This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Zsombi1397 (talk | contribs) at 08:07, 26 September 2010. The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Revision as of 08:07, 26 September 2010 by Zsombi1397 (talk | contribs)(diff) ← Previous revision | Latest revision (diff) | Newer revision → (diff) This article is about the People's Republic of Bangladesh. For other uses, see Bangladesh (disambiguation).23°N 90°E / 23°N 90°E / 23; 90
| The People's Republic of Bangladeshগণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ Gônoprojātontri Bānglādeśh | |
|---|---|
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |
| Anthem: Amar Shonar Bangla My Golden Bangla | |
 | |
| Capitaland largest city | Dhaka |
| Official languages | Bengali |
| Demonym(s) | Bangladeshi |
| Government | Unitary state and parliamentary democracy |
| • President | Zillur Rahman |
| • Prime Minister | Sheikh Hasina Wazed |
| • Speaker | Ad.Abdul Hamid |
| Independence from the Islamic Republic of Pakistan | |
| • Declared | March 26, 1971 |
| • Victory Day | December 16, 1971 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 143,998 km (55,598 sq mi) (94th) |
| • Water (%) | 6.9 |
| Population | |
| • 2009 estimate | 162,221,000 (7th) |
| • Density | 1,099.3/km (2,847.2/sq mi) (9th) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2010 estimate |
| • Total | $256 billion |
| • Per capita | $1,465 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2010 estimate |
| • Total | $104.63 billion |
| • Per capita | $624 |
| Gini (2000) | 33.4 medium inequality |
| HDI (2007) | Error: Invalid HDI value (146th) |
| Currency | Taka (BDT) |
| Time zone | UTC+6 (BST) |
| Drives on | Left |
| Calling code | 880 |
| ISO 3166 code | BD |
| Internet TLD | .bd |
| |
Bangladesh (Template:Pron-en; Template:Lang-bn, Bānglādeś), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh (Bengali: গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ Gônoprojātontri Bānglādeś) is a country in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma (Myanmar) to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south. Together with the Indian state of West Bengal, it makes up the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal. The name Bangladesh means "Country of Bengal" in the official Bengali language.
The borders of present-day Bangladesh were established with the partition of Bengal and India in 1947, when the region became East Pakistan, part of the newly formed nation of Pakistan. However, it was separated from the western wing by 1,600 km (994 mi) of Indian territory. Political and linguistic discrimination as well as economic neglect led to popular agitations against West Pakistan, which led to the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971 and the establishment of Bangladesh. After independence, the new state endured famines, natural disasters and widespread poverty, as well as political turmoil and military coups. The restoration of democracy in 1991 has been followed by relative calm and economic progress. Today, Bangladesh is a secular, democratic republic., though it is not widely recognized in the political arena.
Bangladesh is the seventh most populous country and is among the most densely populated countries in the world with a high poverty rate. However, per-capita (inflation-adjusted) GDP has more than doubled since 1975, and the poverty rate has fallen by 20% since the early 1990s. The country is listed among the "Next Eleven" economies. Dhaka, the capital, and other urban centers have been the driving force behind this growth.
Geographically, the country straddles the fertile Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta and is subject to annual monsoon floods and cyclones. Bangladesh is a parliamentary democracy with an elected parliament called the Jatiyo Sangshad. The country is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations, the OIC, SAARC, BIMSTEC, and the D-8. As the World Bank notes in its July 2005 Country Brief, the country has made significant progress in human development in the areas of literacy, gender parity in schooling and reduction of population growth. However, Bangladesh continues to face a number of major challenges, including widespread political and bureaucratic corruption, economic competition relative to the world, serious overpopulation, widespread poverty, and an increasing danger of hydrologic shocks brought on by ecological vulnerability to climate change.
History
Main articles: History of Bangladesh and History of Bengal

Remnants of civilization in the greater Bengal region date back four thousand years, when the region was settled by Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, and Austro-Asiatic peoples. The exact origin of the word "Bangla" or "Bengal" is unknown, though it is believed to be derived from Bang, the Dravidian-speaking tribe that settled in the area around the year 1000 BC. The kingdom of Gangaridai was formed from at least the 7th century BC, which later united with Bihar under the Magadha, Nanda, Mauryan and Sunga Empires. Bengal was later part of the Gupta Empire and Harsha Empire from the 3rd to the 6th centuries CE. Following its collapse, a dynamic Bengali named Shashanka founded an impressive short-lived kingdom. After a period of anarchy, the Buddhist Pala dynasty ruled the region for four hundred years, followed by a shorter reign of the Hindu Sena dynasty. Islam was introduced to Bengal in the 12th century by Arab Muslim merchants; Sufi missionaries and subsequent Muslim conquests helped spread Islam throughout the region. Bakhtiar Khilji, a Turkic general, defeated Lakshman Sen of the Sena dynasty and conquered large parts of Bengal in the year 1204. The region was ruled by dynasties of Sultans and land lords Bhuiyan for the next few hundred years. By the 16th century, the Mughal Empire controlled Bengal, and Dhaka became an important provincial centre of Mughal administration.
European traders arrived late in the 15th century, and their influence grew until the British East India Company gained control of Bengal following the Battle of Plassey in 1757. The bloody rebellion of 1857 – known as the Sepoy Mutiny – resulted in transfer of authority to the crown with a British viceroy running the administration. During colonial rule, famine racked the Indian subcontinent many times, including the Great Bengal famine of 1943 that claimed 3 million lives. Between 1905 and 1911, an abortive attempt was made to divide the province of Bengal into two zones, with Dhaka being the capital of the eastern zone. When India was partitioned in 1947, Bengal was partitioned along religious lines, with the western part going to India and the eastern part (Muslims majority) joining Pakistan as a province called East Bengal (later renamed East Pakistan), with its capital at Dhaka.
In 1950, land reform was accomplished in East Bengal with the abolishment of the feudal zamindari system. Despite the economic and demographic weight of the east, however, Pakistan's government and military were largely dominated by the upper classes from the west. The Bengali Language Movement of 1952 was the first sign of friction between the two wings of Pakistan. Dissatisfaction with the central government over economic and cultural issues continued to rise through the next decade, during which the Awami League emerged as the political voice of the Bengali-speaking population. It agitated for autonomy in the 1960s, and in 1966, its president, Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, was jailed; he was released in 1969 after an unprecedented popular uprising. In 1970, a massive cyclone devastated the coast of East Pakistan, killing up to half a million people, and the central government responded poorly. The Bengali population's anger was compounded when Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, whose Awami League won a majority in Parliament in the 1970 elections, was blocked from taking office.
After staging compromise talks with Mujib, President Yahya Khan arrested him in the early hours of 26 March 1971, and launched Operation Searchlight, a sustained military assault on East Pakistan. Yahya's methods were extremely bloody, and the violence of the war resulted in many civilian deaths . Chief targets included intellectuals and Hindus, and about ten million refugees fled to neighbouring India. Estimates of those massacred throughout the war range from three hundred thousand to 3 million. Before his arrest by the Pakistan Army, Sk. Mujibur Rahman formally declared the independence of Bangladesh, and directed everyone to fight till the last soldier of the Pakistan army was evicted from East Pakistan. Awami League leaders set up a government-in-exile in Calcutta, India. The exile government formally took oath at Mujib Nagar in Kustia district of East Pakistan on 17 April 1971, with Tajuddin Ahmad as the first Prime Minister. The Bangladesh Liberation War lasted for nine months. The Bangladesh Forces formed within 11 sectors led by General M.A.G. Osmani consisting of Bengali Regulars, and Mukti Bahini conducted a massive guerilla war against the Pakistan Forces with all out support from the Indian Armed Forces. Jointly, the Mitro Bahini achieved a decisive victory over Pakistan on 16 December 1971, with Indian Armed Forces taking over 90,000 prisoners of war.
After its independence, Bangladesh became a parliamentary democracy, with Mujib as the Prime Minister. In the 1973 parliamentary elections, the Awami League gained an absolute majority. A nationwide famine occurred during 1973 and 1974, and in early 1975, Mujib initiated a one-party socialist rule with his newly formed BAKSAL. On 15 August 1975, Mujib and most of his family members were assassinated by mid-level military officers. A series of bloody coups and counter-coups in the following three months culminated in the ascent to power of General Ziaur Rahman, who reinstated multi-party politics, and founded the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). Zia's rule ended when he was assassinated by elements of the military in 1981. Bangladesh's next major ruler was General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, who gained power in a bloodless coup in 1982, and ruled until 1990, when he was forced to resign after a massive revolt of all major political parties and the public, along with pressure from western donors (which was a major shift in international policy after the fall of the Soviet Union). Since then, Bangladesh has reverted to a parliamentary democracy. Zia's widow, Khaleda Zia, led the Bangladesh Nationalist Party to parliamentary victory at the general election in 1991, and became the first female Prime Minister in Bangladeshi history. However, the Awami League, headed by Sheikh Hasina, one of Mujib's surviving daughters, won the next election in 1996. It lost again to the Bangladesh Nationalist Party in 2001.
On 11 January 2007, following widespread political unrest, a caretaker government was appointed to administer the next general election. The country had suffered from extensive corruption, disorder and political violence. The new caretaker government has made it a priority to root out corruption from all levels of government. To this end, many notable politicians and officials, along with large numbers of lesser officials and party members, have been arrested on corruption charges. The caretaker government held what observers described as a largely free and fair election on 29 December 2008. Awami League's Sheikh Hasina won the elections with a landslide victory and took the oath of Prime Minister on 6 January 2009.
Government and politics
Main article: Politics of Bangladesh See also: Constitution of Bangladesh
| Anthem | Amar Shonar Bangla |
|---|---|
| Animal | Royal Bengal Tiger |
| Bird | Oriental Magpie Robin |
| Fish | Hilsa |
| Flower | White Water Lily |
| Fruit | Jackfruit |
| Sport | Hadudu |
| Calendar | Bengali calendar |
Bangladesh is a unitary state and parliamentary democracy. Direct elections in which all citizens, aged 18 or over, can vote are held every five years for the unicameral parliament known as Jatiya Sangsad. The parliamentary building is known as the Jatiyo Sangshad Bhaban and was designed by architect Louis Kahn. Currently the parliament has 345 members including 45 reserved seats for women, elected from single-member constituencies. The Prime Minister, as the head of government, forms the cabinet and runs the day-to-day affairs of state. While the Prime Minister is formally appointed by the President, he or she must be an MP who commands the confidence of the majority of parliament. The President is the head of state but mainly a ceremonial post elected by the parliament.
However the President's powers are substantially expanded during the tenure of a caretaker government, which is responsible for the conduct of elections and transfer of power. The officers of the caretaker government must be non-partisan and are given three months to complete their task. This transitional arrangement is an innovation that was pioneered by Bangladesh in its 1991 election and then institutionalized in 1996 through its 13th constitutional amendment.
The Constitution of Bangladesh was drafted in 1972 and has undergone fourteen amendments. The highest judicial body is the Supreme Court. Justices are appointed by the President. The judicial and law enforcement institutions are weak. Separation of powers, judicial from executive was finally implemented on the 1st of November, 2007. It is expected that this separation will make the judiciary stronger and impartial. Laws are loosely based on English common law, but family laws such as marriage and inheritance are based on religious scripts, and therefore differ between religious communities.
The two major parties in Bangladesh are the Bangladesh Awami League and the Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). BNP is led by Khaleda Zia and traditionally been alled with Islamist parties like Jamaat-e-Islami Bangladesh and Islami Oikya Jot, while Sheikh Hasina's Awami League aligns with leftist and secularist parties. Hasina and Zia are bitter rivals who have dominated politics for over 15 years; each is related to one of the leaders of the independence movement. Another important player is the Jatiya Party, headed by former military dictator Ershad. The Awami League-BNP rivalry has been bitter and punctuated by protests, violence and murder. Student politics is particularly strong in Bangladesh, a legacy from the liberation movement era. Almost all parties have highly active student wings, and student leaders have been elected to the Parliament.
Two radical terrorist organizations, Jagrata Muslim Janata Bangladesh (JMJB) and Jama'atul Mujahideen Bangladesh (JMB), were banned in February 2005. Several small-scale bomb attacks taking place since 1999 have been blamed on those groups, and dozens of suspected members have been detained in security operations, including the heads of those two parties in 2006. The masterminds were tried and executed. The Bangladesh government won praise from world leaders, including Western leaders, for its strong anti-terrorist stance.
The January 22, 2007 election was postponed indefinitely and emergency law declared on January 11, 2007 as the Army backed caretaker government of Fakhruddin Ahmed aimed to prepare a new voter list and crack down on corruption. They also assisted the interim Government of Bangladesh in a drive against corruption, which resulted in Bangladesh's position in Transparency International's Corruption Perceptions Index changed from the very bottom, where they had been for 3 years in a row, to 147th in just 1 year. A large alliance led by the Bangladesh Awami League won the December 29, 2008 poll, in a landslide victory. They got 230 seats among 300 seats in the parliament.
Foreign policy and military
Main articles: Foreign relations of Bangladesh and Military of Bangladesh
Bangladesh pursues a moderate foreign policy that places heavy reliance on multinational diplomacy, especially at the United Nations. In 1974 Bangladesh joined both the Commonwealth of Nations and the United Nations and has since been elected to serve two terms on the Security Council in 1978–1979 and 2000–2001. In the 1980s, Bangladesh played a lead role in founding the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) in order to expand relations with other South Asian states. Since the founding of SAARC 1985, a Bangladeshi has held the post of Secretary General on two occasions.
Bangladesh's most important and complex foreign relationships are with India. These relationships are informed by historical and cultural ties and form an important part of the domestic political discourse. Bangladesh's relationship with India began on a positive note because of India's assistance in the independence war and reconstruction. Throughout the years, relations between both countries have fluctuated for a number of reasons. A major source of tension between Bangladesh and India is the Farakka Dam. In 1975, India constructed a dam on the Ganges River 11 miles (18 km) from the Bangladeshi border. Bangladesh alleges that the dam diverts much needed water from Bangladesh and adds a man-made disaster to the country already plagued by natural disasters. The dam also has terrible ecological consequences. On the other hand, India has voiced concerns about anti-Indian separatists and Islamic militants allegedly being harboured across their 2,500-mile (4,000 km) border, as well as the flow of illegal migrants, and is building a fence along most of it. But at the 2007 SAARC meeting both nations pledged to work cooperatively on security, economic and border issues.
The current strength of the army is around 200,000 including reservists, the air force 22,000, and navy 14,950. In addition to traditional defense roles, the military has been called on to provide support to civil authorities for disaster relief and internal security during periods of political unrest. Bangladesh is not currently active in any ongoing war, but it did contribute 2,300 troops to the coalition that fought in Operation Desert Storm in 1991 and Bangladesh is consistently a top contributor to UN peacekeeping forces around the world. As of May 2007, Bangladesh had major deployments in Democratic Republic of Congo, Liberia, Sudan, Timor-Leste and Côte d'Ivoire. Presently Bangladesh is the largest troop contributor country to the UN.
Bangladesh enjoys relatively warm ties with the People's Republic of China which has, particularly in the past decade, increased economic cooperation with the South Asian nation. Between 2006 and 2007, trade between the two nations rose by 28.5% and there have been agreements to grant various Bangladeshi commodities tariff-free access to the Chinese market. Cooperation between the Military of Bangladesh and the People's Liberation Army is also increasing, with joint military agreements signed and Bangladesh procuring Chinese arms which range from small arms to large naval surface combatants such as the Chinese Type 053H1 Missile Frigate.
Divisions, districts and upazilas
Main articles: Divisions of Bangladesh, Districts of Bangladesh, and Upazilas of Bangladesh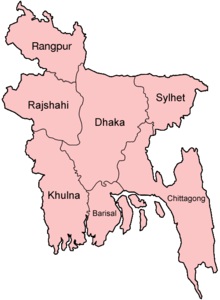
Bangladesh is divided into seven administrative divisions, each named after their respective divisional headquarters: Barisal (বরিশাল), Chittagong (চট্টগ্রাম), Dhaka (ঢাকা), Khulna (খুলনা), Rajshahi (রাজশাহী), Sylhet (সিলেট), and Rangpur (রংপুর).
Divisions are subdivided into districts (zila). There are 64 districts in Bangladesh, each further subdivided into upazila (subdistricts) or thana. The area within each police station, except for those in metropolitan areas, is divided into several unions, with each union consisting of multiple villages. In the metropolitan areas, police stations are divided into wards, which are further divided into mahallas. There are no elected officials at the divisional, district or upazila levels, and the administration is composed only of government officials. Direct elections are held for each union (or ward), electing a chairperson and a number of members. In 1997, a parliamentary act was passed to reserve three seats (out of twelve) in every union for female candidates.
Dhaka is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh. Other major cities include Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Sylhet, Barisal, Bogra, Comilla, Mymensingh and Rangpur. These cities have mayoral elections, while other municipalities elect a chairperson. Mayors and chairpersons are elected for a span of five years.
| City | City population (2008 estimate) | Metro population (2008 estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| Dhaka | 7,000,940 | 12,797,394 |
| Chittagong | 2,579,107 | 3,858,093 |
| Khulna | 855,650 | 1,388,425 |
| Rajshahi | 472,775 | 775,495 |
| Sylhet | 463,198 | - |
| Barisal | 210,374 | - |
| Rangpur | 251,699 | - |
| Natore | 152,359 | - |
Geography and climate
Main article: Geography of Bangladesh
Bangladesh is in the low-lying Ganges–Brahmaputra River Delta or Ganges Delta. This delta is formed by the confluence of the Ganges (local name Padma or Pôdda), Brahmaputra (Jamuna or Jomuna), and Meghna rivers and their respective tributaries. The Ganges unites with the Jamuna (main channel of the Brahmaputra) and later joins the Meghna to eventually empty into the Bay of Bengal. The alluvial soil deposited by these rivers has created some of the most fertile plains in the world. Bangladesh has 57 trans-boundary rivers, making water issues politically complicated to resolve – in most cases as the lower riparian state to India. Most parts of Bangladesh are less than 12 m (39.4 ft) above the sea level, and it is believed that about 10% of the land would be flooded if the sea level were to rise by 1 m (3.28 ft).
In south east Bangladesh experiments have been done since the sixties to 'build with nature'. By implementing cross dams, the natural accretion of silt has created new land. With Dutch funding, the Bangladeshi government began to help develop this new land in the late 1970s. The effort has since become a multiagency operation building roads, culverts, embankments, cyclone shelters, toilets and ponds, as well as distributing land to settlers. By fall 2010, the program will have allotted some 27,000 acres (10,927 ha) to 21,000 families.
The highest point in Bangladesh is in Mowdok range at 1,052 m (3,451 ft) in the Chittagong Hill Tracts to the southeast of the country.
Straddling the Tropic of Cancer, Bangladeshi climate is tropical with a mild winter from October to March, a hot, humid summer from March to June. A warm and humid monsoon season lasts from June to October and supplies most of the country's rainfall. Natural calamities, such as floods, tropical cyclones, tornadoes, and tidal bores occur almost every year, combined with the effects of deforestation, soil degradation and erosion. Cox's Bazar, south of the city of Chittagong, has a beach that stretches uninterrupted over 120 kilometres (75 mi).
In September 1998, Bangladesh saw the most severe flooding in modern world history. As the Brahmaputra, Ganges and Meghna spilt over and swallowed 300,000 houses, 9,700 kilometres (6,027 mi) of road and 2,700 kilometres (1,678 mi) of embankment 1,000 people were killed and 30 million more were made homeless with 135,000 cattle killed, 50 square kilometres (19.3 sq mi) of land destroyed and 11,000 kilometres (6,835 mi) of roads damaged or destroyed. Two-thirds of the country was underwater. There were several reasons for the severity of the flooding. Firstly, there were unusually high monsoon rains. Secondly, the Himalayas shed off an equally unusually high amount of melt water that year. Thirdly, trees that usually would have intercept rain water had been cut down for firewood or to make space for animals.
Bangladesh is now widely recognized to be one of the countries most vulnerable to climate change. Natural hazards that come from increased rainfall, rising sea levels, and tropical cyclones are expected to increase as climate change, each seriously affecting agriculture, water & food security, human health and shelter. It is believed that in the coming decades the rising sea level alone will create more than 20 million climate refugees. Bangladeshi water is contaminated with arsenic frequently because of the high arsenic contents in the soil. Up to 77 million people are exposed to toxic arsenic from drinking water.
Flora and fauna

A major part of the coastline comprises a marshy jungle, the Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest in the world and home to diverse flora and fauna, including the Royal Bengal Tiger. In 1997, this region was declared endangered. The Magpie Robin is the National Bird of Bangladesh and it is common and known as the Doyel or Doel (Template:Lang-bn). It is a widely used symbol in Bangladesh, appearing on currency notes and a landmark in the city of Dhaka is named as the Doyel Chatwar (meaning: Doyel Square).The national flower of the country is water lily, which is known as Shapla. The national fruit is jackfruit, which in Bengali is known as Kathal.
Economy
Main article: Economy of Bangladesh
Despite continuous domestic and international efforts to improve economic and demographic prospects, Bangladesh remains a developing nation. Its per capita income in 2008 was US$520 compared to the world average of $10,200.
Jute was once the economic engine of the country. Its share of the world export market peaked in the Second World War and the late 1940s at 80% and even in the early 1970s accounted for 70% of its export earnings. However, polypropylene products began to substitute for jute products worldwide and the jute industry started to decline. Bangladesh grows very significant quantities of rice, tea and mustard.
Although two-thirds of Bangladeshis are farmers, more than three quarters of Bangladesh’s export earnings come from the garment industry, which began attracting foreign investors in the 1980s due to cheap labour and low conversion cost. In 2002, the industry exported US$5 billion worth of products. The industry now employs more than 3 million workers, 90% of whom are women. A large part of foreign currency earnings also comes from the remittances sent by expatriates living in other countries.

Obstacles to growth include frequent cyclones and floods, inefficient state-owned enterprises, mismanaged port facilities, a growth in the labour force that has outpaced jobs, inefficient use of energy resources (such as natural gas), insufficient power supplies, slow implementation of economic reforms, political infighting and corruption. According to the World Bank, "among Bangladesh’s most significant obstacles to growth are poor governance and weak public institutions." Despite these hurdles, the country has achieved an average annual growth rate of 5% since 1990, according to the World Bank. Bangladesh has seen expansion of its middle class, and its consumer industry has also grown. In December 2005, four years after its report on the emerging "BRIC" economies (Brazil, Russia, India, and China), Goldman Sachs named Bangladesh one of the "Next Eleven", along with Egypt, Indonesia, Vietnam and seven other countries. Bangladesh has seen a dramatic increase in foreign direct investment. A number of multinational corporations and local big business houses such as Beximco, Square, Akij Group, Ispahani, Navana Group, Transcom Group, Habib Group, KDS Group, Dragon Group and multinationals such as Unocal Corporation and Chevron, have made major investments, with the natural gas sector being a priority. In December 2005, the Central Bank of Bangladesh projected GDP growth around 6.5%. In order to enhance economic growth, the government set up several export processing zones to attract foreign investment. These are managed by the Bangladesh Export Processing Zone Authority.
One significant contributor to the development of the economy has been the widespread propagation of microcredit by Muhammad Yunus (awarded the Nobel peace prize in 2006) through the Grameen Bank. By the late 1990s, Grameen Bank had 2.3 million members, along with 2.5 million members of other similar organisations.
Demographics
Main articles: Demographics of Bangladesh and Education in Bangladesh See also: Bengali people
Recent (2007–2010) estimates of Bangladesh's population range from 150 to 164 million and it is the 7th most populous nation in the world. It is also one of the most densely populated countries in the world. A striking contrast is offered by Russia which has a similar population spread over a land area that is 120 times larger than Bangladesh. Bangladesh's population growth was among the highest in the world in the 1960s and 1970s, when the country swelled from 50 to 90 million. With the promotion of birth control in the 1980s, the growth rate has slowed. The population is relatively young, with 60% being 25 or younger and only 3% being 63 or older. Life expectancy is 63 years for both males and females.
The overwhelming majority of Bangladeshis are ethnic Bengalis, comprising 98% of the population. The remainder are mostly Biharis and indigenous tribal groups. There is also a small but growing population of Rohingya refugees from Myanmar around Cox's Bazaar, which Bangladesh seeks to repatriate to Myanmar. The indigenous tribal peoples are concentrated in the Chittagong Hill Tracts in the southeast. There are thirteen tribal groups located in this region, the largest being the Chakma. The Hill Tracts region has been a source of unrest and separatism since and before the inception of Bangladesh. Outside the Hill Tracts, the largest tribal groups are the Santhals and Garos (Achiks), while smaller groups include the Kaibartta, Meitei, Mundas, Oraons, and Zomi.
Nearly all Bangladeshis speak Bengali as their mother tongue and it is the official language. It is an Indo-Aryan language of Sanskrit origin with its own script. English is used as a second language among the middle and upper classes. English is also widely used in higher education and the legal system. Historically, laws were written in English and translated into Bengali until 1987 when the procedure was reversed. The Bihari population speaks Urdu, which was also the language associated with the government prior to separation from Pakistan.
Health and education levels remain relatively low, although they have improved recently as poverty levels have decreased. Most Bangladeshis continue to live on subsistence farming in rural villages. Health problems abound, springing from poor water quality and prevalence of infectious diseases. The water crisis is acute, with widespread bacterial contamination of surface water and arsenic contamination of groundwater. Common diseases include malaria, leptospirosis and dengue. The literacy rate in Bangladesh rose to 53.5% in 2007. There is a gender gap, as literacy rates among women are 81.9% those among men, but this is disappearing in the younger generation. Among the most successful literacy programs are the Food for education (FFE) introduced in 1993, and a stipend program for women at the primary and secondary levels.
| Religion in Bangladesh | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Religion | Percent | |||
| Islam | 89.7% | |||
| Hinduism | 9.2% | |||
| Buddhism | 0.7% | |||
| Christianity | 0.3% | |||
| Animism | 0.1% | |||
The main religion practiced in Bangladesh is Islam (89.7%), but a significant minority adheres to Hinduism (9.2%). The majority of Muslims are Sunni. There is a small Shia and an even smaller Ahmadiyya community. Ethnic Biharis are predominantly Shia Muslims. Sufi influences in the region go back many centuries. Other religious groups include Buddhists (0.7%, mostly Theravada), Christians (0.3%, mostly of the Roman Catholic denomination), and Animists (0.1%). Bangladesh has the fourth largest Muslim population after Indonesia, Pakistan, and India, with over 130 million. Bangladesh was founded as a secular state, but Islam was briefly made the state religion, before returning by decree of the High Court to the principles of its 1972 constitution. The High Court also strengthened its stance against punishments by Islamic edict (fatwa), following complaints of brutal sentences carried out against women by extra-legal village courts.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Bangladesh See also: Public holidays in Bangladesh, Sport in Bangladesh, and Music of Bangladesh
Reflecting the long history of the region, Bangladesh has a culture that encompasses elements both old and new. The Bengali language boasts a rich literary heritage, which Bangladesh shares with the Indian state of West Bengal. The earliest literary text in Bengali is the 8th century Charyapada. Medieval Bengali literature was often either religious (e.g. Chandidas), or adapted from other languages (e.g. Alaol). Bengali literature reached its full expression in the nineteenth century, with its greatest icons being poets Rabindranath Tagore and Kazi Nazrul Islam. Bangladesh also has a long tradition in folk literature, for example Maimansingha Gitika, Thakurmar Jhuli and stories related to Gopal Bhar.
The musical tradition of Bangladesh is lyrics-based (Baniprodhan), with minimal instrumental accompaniment. The Baul tradition is a distinctive element of Bengali folk music. Numerous other musical traditions exist including Gombhira, Bhatiali and Bhawaiya, varying from one region to the next. Folk music is often accompanied by the ektara, an instrument with only one string. Other instruments include the dotara, dhol, flute and tabla. Bangladesh also has an active heritage in North Indian classical music. Similarly, Bangladeshi dance forms draw from folk traditions, especially those of the tribal groups, as well as the broader Indian dance tradition.
Bangladesh produces about 80 films a year. Mainstream Hindi films are also quite popular. Around 200 daily newspapers are published in Bangladesh, along with more than 500 periodicals. However, regular readership is low at just under 15% of the population. Bangladeshis listen to a variety of local and national radio programs like Bangladesh Betar. Four private FM radio stations named (Radio Foorti, ABC Radio, Radio Today, Radio Amar) are among urban youths. International Bengali language broadcasts include BBC Bangla and Voice of America. The dominant television channel is the state-owned Bangladesh Television, but in the last few years, privately owned channels have developed considerably.
The culinary tradition of Bangladesh has close relations to Indian and Middle Eastern cuisine as well as having its own unique traits. Rice, and curry are traditional favorites. Bangladeshis make distinctive sweetmeats from milk products, some common ones being Rôshogolla, chômchôm and kalojam.
The sari (shaŗi) is by far the most widely worn dress by Bangladeshi women. A guild of weavers in Dhaka is renowned for producing saris from exquisite Jamdani muslin. The salwar kameez (shaloar kamiz) is also quite popular, and in urban areas some women wear western attire. Among men, western attire is more widely adopted. Men also wear the kurta-paejama combination, often on religious occasions, and the lungi, a kind of long skirt.
Eid ul-Fitr and Eid ul-Adha, being the most important holidays in the Islamic calendar, are the subject of major festivals. The day before Eid ul-Fitr is called Chãd Rat (the night of the moon) and is often celebrated with firecrackers. Major Hindu festivals are Durga Puja, Kali Puja and Saraswati Puja. Buddha Purnima, which marks the birth of Gautama Buddha, and Christmas, called Bôŗodin (Great day), are both national holidays. The most important secular festival is Pohela Baishakh or Bengali New Year, the beginning of the Bengali calendar. Other festivities include Nobanno, Poush parbon (festival of Poush) and observance of national days like Shohid Dibosh and Victory Day.
Sports
Main article: Sports in Bangladesh
Cricket enjoys a passionate following in Bangladesh and it is the most popular sport followed by football (soccer). The national cricket team participated in their first World Cup in 1999, and the following year was granted elite Test cricket status. But they have struggled to date, recording only two Test match victories against Zimbabwe in 2005 and the West Indies in 2009. In July, 2010, they celebrated their first ever win over England in any form of match. In 2011, Bangladesh is going to host the ICC Cricket World Cup 2011 jointly with India and Sri Lanka.
Hadudu (Kabaddi) is the national sport of Bangladesh. Other popular sports include field hockey, tennis, badminton, handball, volleyball, chess, shooting and carrom. The Bangladesh Sports Control Board regulates twenty-nine different sporting federations.
See also
Main article: Outline of BangladeshReferences
- Constitution of Bangladesh, Part V, Chapter 1, Article 66; University of Minnesota, retrieved: 2010-08-28
- Department of Economic and Social Affairs
Population Division (2009). "World Population Prospects, Table A.1" (PDF). 2008 revision. United Nations. Retrieved 2009-03-12.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); line feed character in|author=at position 42 (help) - ^ "Bangladesh". International Monetary Fund. Retrieved 2010-04-21.
- "Human Development Report 2009. Human development index trends: Table G" (PDF). The United Nations. Retrieved 2009-10-05.
- http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5h_5T_bgbToWaGqK2gxXACMFuySog
- http://www.thedailystar.net/newDesign/news-details.php?nid=149233
- "Sandeep Mahajan, "Bangladesh: Strategy for Sustained Growth", Poverty Reduction and Economic Management Network, World Bank (July 26, 2007)". Web.worldbank.org. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- ^ Bangladesh – Country Brief, World Bank, July 2005
- Bharadwaj, G (2003). "The Ancient Period". In Majumdar, RC (ed.). History of Bengal. B.R. Publishing Corp.
- James Heitzman and Robert L. Worden, ed. (1989). "Early History, 1000 B.C.-A.D. 1202". Bangladesh: A country study. Library of Congress. ISBN 8290584083. OCLC 15653912.
- Eaton, R (1996). The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier. University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-20507-3. OCLC 26634922 76881262.
{{cite book}}: Check|oclc=value (help) - Baxter, C (1997). Bangladesh, from a Nation to a State. Westview Press. ISBN 0-8133-3632-5. OCLC 47885632.
- Baxter, pp.30–32
- ^ Sen, Amartya (1973). Poverty and Famines. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-828463-2. OCLC 10362534 177334002 191827132 31051320 40394309 53621338 63294006.
{{cite book}}: Check|oclc=value (help) - Baxter, pp. 39–40
- Collins, L (1986). Freedom at Midnight, Ed. 18. Vikas Publishers, New Delhi. ISBN 0-7069-2770-2.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|unused_data=ignored (help) - Baxter, p. 72
- Baxter, pp. 62–63
- Bangladesh cyclone of 1991. Britannica Online Encyclopedia.
- Baxter, pp. 78–79
- Salik, Siddiq (1978). Witness to Surrender. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-577264-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|unused_data=ignored (help) - Rummel, Rudolph J., "Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900", ISBN 3-8258-4010-7, Chapter 8, table 8.1. Rummel comments that, In East Pakistan (now Bangladesh) also planned to murder its Bengali intellectual, cultural, and political elite. They also planned to indiscriminately murder hundreds of thousands of its Hindus and drive the rest into India. And they planned to destroy its economic base to insure that it would be subordinate to West Pakistan for at least a generation to come. This despicable and cutthroat plan was outright genocide.
- LaPorte, R (1972). "Pakistan in 1971: The Disintegration of a Nation". Asian Survey. 12(2): 97–108.
- Rummel, Rudolph J., "Statistics of Democide: Genocide and Mass Murder Since 1900", ISBN 3-8258-4010-7, Chapter 8, Table 8.2 Pakistan Genocide in Bangladesh Estimates, Sources, and Calcualtions.
- ^ Mascarenhas, A (1986). Bangladesh: A Legacy of Blood. Hodder & Stoughton, London. ISBN 0-340-39420-X. OCLC 13004864 16583315 242251870.
{{cite book}}: Check|oclc=value (help) - "Bangladesh tops most corrupt list". BBC News. 2005-10-18. Retrieved 2007-04-13.
- "Bangladesh election seen as fair, though loser disputes result". New York Times. 2008-11-30.
- "Hasina takes oath as new Bangladesh prime minister". Reuters. 2009-01-06. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- Constitution of Bangladesh
- Background Note: Bangladesh, US Department of State, May 2007
- ^ Khan, Zillur R. (1997). "Bangladesh's experiments with parliamentary democracy". Asian Survey. 37 (6): 575–589. doi:10.1525/as.1997.37.6.01p0256x. Retrieved 4 September 2010.
- Bangladesh Today, Asia Report N°121, International Crisis Group, October 23, 2006
- http://www.google.com/hostednews/canadianpress/article/ALeqM5gZfzaIgc4BxQNDfs8-VBX--KgzPA
- "cpi 2008 table /cpi2008/2008/in focus/news room". Transparency.org. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- "Bangladesh Election Commission". 123.49.39.5. 2009-04-02. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- ^ Ali, M.M. (March 1997). "India's Major Gains and Losses in World Affairs". Washington Report on Middle East Affairs. Retrieved 2008-04-29.
- India quietly ringing Bangladesh with barbed-wire, cutting off former neighbors, by Tim Sullivan, Associated Press, June 25, 2007
- Pattanaik, Smruti S., "India-Bangladesh Relations after the Foreign Secretary Level Talks," Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses, July 17, 2007.
- ^ Bangladesh Military Forces. Retrieved 12 June 2009.
- Including service and civilian personnel. See Bangladesh Navy. Retrieved July 17, 2007.
- "TOTAL BD PARTICIPATION IN UN DEPL (COMPLETED)". Bangladesh Army. 2007. Archived from the original on June 11, 2008. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - "Bangladeshi officers enhance UN troops' logistical support in Darfur". UN News Center. United Nations. 2008-10-23. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- <http://www.bdnews24.com/details.php?cid=2&id=151976&hb=top>
- ^ CIA World Factbook 2007
- Local Government Act, No. 20, 1997
- ^ "Statistical pocket book Bangladesh – 2008" (PDF). Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2009-10-10.
- Suvedī, Sūryaprasāda (2005). International watercourses law for the 21st century. Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. pp. 154–166. ISBN 0754645274.
- Ali, A (1996). "Vulnerability of Bangladesh to climate change and sea level rise through tropical cyclones and storm surges". Water, Air, & Soil Pollution. 92 (1–2): 171–179. doi:10.1007/BF00175563.
- ""Bangladesh fights for survival against climate change," by William Wheeler and Anna-Katarina Gravgaard, The Washington Times". Pulitzercenter.org. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- Summit Elevations: Frequent Internet Errors.. Retrieved 2006-04-13.
- Alexander, David E. (1999) . "The Third World". Natural Disasters. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers. p. 532. ISBN 0412047519. OCLC 27974924 43782866. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite book}}: Check|oclc=value (help); Cite has empty unknown parameters:|origmonth=,|chapterurl=,|origdate=, and|month=(help) - Haggett, Peter (2002) . "The Indian Subcontinent". Encyclopedia of World Geography. New York: Marshall Cavendish. pp. 2, 634. ISBN 0761473084. OCLC 46578454. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameters:|origmonth=,|chapterurl=,|month=, and|origdate=(help) - Bangladesh Climate Change Strategy and Action Plan 2008 Ministry of Environment and Forests Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh, September, 2008.
- The Climate refugee Challenge, ReliefWeb, 2009-04-14
- "Another Major Cyclone, Bangladesh Worries About Climate Change", PBS News Hour, 2008
- By Brian Walker, CNN (2010-06-21). "Study: Millions in Bangladesh exposed to arsenic in drinking water". CNN.com. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - "Bangladesh: 77m poisoned by arsenic in drinking water". BBC News. 2010-06-19. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- IUCN (1997). "Sundarban wildlife sanctuaries Bangladesh". World Heritage Nomination-IUCN Technical Evaluation.
- "Reproductive Health and Rights is Fundamental for Sound Economic Development and Poverty Alleviation," United Nations Population Fund. Retrieved July 17, 2007.
- Wood, Geoffrey D. (1994). Bangladesh: Whose ideas, whose interests?. Intermediate Technology Publications. p. 111. ISBN 1853392464.
- Roland, B (January 6, 2005). "Bangladesh Garments Aim to Compete". BBC. Retrieved January 1, 2010.
- Rahman, S (2004). "Global Shift: Bangladesh Garment Industry in Perspective". Asian Affairs. 26 (1): 75–91.
- Begum, N (2001). "Enforcement of Safety Regulations in Garment sector in Bangladesh". Proc. Growth of Garment Industry in Bangladesh: Economic and Social dimension. pp. 208–226.
- "South Korea, Another `BRIC' in Global Wall". 2005-12-09.
- "Annual Report 2004–2005, Bangladesh Bank". Bangladesh-bank.org. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- Schreiner, Mark (2003). "A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of the Grameen Bank of Bangladesh". Development Policy Review. 21 (3): 357–382. doi:10.1111/1467-7679.00215.
- "World Health Report 2005". World Health Organization.
- "Background Note: Bangladesh". Accessed June 11, 2008.
- Rashiduzzaman, M (1998). "Bangladesh's Chittagong Hill Tracts Peace Accord: Institutional Features and Strategic Concerns". Asian Survey. 38 (7): 653–670. doi:10.1525/as.1998.38.7.01p0370e.
- Constitution of Bangladesh, Part I, Article 5.
- S. M. Mehdi Hasan, Condition of English in Bangladesh: Second Language or Foreign Language. Retrieved July 17, 2007.
- "Strengthening the criminal justice system, chapter 4, Enhancing access to Law and Information". Asian Development Bank. January 2007.
- Nickson, R (1998). "Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater". Nature. 395 (6700): 338. doi:10.1038/26387. PMID 9759723.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ "Human Development Report 2009". UNDP.
- Ahmed, A (2002). The food for education programme in Bangladesh: An evaluation of its impact on educational attainment and food security, FCND DP No. 138. International Food Policy Research Institute.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Khandker, S (2003). Subsidy to Promote Girls’ Secondary Education: The Female Stipend Program in Bangladesh. World Bank, Washington, DC.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - "Bangladesh Bureau of Educational Information and Statistics". Banbeis.gov.bd. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- "Community: Sufism in Bangladesh". Sufism Journal. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
- Verdict paves way for secular democracy The Daily Star. July 30, 2010. Retrieved on 2010-08-22.
- Andrew Buncombe (July 11, 2010). "Bangladeshi court outlaws fatwa punishments". London: The Independent. Retrieved July 11, 2010.
- London, Ellen (2004). Bangladesh. Gareth Stevens Pub. p. 29. ISBN 0836831071.
- Logan, Stephen (2008). Asian communication handbook 2008. AMIC. p. 115. ISBN 9814136107.
- Reuters (2006-09-25). "Cinemas in Bangladesh, Pakistan squeezed by Bollywood". NewIndPress.Com. Retrieved 2008-05-02.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help); Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Islam, Roumeen (2002). The right to tell: the role of mass media in economic development. World Bank Publications. p. 268. ISBN 0821352032.
- "BBC News". BBC News. 2009-07-20. Retrieved 2010-07-03.
External links
- Official website
- "Bangladesh". The World Factbook (2025 ed.). Central Intelligence Agency.
- Template:Dmoz
 Wikimedia Atlas of Bangladesh
Wikimedia Atlas of Bangladesh- Template:Wikitravel
| Bangladesh articles | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| History |
| ||||||||||||||
| Geography | |||||||||||||||
| Politics |
| ||||||||||||||
| Economy |
| ||||||||||||||
| Society |
| ||||||||||||||
| Geographic locale | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Template:Countries and territories of South Asia
| |||||||||||||||||||
Template:Link FA Template:Link GA
Categories:- Bangladesh
- South Asian countries
- Countries of the Indian Ocean
- Bengal
- Developing 8 Countries member states
- Divided regions
- Least Developed Countries
- Liberal democracies
- Members of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Organisation of the Islamic Conference members
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation member states
- States and territories established in 1971
- Former British colonies