 decades, terrestrial temperature has not correlated with sunspot trends. The top plot is of sunspots, while below is the global atmospheric temperature trend. El Chichón and Pinatubo were volcanoes, while El Niño is part of ocean variability. The effect of greenhouse gas emissions is on top of those fluctuations.Multiple factors have affected terrestrial climate change, including internal forcings and human influences such as greenhouse gas emissions and land use change on top of any effects of solar variability.
1979–2009: Over the past 3 decades, terrestrial temperature has not correlated with sunspot trends. The top plot is of sunspots, while below is the global atmospheric temperature trend. El Chichón and Pinatubo were volcanoes, while El Niño is part of ocean variability. The effect of greenhouse gas emissions is on top of those fluctuations.Multiple factors have affected terrestrial climate change, including internal forcings and human influences such as greenhouse gas emissions and land use change on top of any effects of solar variability.
Several hypotheses describe how solar variations may affect Earth. Some variations, such as changes in the size of the Sun, are only of interest in the field of astronomy.
Total irradiance
- Total solar irradiance (TSI) changes slowly on decadal and longer timescales.
- The variation during recent solar magnetic activity cycles is about 0.1% (peak-to-peak).
- Variations corresponding to solar changes with periods of 9–13, 18–25, and >100 years have been detected in sea-surface temperatures.
- In contrast to older reconstructions, most recent TSI reconstructions point to an increase of only about 0.05% to 0.1% between Maunder Minimum and the present.
- Different TSI composite reconstructions of satellite observations show different trends since 1980; see the global warming section below.
Ultraviolet irradiance
- Ultraviolet irradiance (EUV) varies by approximately 1.5 percent from solar maxima to minima, for 200 to 300 nm UV.
- Energy changes in the UV wavelengths involved in production and loss of ozone have atmospheric effects.
- The 30 hPa atmospheric pressure level has changed height in phase with solar activity during solar cycles 20-23.
- UV irradiance increase causes higher ozone production, leading to stratospheric heating and to poleward displacements in the stratospheric and tropospheric wind systems.
- A proxy study estimated that UV has increased by 3.0% since the Maunder Minimum.
Solar wind and magnetic flux
- A more active solar wind and stronger magnetic field reduces the flux of galactic cosmic rays striking the Earth's atmosphere.
- Variations affect heliosphere size and intensity the volume larger than the Solar System filled with solar wind particles.
- Cosmogenic production of C and Cl show changes tied to solar activity. The production rate of Be and TSI over the past millennium is more complicated because of possible climate influence of Be deposition rate, causing errors in the inferred Be formation rate.
- Cosmic ray ionization in the upper atmosphere does change, but significant effects are not obvious.
- As the solar coronal-source magnetic flux doubled during the past century, the cosmic-ray flux decreased by about 15%.
- The Sun's total magnetic flux rose by a factor of 1.41 from 1964–1996 and by a factor of 2.3 since 1901.
Cosmic ray-clouds claim
Various speculations about cosmic rays include:
- Tinsley and Yu claimed that changes in ionization affect the aerosol abundance that serves as the condensation nucleus for cloud formation. During periods of low solar activity (during solar minima), more cosmic rays reach Earth, potentially creating ultra-small aerosol particles as precursors to cloud condensation nuclei. Clouds formed from greater amounts of condensation nuclei are brighter, longer lived and likely to produce less precipitation.
- A change in cosmic rays could cause an increase in certain types of clouds, affecting Earth's albedo.
- Several percent variation in cosmic rays and in tropospheric ionization occurs when the interplanetary magnetic field changes over the solar cycle, greater than the typically 0.1% variation in total solar irradiance.
- Particularly at high latitudes, with less shielding from Earth's magnetic field, cosmic ray variation may impact terrestrial low altitude cloud cover (unlike a lack of correlation with high altitude clouds), partially influenced by the solar-driven interplanetary magnetic field (as well as passage through the galactic arms over longer timeframes).
Three subsequent papers claimed that production of clouds via cosmic rays could not be explained by nucleation particles. Accelerator results failed to produce sufficient, and sufficiently large, particles to result in cloud formation; this includes observations after a major solar storm. Observations after Chernobyl do not show any induced clouds.
A 2002 paper immediately refuted Svensmark's hypothesis. Multiple 2013 papers, and a 2015 paper could find no correlation between cosmic ray levels and global temperature on the multidecadal timescale of recent warming, as cosmic ray levels do not show a corresponding trend, on multidecadal or longer timescales.
The claim that recent warming is due to cosmic rays is not considered credible.
Other variation effects
Interaction of solar particles, the solar magnetic field and the Earth's magnetic field cause variations in the particle and electromagnetic fields at the planetary surface. Extreme solar events can affect electrical devices. Weakening of the Sun's magnetic field is believed to increase the number of interstellar cosmic rays which reach Earth's atmosphere, altering the types of particles reaching the surface.
Geomagnetic effects

The Earth's polar aurorae are visual displays created by interactions between the solar wind, the solar magnetosphere, the Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's atmosphere. Variations in any of these affect aurora displays. Solar coronal mass ejections, associated with high solar activity, produce enhanced auroral activity, and visible aurorae at lower than usual latitudes.
Sudden changes can cause the intense disturbances in the Earth's magnetic fields that are called geomagnetic storms.
Solar proton events
Energetic protons can reach Earth within 30 minutes of a major flare's peak. During such a solar proton event, Earth is showered in energetic solar particles (primarily protons) released from the flare site. Some of these particles spiral down Earth's magnetic field lines, penetrating the upper layers of our atmosphere where they produce additional ionization and may significantly increase the radiation environment.
Galactic Cosmic rays
Main article: Cosmic ray| This section includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this section by introducing more precise citations. (July 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
An increase in solar activity (more sunspots) is accompanied by an increase in the "solar wind," which is an outflow of ionized particles, mostly protons and electrons, from the sun. The Earth's geomagnetic field, the solar wind and the solar magnetic field deflect galactic cosmic rays (GCR). A decrease in solar activity increases the GCR penetration of the troposphere and stratosphere. GCR particles are the primary source of ionization in the troposphere above 1 km (below 1 km, radon is a dominant source of ionization in many areas).
Levels of GCRs have been indirectly recorded by their influence on the production of carbon-14 and beryllium-10. The hypothesized Hallstatt solar cycle length of approximately 2300 years is reflected by climatic Dansgaard-Oeschger events. The 80–90-year solar Gleissberg cycles appear to vary in length depending upon the lengths of the concurrent 11-year solar cycles.
Carbon-14 production

The production of carbon-14 (radiocarbon: C) also is related to solar activity. Carbon-14 is produced in the upper atmosphere when cosmic ray bombardment of atmospheric nitrogen (N) induces the Nitrogen to undergo β+ decay, thus transforming into an unusual isotope of carbon with an atomic weight of 14 rather than the more common 12. Because cosmic rays are partially excluded from the Solar System by the outward sweep of magnetic fields in the solar wind, increased solar activity results in a reduction of cosmic rays reaching the Earth's atmosphere and thus reduces C production. Thus the cosmic ray intensity and carbon-14 production vary inversely to the general level of solar activity.
Therefore, the atmospheric C concentration is lower during sunspot maxima and higher during sunspot minima. By measuring the captured C in wood and counting tree rings, production of radiocarbon relative to recent wood can be measured and dated. A reconstruction of the past 10,000 years shows that the C production was much higher during the mid-Holocene 7,000 years ago and decreased until 1,000 years ago. In addition to variations in solar activity, the long term trends in carbon-14 production are influenced by changes in the Earth's geomagnetic field and by changes in carbon cycling within the biosphere (particularly those associated with changes in the extent of vegetation since the last ice age)
Solar variation and climate
See also: Radiative forcing and Climate sensitivity
Both long-term and short-term variations in solar activity are hypothesized to affect global climate, but it has proven challenging to directly quantify the link.
As discussed above, three mechanisms are proposedby which solar variations affect climate:
- Solar irradiance changes directly affecting the climate ("Radiative forcing"). This is generally considered to be a minor effect, as the amplitudes of the variations in solar irradiance are too small to have significant effect absent some amplification process.
- Variations in the ultraviolet component. The UV component varies by more than the total, so if UV were for some (as yet unknown) reason to have a disproportionate effect, this might explain a larger solar signal.
- Effects mediated by changes in cosmic rays (which are affected by the solar wind) such as changes in cloud cover.
Early research attempted to find a correlation between weather and sunspot activity, mostly without notable success. Later research has concentrated more on correlating solar activity with global temperature.
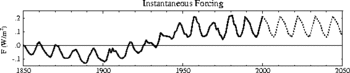
Crucial to the understanding of possible solar impact on terrestrial climate is accurate measurement of solar forcing. Unfortunately accurate measurement of incident solar radiation is only available since the satellite era, and even that is open to dispute: different groups find different values, due to different methods of cross-calibrating measurements taken by instruments with different spectral sensitivity. Scafetta and Willson found significant variations of solar luminosity between 1980 and 2000. But Lockwood and Frohlich find that solar forcing has declined since 1987.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Third Assessment Report (TAR) concluded that the measured magnitude of recent solar variation is much smaller than the amplification effect due to greenhouse gases, but acknowledged that scientific understanding is poor with respect to solar variation.
Estimates of long-term solar irradiance changes have decreased since the TAR. However, empirical results of detectable tropospheric changes have strengthened the evidence for solar forcing of climate change. The most likely mechanism is considered to be some combination of direct forcing by TSI changes and indirect effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on the stratosphere. Least certain are indirect effects induced by galactic cosmic rays.
In 2002, Lean et al. stated that while "There is ... growing empirical evidence for the Sun's role in climate change on multiple time scales including the 11-year cycle", "changes in terrestrial proxies of solar activity (such as the 14C and 10Be cosmogenic isotopes and the aa geomagnetic index) can occur in the absence of long-term (i.e., secular) solar irradiance changes ... because the stochastic response increases with the cycle amplitude, not because there is an actual secular irradiance change." They conclude that because of this, "long-term climate change may appear to track the amplitude of the solar activity cycles," but that "Solar radiative forcing of climate is reduced by a factor of 5 when the background component is omitted from historical reconstructions of total solar irradiance ...This suggests that general circulation model (GCM) simulations of twentieth century warming may overestimate the role of solar irradiance variability." More recently, a study and review of existing literature published in Nature in September 2006 suggests that the evidence is solidly on the side of solar brightness having relatively little effect on global climate, with little likelihood of significant shifts in solar output over long periods of time. Lockwood and Fröhlich, 2007, find that there "is considerable evidence for solar influence on the Earth's pre-industrial climate and the Sun may well have been a factor in post-industrial climate change in the first half of the last century," but that "over the past 20 years, all the trends in the Sun that could have had an influence on the Earth's climate have been in the opposite direction to that required to explain the observed rise in global mean temperatures." In a study that brought geomagnetic activity into the discussion, as a measure of known solar-terrestrial interaction, Love et al. found a statistically significant correlation between sunspots and geomagnetic activity, but they found no statistically significant correlation between global surface temperature and either sunspot number or geomagnetic activity.
Benestad and Schmidt concluded that "the most likely contribution from solar forcing a global warming is 7 ± 1% for the 20th century and is negligible for warming since 1980." This paper disagrees with Scafetta and West, who claimed that solar variability has a significant effect on climate forcing. Based on correlations between specific climate and solar forcing reconstructions, they argue that a "realistic climate scenario is the one described by a large preindustrial secular variability (e.g., the paleoclimate temperature reconstruction by Moberg et al.) with TSI experiencing low secular variability (as the one shown by Wang et al.). Under this scenario, according to Scafetta and West, the Sun might have contributed 50% of the observed global warming since 1900. Stott et al. estimate that the residual effects of the prolonged high solar activity during the last 30 years account for between 16% and 36% of warming from 1950 to 1999.
Effect on global warming
Recent rises in Earth average temperature cannot be explained by solar radiative forcing as its primary cause. This has been deduced via multiple, independent lines of evidence:
Direct measurement and time series
Neither direct measurements nor proxies of solar variation correlate well with Earth global temperature, particularly in recent decades.
Diurnal criterion
Globally, average diurnal temperature range has decreased. That is, daytime temperatures have not risen as fast as nighttime temperatures have warmed. This is the opposite of the expected warming if solar energy (falling primarily or wholly on Earth's dayside, depending on energy regime) were the principal means of forcing. It is, however, the expected pattern if greenhouse gases were preventing radiative escape, which is more prevalent on Earth's nightside.
Hemispheric and latitudinal criteria
The Northern Hemisphere is warming faster than the Southern Hemisphere. This is the opposite of the expected pattern if the Sun, currently closer to the Earth during Austral Summer, were the principal climate forcing. In particular, the Southern Hemisphere, with more ocean area and less land area, has a lower albedo ("whiteness") and absorbs more light. The Northern Hemisphere, however, has a higher population, industry, and emissions.
Furthermore, the Arctic region is not only warming faster than the Antarctic, but faster than northern mid-latitudes and subtropics, despite polar regions receiving less sun than lower latitudes.
Altitude criterion
Solar forcing should warm Earth's atmosphere roughly evenly by altitude, with some variation by wavelength/energy regime. However, the atmosphere is warming at lower altitudes, and actually cooling at higher altitudes. This is the expected pattern if greenhouse gases are driving temperature, as on Venus.
Solar variation theory
A 1994 U.S. National Academy of Sciences study concluded that TSI variations were the most likely cause of significant climate change in the pre-industrial era, before significant human-generated carbon dioxide entered the atmosphere.
Scafetta and West correlated solar proxy data and lower tropospheric temperature for the preindustrial era, before significant anthropogenic greenhouse forcing, suggesting that TSI variations may have contributed to 50% of the global warming observed between 1900 and 2000 (although they conclude "our estimates about the solar effect on climate might be overestimated and should be considered as an upper limit.") This contrasts with the results from GCMs that predict solar forcing of climate through direct radiative forcing is too small to explain a significant contribution. The relative significance of solar variability and other forcings of climate change during the industrial era is an area of ongoing research.
In 2000, Stott and others reported on the most comprehensive model simulations of 20th century climate to that date. Their study looked at both "natural forcing agents" (solar variations and volcanic emissions) as well as "anthropogenic forcing" (greenhouse gases and sulphate aerosols). They found that "solar effects may have contributed significantly to the warming in the first half of the century although this result is dependent on the reconstruction of total solar irradiance that is used. In the latter half of the century, we find that anthropogenic increases in greenhouses gases are largely responsible for the observed warming, balanced by some cooling due to anthropogenic sulphate aerosols, with no evidence for significant solar effects." Stott's group found that combining these factors enabled them to closely simulate global temperature changes throughout the 20th century. They predicted that continued greenhouse gas emissions would cause additional future temperature increases "at a rate similar to that observed in recent decades". It should be noted that their solar forcing included "spectrally resolved changes in solar irradiance" but not indirect effects mediated through cosmic rays. In addition, the study notes "uncertainties in historical forcing" — in other words, past natural forcing may still be having a delayed warming effect, most likely due to the oceans. A graphical representation of the relationship between natural and anthropogenic factors contributing to climate change appears in "Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis", a report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Stott's 2003 work largely revised his assessment, and found a significant solar contribution to recent warming, although still smaller (between 16 and 36%) than that of greenhouse gases.
Sami Solanki, the director of the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany said:
The sun has been at its strongest over the past 60 years and may now be affecting global temperatures... the brighter sun and higher levels of so-called "greenhouse gases" both contributed to the change in the Earth's temperature, but it was impossible to say which had the greater impact.
Nevertheless, Solanki agrees with the scientific consensus that the marked upswing in temperatures since about 1980 is attributable to human activity.
"Just how large this role is, must still be investigated, since, according to our latest knowledge on the variations of the solar magnetic field, the significant increase in the Earth's temperature since 1980 is indeed to be ascribed to the greenhouse effect caused by carbon dioxide."
Little Ice Age
Main article: Little Ice AgeOne historical long-term correlation between solar activity and climate change is the 1645–1715 Maunder minimum, a period of little or no sunspot activity which partially overlapped the "Little Ice Age" during which cold weather prevailed in Europe. The Little Ice Age encompassed roughly the 16th to the 19th centuries It is debated whether the low solar activity caused the cooling, or whether the cooling was caused by other factors.
The Spörer Minimum was linked to a significant cooling period between 1460 and 1550. Other indicators of low solar activity during this period are levels of the isotopes carbon-14 and beryllium-10.
A 2012 paper linked the Little Ice Age to an "unusual 50-year-long episode with four large sulfur-rich explosive eruptions," and claimed "large changes in solar irradiance are not required" to explain the phenomenon.
A 2010 paper suggested that a new 90-year period of low solar activity would reduce global average temperatures by about 0.3 °C, which would not be enough to offset the forecasted average global temperature increase due to increased forcing from rising levels of greenhouse gases.
Correlations to solar cycle length
In 1991, Friis-Christensen and Lassen claimed a strong correlation of the length of the solar cycle with temperature changes throughout the northern hemisphere. Initially, they used sunspot and temperature measurements from 1861 to 1989 and later extended the period using climate records dating back four centuries. They reported that the relationship appeared to account for nearly 80 per cent of the measured temperature changes over this period.
The mechanism behind these correlations is a matter of speculation. Laut's 2003 paper identified problems with some of these correlation analyses. Damon and Laut claimed that
the apparent strong correlations displayed on these graphs have been obtained by incorrect handling of the physical data. The graphs are still widely referred to in the literature, and their misleading character has not yet been generally recognized.
Damon and Laut stated that when the graphs are corrected for filtering errors, the sensational agreement with the recent global warming, which drew worldwide attention, totally disappeared.
In 2000, Lassen and Thejll updated Friis-Christensen and Lassen's 1991 research (which originally only went to 1989) and concluded that while the solar cycle accounted for about half the temperature rise since 1900, it failed to explain a rise of 0.4 °C since 1980. A 2005 review by Benestad found that the solar cycle did not follow Earth's global mean surface temperature.
Solar variation and weather
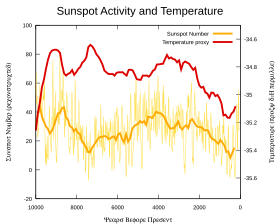
Solar activity may also impact regional climates, such as for the rivers Paraná and Po. Measurements from NASA's Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment show that solar UV output is more variable than the total solar irradiance. Climate modelling suggests that low solar activity may result in, for example, colder winters in the US and northern Europe and milder winters in Canada and southern Europe, with little change in globally averages. More broadly, links have been suggested between solar cycles, global climate and events like El Nino. Hancock and Yarger found "statistically significant relationships between the double sunspot cycle and the 'January thaw' phenomenon along the East Coast and between the double sunspot cycle and 'drought' (June temperature and precipitation) in the Midwest."
Recent research at CERN's CLOUD facility examined links between cosmic rays and cloud condensation nuclei, demonstrating the effect of high-energy particulate radiation in nucleating aerosol particles that are precursors to cloud condensation nuclei. Kirby (CLOUD team leader) said, "At the moment, it actually says nothing about a possible cosmic-ray effect on clouds and climate, but it's a very important first step."
1983–1994 global low cloud formation data from the International Satellite Cloud Climatology Project (ISCCP) was highly correlated with galactic cosmic ray (GCR) flux; subsequent to this period, the correlation breaks down. Changes of 3–4% in cloudiness and concurrent changes in cloud top temperatures correlated to the 11 and 22-year solar (sunspot) cycles, with increased GCR levels during "antiparallel" cycles. Global average cloud cover change was measured at 1.5–2%. Several GCR and cloud cover studies found positive correlation at latitudes greater than 50° and negative correlation at lower latitudes. However, not all scientists accept this correlation as statistically significant, and some that do attribute it to other solar variability (e.g. UV or total irradiance variations) rather than directly to GCR changes. Difficulties in interpreting such correlations include the fact that many aspects of solar variability change at similar times, and some climate systems have delayed responses.
Historical perspective
Physicist and historian Spencer R. Weart in The Discovery of Global Warming (2003) writes:
The study of cycles was generally popular through the first half of the century. Governments had collected a lot of weather data to play with and inevitably people found correlations between sun spot cycles and select weather patterns. If rainfall in England didn't fit the cycle, maybe storminess in New England would. Respected scientists and enthusiastic amateurs insisted they had found patterns reliable enough to make predictions. Sooner or later though every prediction failed. An example was a highly credible forecast of a dry spell in Africa during the sunspot minimum of the early 1930s. When the period turned out to be wet, a meteorologist later recalled "the subject of sunspots and weather relationships fell into dispute, especially among British meteorologists who witnessed the discomfiture of some of their most respected superiors." Even in the 1960s he said, "For a young researcher to entertain any statement of sun-weather relationships was to brand oneself a crank."
See also
|
|
References
Footnotes
- ^ Active Cavity Radiometer Irradiance Monitor (ACRIM) total solar irradiance monitoring 1978 to present (Satellite observations of total solar irradiance); access date 2012-02-03
- Willson, R. C.; Mordvinov, A. V. (2003). "Secular total solar irradiance trend during solar cycles 21–23". Geophys. Res. Lett. 30 (5): 1199. Bibcode:2003GeoRL..30e...3W. doi:10.1029/2002GL016038.
- "Construction of a Composite Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) Time Series from 1978 to present". Physikalisch-Meteorologisches Observatorium Davos (PMOD). Retrieved 5 October 2005.
- ^ Ineson S., Scaife A.A., Knight J.R., Manners J.C., Dunstone N.J., Gray L.J., Haigh J.D. (9 October 2011). "Solar forcing of winter climate variability in the Northern Hemisphere". Nature Geoscience. 4 (11): 753–7. Bibcode:2011NatGe...4..753I. doi:10.1038/ngeo1282.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Willson, Richard C.; H.S. Hudson (1991). "The Sun's luminosity over a complete solar cycle". Nature. 351 (6321): 42–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.351...42W. doi:10.1038/351042a0.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "Solar Forcing of Climate". Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis. Retrieved 10 March 2005.
- ^ Weart, Spencer (2003). "Changing Sun, Changing Climate?". The Discovery of Global Warming. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-01157-0. Retrieved 17 April 2008.
- Committee on Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years, Board on Atmospheric Sciences and Climate, Division on Earth and Life Studies, National Research Council of the National Academies. (2006). "Climate Forcings and Climate Models". In North, Gerald R.; Biondi, Franco; Bloomfield, Peter; Christy, John R. (eds.). Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years. National Academies Press. ISBN 0-309-10225-1. Retrieved 1 February 2012.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|displayeditors=ignored (|display-editors=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Lean, Judith (2000). "Evolution of the Sun's Spectral Irradiance Since the Maunder Minimum". Geophysical Research Letters. 27 (16): 2425–8. Bibcode:2000GeoRL..27.2425L. doi:10.1029/2000GL000043.
- ^ Scafetta, N.; West, B. J. (2006). "Phenomenological solar signature in 400 years of reconstructed Northern Hemisphere temperature record". Geophys. Res. Lett. 33 (17): L17718. Bibcode:2006GeoRL..3317718S. doi:10.1029/2006GL027142. Cite error: The named reference "Scafetta06" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Changes in Solar Brightness Too Weak To Explain Global Warming" (Press release). UCAR. 13 September 2006. Retrieved 18 April 2007.
- "Great Moments in the History of Solar Physics 1". Great Moments in the History of Solar Physics. Archived from the original on 1 March 2006. Retrieved 19 March 2006.
- Arctowski, Henryk (1940). "On Solar Faculae and Solar Constant Variations" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 26 (6): 406–11. Bibcode:1940PNAS...26..406A. doi:10.1073/pnas.26.6.406. PMC 1078196. PMID 16588370.
- ^ Fritts, Harold C. (1976). Tree rings and climate. Boston: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-268450-8.
- "William Herschel (1738–1822)". High Altitude Observatory. Archived from the original on 7 June 2007. Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- Camp, Charles D.; Tung, Ka-Kit; Quinif, Yves; Kaufman, Olivier; Van Ruymbeke, Michel; Vandiepenbeeck, Marc; Camelbeeck, Thierry (2006). "The Influence of the Solar Cycle and QBO on the Late Winter Stratospheric Polar Vortex" (PDF). Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union. 87 (52): Fall Meet. Suppl., Abstract #A11B–0862. Retrieved 28 April 2009.
- "welcome to pmodwrc". pmodwrc.ch.
- Richard C. Willson, Alexander V. Mordvinov (2003). "Secular total solar irradiance trend during solar cycles 21–23". Geophysical Research Letters. 30 (5): 1199. Bibcode:2003GeoRL..30e...3W. doi:10.1029/2002GL016038.
- Steven DeWitte, Dominiqu Crommelynck, Sabri Mekaoui, and Alexandre Joukoff (2004). "Measurement and uncertainty of the long-term total solar irradiance trend". Solar Physics. 224 (1–2): 209–216. Bibcode:2004SoPh..224..209D. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-5698-7.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fröhlich, C. and J. Lean (2004). "Solar Radiative Output and its Variability: Evidence and Mechanisms". Astronomy and Astrophysical Review. 12 (4): 273–320. Bibcode:2004A&ARv..12..273F. doi:10.1007/s00159-004-0024-1.
- Eddy, J.A. (1990). "Samuel P. Langley (1834–1906)". Journal for the History of Astronomy. 21: 111–20. Bibcode:1990JHA....21..111E.
- Foukal, P. V.; Mack, P. E.; Vernazza, J. E. (1977). "The effect of sunspots and faculae on the solar constant". The Astrophysical Journal. 215: 952. Bibcode:1977ApJ...215..952F. doi:10.1086/155431.
- ^ Willson RC, Gulkis S, Janssen M, Hudson HS, Chapman GA (February 1981). "Observations of Solar Irradiance Variability". Science. 211 (4483): 700–2. Bibcode:1981Sci...211..700W. doi:10.1126/science.211.4483.700. PMID 17776650.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - J. R. Hickey, B. M. Alton, H. L. Kyle and E. R. Major (1988). "Observation of total solar irradiance (TSI) variability from Nimbus satellites". Advances in Space Research. 8 (7): 5–10. Bibcode:1988AdSpR...8....5H. doi:10.1016/0273-1177(88)90164-0.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Rodney Viereck, NOAA Space Environment Center. The Sun-Climate Connection
- Dziembowski, W. A.; Gough, D. O.; Houdek, G.; Sienkiewicz, R. (1 December 2001). "Oscillations of alpha UMa and other red giants". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 328 (2): 601–610. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04894.x. ISSN 0035-8711.
- Usoskin, Ilya G.; Solanki, Sami K.; Schüssler, Manfred; Mursula, Kalevi; Alanko, Katja (2003). "A Millennium Scale Sunspot Number Reconstruction: Evidence For an Unusually Active Sun Since the 1940's". Physical Review Letters. 91 (21): 211101. arXiv:astro-ph/0310823. Bibcode:2003PhRvL..91u1101U. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.91.211101.
- ^ David H. Hathaway, "The Solar Cycle", Living Reviews in Solar Physics, March 2010, Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany. ISSN 1614-4961 (accessed 19 July 2015)
- Sonett, C. P.; Finney, S. A.; Berger, A. (24 April 1990). "The Spectrum of Radiocarbon". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 330 (1615): 413–26. Bibcode:1990RSPTA.330..413S. doi:10.1098/rsta.1990.0022.
- ^ Braun, H; Christl, M; Rahmstorf, S; Ganopolski, A; Mangini, A; Kubatzki, C; Roth, K; Kromer, B (10 November 2005). "Possible solar origin of the 1,470-year glacial climate cycle demonstrated in a coupled model". Nature. 438 (7065): 208–11. Bibcode:2005Natur.438..208B. doi:10.1038/nature04121. PMID 16281042.
- "The Sun and Climate" (PDF). U.S. Geological Survey. Fact Sheet 0095-00.
- Vasiliev, S. S.; Dergachev, V. A. (2002). "The ~ 2400-year cycle in atmospheric radiocarbon concentration: bispectrum of C data over the last 8000 years" (PDF). ANGEO. 20 (1): 115–20. Bibcode:2002AnGeo..20..115V. doi:10.5194/angeo-20-115-2002.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - Xapsos, M. A.; Burke, E. A. (July 2009). "Evidence of 6 000-Year Periodicity in Reconstructed Sunspot Numbers". Solar Physics. 257 (2): 363–9. Bibcode:2009SoPh..257..363X. doi:10.1007/s11207-009-9380-3.
- Damon, Paul E.; Jirikowic, John L. (31 March 2006). "The Sun as a low-frequency harmonic oscillator". Radiocarbon. 34 (2): 199–205. doi:10.2458/azu_js_rc.34.1450. ISSN 0033-8222.
- Perry, Charles A.; Hsu, Kenneth J.; Usoskin, Ilya G. (2000). "Geophysical, archaeological, and historical evidence support a solar-output model for climate change" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (23): 12433–8. Bibcode:2000PNAS...9712433P. doi:10.1073/pnas.230423297. PMC 18780. PMID 11050181.
- Hathaway, David H.; Wilson, Robert M. (2004). "What the Sunspot Record Tells Us About Space Climate" (PDF). Solar Physics. 224 (1–2): 5–19. Bibcode:2004SoPh..224....5H. doi:10.1007/s11207-005-3996-8. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 January 2006. Retrieved 19 April 2007.
- Damon, Paul E., and Sonett, Charles P., "Solar and terrestrial components of the atmospheric C-14 variation spectrum.]," In The Sun in Time, Vol. 1, pp. 360-388, University of Arizona Press, Tucson AZ (1991). Abstract (accessed 16 July 2015)
- see table in "Solar Variability: climatic change resulting from changes in the amount of solar energy reaching the upper atmosphere". Introduction to Quaternary Ecology. Retrieved 16 July 2015.
- Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, Total Solar Irradiance Data (retrieved 16 July 2015)
- ^ Board on Global Change, Commission on Geosciences, Environment, and Resources, National Research Council. (1994). Solar Influences on Global Change. Washington, D.C: National Academy Press. p. 36. ISBN 0-309-05148-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Wang, Y.-M.; Lean, J. L.; Sheeley, N. R. (2005). "Modeling the Sun's magnetic field and irradiance since 1713" (PDF). The Astrophysical journal. 625 (1): 522–38. Bibcode:2005ApJ...625..522W. doi:10.1086/429689.
- Krivova, N. A.; Balmaceda, L.; Solanki, S. K. (2007). "Reconstruction of solar total irradiance since 1700 from the surface magnetic flux". A&A. 467 (1): 335–46. Bibcode:2007A&A...467..335K. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066725.
- Steinhilber, F.; Beer, J.; Fröhlich, C. (2009). "Total solar irradiance during the Holocene". Geophys. Res. Lett. 36 (19): L19704. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..3619704S. doi:10.1029/2009GL040142.
- Lean, J. (14 April 1989). "Contribution of Ultraviolet Irradiance Variations to Changes in the Sun's Total Irradiance". Science. 244 (4901): 197–200. Bibcode:1989Sci...244..197L. doi:10.1126/science.244.4901.197. PMID 17835351.
1 percent of the sun's energy is emitted at ultraviolet wavelengths between 200 and 300 nanometers, the decrease in this radiation from 1 July 1981 to 30 June 1985 accounted for 19 percent of the decrease in the total irradiance
(19% of the 1/1366 total decrease is 1.4% decrease in UV) - Haigh, J D (17 May 1996). "The Impact of Solar Variability on Climate". Science. 272 (5264): 981–984. doi:10.1126/science.272.5264.981.
- Fligge, M.; Solanki, S. K. (2000). "The solar spectral irradiance since 1700" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 27 (14): 2157–2160. Bibcode:2000GeoRL..27.2157F. doi:10.1029/2000GL000067. Retrieved 12 June 2011.
- Committee on the Effects of Solar Variability on Earth's Climate; Space Studies Board; Division on Engineering and Physical Science; National Research Council. "The Effects of Solar Variability on Earth's Climate: A Workshop Report - The National Academies Press". nap.edu.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Field, C.; Schmidt, G.; Koch, D.; Salyk, C. (11 August 200). "Modeling production and climate- related impacts on 10 Be concentration in ice cores". J. Geophys. Res. doi:10.1029/2005JD006410. Retrieved July 2015.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ Tinsley, Brian A.; Yu, Fangqun (2004). "Atmospheric Ionization and Clouds as Links Between Solar Activity and Climate" (PDF). In Pap, Judit M.; Fox, Peter (eds.). Solar Variability and its Effects on Climate. Vol. 141. American Geophysical Union. pp. 321–339. ISBN 0-87590-406-8. Retrieved 19 April 2007.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ "CERN's CLOUD experiment provides unprecedented insight into cloud formation" (Press release). CERN. 25 August 2011. Retrieved 3 November 2011.
- ^ Shaviv, Nir J (2005). "On climate response to changes in the cosmic ray flux and radiative budget" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research. 110 (A08105). arXiv:physics/0409123. Bibcode:2005JGRA..11008105S. doi:10.1029/2004JA010866. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- ^ Svensmark, Henrik (2007). "Cosmoclimatology: a new theory emerges". Astronomy & Geophysics. 48 (1): 1.18 – 1.24. Bibcode:2007A&G....48a..18S. doi:10.1111/j.1468-4004.2007.48118.x.
- ^ Svensmark, Henrik (1998). "Influence of Cosmic Rays on Earth's Climate" (PDF). Physical Review Letters. 81 (22): 5027–5030. Bibcode:1998PhRvL..81.5027S. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.5027. Retrieved 17 June 2011.
- Shaviv, Nir J and Veizer, Ján (2003). "Celestial driver of Phanerozoic climate?". Geological Society of America. 13 (7): 4. doi:10.1130/1052-5173(2003)013<0004:CDOPC>2.0.CO;2.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Pierce, J.; Adams, P. (2009). "Can cosmic rays affect cloud condensation nuclei by altering new particle formation rates?". Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (9): 36.
- Snow-Kropla, E.; et al. (April 2011). "Cosmic rays, aerosol formation and cloud-condensation nuclei: sensitivities to model uncertainties". Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics. 11 (8): 4001.
- ^ Erlykin, A.; et al. (August 2013). "A review of the relevance of the 'CLOUD' results and other recent observations to the possible effect of cosmic rays on the terrestrial climate". Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics. 121 (3): 137.
- Sloan, T.; Wolfendale, A. (June 2007). "Cosmic Rays and Global Warming". 30TH INTERNATIONAL COSMIC RAY CONFERENCE, Merida, Mexico.
- Sun, B.,; Bradley, R. (2002). "Solar influences on cosmic rays and cloud formation: A reassessment". Journal of Geophysical Research. 107 (D14).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Benestad, R (September 2013). "Are there persistent physical atmospheric responses to galactic cosmic rays?". Environmental Research Letters. 8 (3): 035049.
- Sloan, T.; Wolfendale, A. (November 2013). "Cosmic rays, solar activity and the climate". Environmental Research Letters. 8 (4): 045022.
- Krissansen-Totton, J.,; Davies, R. (October 2013). "Investigation of cosmic ray–cloud connections using MISR". Geophysical Research Letters. 40 (19): 5240.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Tsonis, A.,; Deyle, E.; et al. (March 2015). "Dynamical evidence for causality between galactic cosmic rays and interannual variation in global temperature". PNAS. 112 (11).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Do Cosmic Rays Cause Global Warming?". July 2011. Retrieved Mar 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - "Finally. Cosmic Ray Theory of Climate Change Dead". November 12, 2013. Retrieved Mar 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - "Cosmic rays fall cosmically behind humans in explaining global warming". November 12, 2013. Retrieved Mar 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - "MYTH #24: It's cosmic rays". Retrieved Mar 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - Sloan, T.; Wolfendale, A. (December 2013). "Cosmic rays and climate change over the past 1000 million years". New Astronomy. 25: 45.
- Feng, F.,; Bailer-Jones, C. (2013). "Assessing the Influence of the Solar Orbit on Terrestrial Biodiversity". Astrophysical Journal. 768 (2): 152.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - "Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis: 6.11.2.2 Cosmic rays and clouds". 2001. Retrieved March 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - Brown, Paul (November 8, 2013). "Cosmic rays add little to climate change". Retrieved Mar 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|access-date=(help) - Kollipara, P. (12 March 2015). "No, cosmic rays aren't causing global warming". Washington Post.
- "Astronomy: On the Sunspot Cycle". Retrieved 27 February 2008.
- Joanna D. Haigh "The Sun and the Earth’s Climate", Living Reviews in Solar Physics (access date 31 January 2012
- Scafetta, Nicola; Willson, Richard (2009). "ACRIM-gap and Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) trend issue resolved using a surface magnetic flux TSI proxy model". Geophysical Research Letter. 36 (5): L05701. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..3605701S. doi:10.1029/2008GL036307.
- Lockwood, Mike; Fröhlich, Claus (8 June 2008). "Recent oppositely directed trends in solar climate forcings and the global mean surface air temperature. II. Different reconstructions of the total solar irradiance variation and dependence on response time scale". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 464 (2094): 1367–85. Bibcode:2008RSPSA.464.1367L. doi:10.1098/rspa.2007.0347.
- Template:AR4
- Houghton, J.T.; Ding, Y.; Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M., eds. (2001). "6.11 Total Solar Irradiance—Figure 6.6: Global, annual mean radiative forcings (1750 to present)". Climate Change 2001: Working Group I: The Scientific Basis. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Retrieved 15 April 2007.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|displayeditors=ignored (|display-editors=suggested) (help) - "2.7 Natural Forcings". ipcc.ch.
- Lean, J.L.; Wang, Y.-M; Sheeley Jr., N.R (2002). "The effect of increasing solar activity on the Sun's total and open magnetic flux during multiple cycles: Implications for solar forcing of climate". Geophysical Research Letters. 29 (24): 77–1~77–4. Bibcode:2002GeoRL..29x..77L. doi:10.1029/2002GL015880.
- Foukal, P.; Fröhlich, C.; Spruit, H.; Wigley, T. M. L. (2006). "Variations in solar luminosity and their effect on the Earth's climate" (PDF). Nature. 443 (7108): 161–6. Bibcode:2006Natur.443..161F. doi:10.1038/nature05072. PMID 16971941.
- Lockwood, Mike; Claus Fröhlich (2007). "Recent oppositely directed trends in solar climate forcings and the global mean surface air temperature" (PDF). Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 463 (2086): 2447. Bibcode:2007RSPSA.463.2447L. doi:10.1098/rspa.2007.1880.
Our results show that the observed rapid rise in global mean temperatures seen after 1985 cannot be ascribed to solar variability, whichever of the mechanisms is invoked and no matter how much the solar variation is amplified.
- Love, J. J.; Mursula, K.; Tsai, V. C.; Perkins, D. M. (2013). "Are secular correlations between sunspots, geomagnetic activity, and global temperature significant?". Geophysical Research Letters. 38. Bibcode:2011GeoRL..3821703L. doi:10.1029/2011GL049380.
- Benestad,, R. E.; G. A. Schmidt (21 July 2009). "Solar trends and global warming" (PDF). Journal of Geophysical Research – Atmospheres. 114. Bibcode:2009JGRD..11414101B. doi:10.1029/2008JD011639.
the most likely contribution from solar forcing a global warming is 7 ± 1% for the 20th century and is negligible for warming since 1980.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ Scafetta, N.; West, B. J. (2007). "Phenomenological reconstructions of the solar signature in the Northern Hemisphere, surface temperature records since 1600" (PDF). J. Geophys. Res. 112: D24S03. Bibcode:2007JGRD..11224S03S. doi:10.1029/2007JD008437. (access date 2012-1-31)
- Moberg, A; Sonechkin, DM; Holmgren, K; Datsenko, NM; Karlén, W; Lauritzen, SE (2005). "Highly variable Northern Hemisphere temperatures reconstructed from low- and high-resolution proxy data". Nature. 433 (7026): 613–7. Bibcode:2005Natur.433..613M. doi:10.1038/nature03265. PMID 15703742.
- Wang, Y.‐M.; Lean, J. L.; Sheeley, N. R. (May 2005). "Modeling the Sun's Magnetic Field and Irradiance since 1713". The Astrophysical Journal. 625: 522–38. Bibcode:2005ApJ...625..522W. doi:10.1086/429689.)
- ^ Stott, Peter A.; Gareth S. Jones; John F. B. Mitchell (2003). "Do Models Underestimate the Solar Contribution to Recent Climate Change" (PDF). Journal of ClimateDecember. 16 (24): 4079–4093. Bibcode:2003JCli...16.4079S. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016<4079:DMUTSC>2.0.CO;2. Retrieved 5 October 2005. Cite error: The named reference "Stott2003" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Schurer, A.; et al. (December 2013). "Small influence of solar variability on climate over the past millennium". Nature Geoscience. 7: 104–108. doi:10.1038/ngeo2040.
- Lockwood, L.; Fröhlich, C. (October 2007). "Recent oppositely directed trends in solar climate forcings and the global mean surface air temperature". Proceedings of the Royal Society A. 463 (2086): 2447–2460. Bibcode:2007RSPSA.463.2447L. doi:10.1098/rspa.2007.1880.
- Foukal, P.; et al. (September 2006). "Variations in solar luminosity and their effect on the Earth's climate". Nature. 443 (7108): 161–166. doi:10.1038/nature05072. PMID 16971941.
- Karl, Thomas; et al. (1993). "A New Perspective on Recent Global Warming: Asymmetric Trends of Daily Maximum and Minimum Temperature". Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society. 74: 1007–1023. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1993)074<1007:anporg>2.0.co;2.
- Braganza, K; et al. (July 2004). "Diurnal temperature range as an index of global climate change during the twentieth century". Geophysical Research Letters. 31 (13). Bibcode:2004GeoRL..3113217B. doi:10.1029/2004gl019998.
- Zhou, L.; et al. (August 2009). "Detection and attribution of anthropogenic forcing to diurnal temperature range changes from 1950 to 1999: comparing multi-model simulations with observations". Climate Dynamics. 35: 1289–1307. doi:10.1007/s00382-009-0644-2.
- Peng, S.; et al. (June 2004). "Rice yields decline with higher night temperature from global warming". Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences. 35 (27): 9971–9975.
- Armstrong, A. (February 2013). "Northern warming". Nature Geoscience. 6. doi:10.1038/ngeo1763.
- Jones1, P. D.; Parker, D. E.; Osborn1, T. J.; Briffa1, K. R. "Global and Hemispheric Temperature Anomalies - Land and Marine Instrumental Records". doi:10.3334/CDIAC/cli.002. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - Lewis, H.; et al. (April 2005). "Response of the Space Debris Environment to Greenhouse Cooling". Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Space Debris: 243.
- Ford, Matt (20 February 2008). "Unpacking interplay of solar variability and climate changeA trio of researchers discuss the current understanding of the effect sola". Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- Picone, J.; Lean, J.; et al. (2005). "Global Change in the Thermosphere: Compelling Evidence of a Secular Decrease in Density". 2005 NRL Review: 225–227.
- Hansen, J (2005). "Efficacy of climate forcings". J. Geophys. Res. 110: D18104. Bibcode:2005JGRD..11018104H. doi:10.1029/2005JD005776.
- ^ Stott, Peter A.; et al. (2000). "External Control of 20th Century Temperature by Natural and Anthropogenic Forcings". Science. 290 (5499): 2133–7. Bibcode:2000Sci...290.2133S. doi:10.1126/science.290.5499.2133. PMID 11118145.
- Carslaw, K.S.; Harrison, R. G.; Kirkby, J. (2002). "Cosmic Rays, Clouds, and Climate". Science. 298 (5599): 1732–7. Bibcode:2002Sci...298.1732C. doi:10.1126/science.1076964. PMID 12459578.
{{cite journal}}:|access-date=requires|url=(help);|format=requires|url=(help) - "graphical representation". Retrieved 5 October 2005.
- Houghton, J.T.; Ding, Y.; Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M. (eds.). "Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis". Retrieved 5 October 2005.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|displayeditors=ignored (|display-editors=suggested) (help) - Leidig, Michael (18 July 2004). "Hotter-burning sun warming the planet". The Washington Times. Retrieved 18 April 2007.
- "How Strongly Does the Sun Influence the Global Climate? — Studies at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research reveal: solar activity affects the climate but plays only a minor role in the current global warming" (Press release). Max Planck Society. 2 August 2004. Retrieved 16 April 2007.
- H. H. Lamb, "The cold Little Ice Age climate of about 1550 to 1800," in Climate: present, past and future, London: Methuen. p. 107 (1972). ISBN 0-416-11530-6
- Emmanuel Le Roy Ladurie (1971). Times of Feast, Times of Famine: a History of Climate Since the Year 1000. Barbara Bray. Garden City, NY: Doubleday. ISBN 0-374-52122-0. OCLC 164590.
- "Environment". solarstorms.org.
- Geoffrey Parker, Lesley M. Smith (1997). The general crisis of the seventeenth century. Routledge. pp. 287, 288. ISBN 978-0-415-16518-1.
- Crowley, Thomas J. (14 July 2000). "Causes of Climate Change Over the Past 1000 Years". Science. 289 (5477): 270–7. Bibcode:2000Sci...289..270C. doi:10.1126/science.289.5477.270. PMID 10894770.
- "Abrupt onset of the Little Ice Age triggered by volcanism and sustained by sea-ice/ocean feedbacks". Geophysical Research Letters. 39. 31 January 2012. doi:10.1029/2011GL050168.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|authors=ignored (help) - "A quiet sun won't save us from global warming". New Scientist. 26 February 2010. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- Friis-Christensen, E.; Lassen, K. (1 November 1991). "Length of the Solar Cycle: An Indicator of Solar Activity Closely Associated with Climate". Science. 254 (5032): 698–700. Bibcode:1991Sci...254..698F. doi:10.1126/science.254.5032.698. PMID 17774798. as PDF
- Laut, Peter (May 2003). "Solar activity and terrestrial climate: an analysis of some purported correlations". J Atmos Sol Terr Phys. 65 (7): 801–12. Bibcode:2003JASTP..65..801L. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(03)00041-5.
- ^ Damon, Paul E.; Paul Laut (28 September 2004). "Pattern of Strange Errors Plagues Solar Activity and Terrestrial Climate Data" (PDF). Eos, Transactions, American Geophysical Union. 85 (39): 370–4. Bibcode:2004EOSTr..85..370D. doi:10.1029/2004EO390005. Retrieved 5 October 2005.; see also discussion and references at skeptical science Cite error: The named reference "DamonLaut2004" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- Adler, Robert (6 May 2000). "Don't blame the Sun" (2237). New Scientist. Retrieved 19 April 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Benestad, R.E. (13 August 2005). "A review of the solar cycle length estimates". Geophys. Res. Let. 32 (15): L15714. Bibcode:2005GeoRL..3215714B. doi:10.1029/2005GL023621.
- Pablo J.D. Mauas & Andrea P. Buccino. "Long-term solar activity influences on South American rivers" page 5. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics on Space Climate, March 2010. Accessed: 20 September 2014.
- D. Zanchettin, A. Rubino, P. Traverso, and M. Tomasino. "" JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113, D12102, doi:10.1029/2007JD009157, 19 June 2008. Accessed: 20 September 2014.
- "National Science Foundation (NSF) News - Solar Cycle Linked to Global Climate - NSF - National Science Foundation". nsf.gov.
- Hancock DJ, Yarger DN (1979). "Cross-Spectral Analysis of Sunspots and Monthly Mean Temperature and Precipitation for the Contiguous United States". Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences. 36 (4): 746–753. Bibcode:1979JAtS...36..746H. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1979)036<0746:CSAOSA>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1520-0469.
- "Cloud formation may be linked to cosmic rays" (Press release). Nature News. 24 August 2011. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- Kirkby J; Curtius J; Almeida J; Dunne E; Duplissy J; et al. (25 August 2011). "Role of sulphuric acid, ammonia and galactic cosmic rays in atmospheric aerosol nucleation". Nature. 476 (7361): 429–433. Bibcode:2011Natur.476..429K. doi:10.1038/nature10343. PMID 21866156.
- E. Pallé, C.J. Butler, K. O'Brien (2004). "The possible connection between ionization in the atmosphere by cosmic rays and low level clouds" (PDF). Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics. 66 (18): 1779. Bibcode:2004JASTP..66.1779P. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2004.07.041.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Pallé, E. (2005). "Possible satellite perspective effects on the reported correlations between solar activity and clouds" (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 32 (3): L03802.1–4. Bibcode:2005GeoRL..3203802P. doi:10.1029/2004GL021167.
- "Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis". Retrieved 5 October 2005.
- Shaviv, Nir J.; Veizer, Ján (2003). "Celestial driver of Phanerozoic climate?". GSA Today. 13 (7): 4–10. doi:10.1130/1052-5173(2003)013<0004:CDOPC>2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1052-5173.
- "Cosmic Rays, Carbon Dioxide, and Climate" (PDF). Retrieved 5 October 2005.
General references
- Abbot, C. G. (1966). "Solar Variation, A Weather Element" (PDF). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 56 (6): 1627–34. Bibcode:1966PNAS...56.1627A. doi:10.1073/pnas.56.6.1627. PMC 220145. PMID 16591394.
- Willson, Richard C.; H.S. Hudson (1991). "The Sun's luminosity over a complete solar cycle". Nature. 351 (6321): 42–4. Bibcode:1991Natur.351...42W. doi:10.1038/351042a0.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - "The Sun and Climate". U.S. Geological Survey Fact Sheet 0095-00. Retrieved 21 February 2005.
- "The Sun's role in Climate Changes" (PDF). Proc. of The International Conference on Global Warming and The Next Ice Age, 19–24 August 2001, Halifax, Nova Scotia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 October 2004. Retrieved 21 February 2005.
- White, Warren B.; Lean, Judith; Cayan, Daniel R.; Dettinger, Michael D. (1997). "Response of global upper ocean temperature to changing solar irradiance". Journal of Geophysical Research. 102 (C2): 3255–66. Bibcode:1997JGR...102.3255W. doi:10.1029/96JC03549.
- Foukal, Peter; et al. (1977). "The effects of sunspots and faculae on the solar constant". Astrophysical Journal. 215: 952. Bibcode:1977ApJ...215..952F. doi:10.1086/155431.
- Dziembowski, W.A.; P.R. Goode; J. Schou (2001). "Does the sun shrink with increasing magnetic activity?". Astrophysical Journal. 553 (2): 897–904. arXiv:astro-ph/0101473. Bibcode:2001ApJ...553..897D. doi:10.1086/320976.
- Stetson, H.T. (1937). Sunspots and Their Effects. New York: McGraw Hill.
- Yaskell, Steven Haywood (31 December 2012). Grand Phases On The Sun: The case for a mechanism responsible for extended solar minima and maxima. Trafford Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4669-6300-9.
External links
- Gerrit Lohmann, Norel Rimbu, Mihai Dima (2004). "Climate signature of solar irradiance variations: analysis of long-term instrumental, historical, and proxy data". International Journal of Climatology. 24 (8): 1045–56. Bibcode:2004IJCli..24.1045L. doi:10.1002/joc.1054.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - NOAA / NESDIS / NGDC (2002) Solar Variability Affecting Earth NOAA CD-ROM NGDC-05/01. This CD-ROM contains over 100 solar-terrestrial and related global data bases covering the period through April 1990.
- Solanki, S.K.; Fligge, M. (2001). "Long-term changes in solar irradiance". In Wilson, A. (ed.). Proceedings of the 1st Solar and Space Weather Euroconference, 25-29 September 2000, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Tenerife, Spain. ESA Publications Division. pp. 51–60. ISBN 9290926937. ESA SP-463.
- Solanki, S.K.; Fligge, M. (2000). "Reconstruction of past solar irradiance". Space Science Review. 94 (1/2): 127–38. doi:10.1023/A:1026754803423.
- Reid, George C. (1995). "The sun-climate question: Is there a real connection?". Rev. Geophys. 33 (Suppl): 535. Bibcode:1995RvGeS..33..535R. doi:10.1029/95RG00103. Aeronomy Laboratory, NOAA/ERL, Boulder, Colorado. U.S. National Report to IUGG, 1991–1994
- Recent Total Solar Irradiance data updated every Monday
| Climate change | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||