| Revision as of 10:41, 18 August 2010 editCunibertus (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users2,560 edits Undid revision 379130247 by ZjarriRrethues (talk)← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 15:45, 24 October 2024 edit undo93.66.66.250 (talk)No edit summary | ||
| (155 intermediate revisions by 96 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{short description|Ancient people of Sicily}} | |||
| ] | |||
| The '''Sicani''' (] ''Σικανοί'' - ''Sikanoi'') or '''Sicanians''' were one of three ] of ] present at the time of ]n and ] colonization. | |||
| ] and the ], in ] around 11th century BC (before the arrival of the ] and the ]).]] | |||
| The '''Sicani''' or '''Sicanians''' were one of three ]s of ] present at the time of ]n and ] ]. The Sicani dwelt east of the ] and west of the ], having, according to ],<ref>Diod., v.6.3-4</ref> the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river (]) after a series of battles between these tribes. | |||
| ==History== | ==History== | ||
| The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian ],<ref>Thucydides, ''His.'' VI,2,3,4.</ref> claims that the Sicani originated on the ], from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the ].<ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.experiencefestival.com/a/Sicily_-_History/id/5462681|publisher=Experience Festival|title=Sicily: Encyclopedia II – Sicily – History|date=7 October 2007|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20131231001248/http://www.experiencefestival.com/a/Sicily_-_History/id/5462681|archivedate=31 December 2013}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=A7kGAAAAQAAJ&q=segre+sicano&pg=PA11|publisher=Ensayo historico|title=Aapologetico de la literatura española contra los opiniones|date=7 October 2007}}</ref> (The name Sicanus has been linked to the modern river known in ] as the ].) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian ].<ref>{{cite news|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=L-VmL59CfkcC&q=Thucydides+Sicani&pg=PA47|title=Greek Identity in the Western Mediterranean|year=2004|isbn=9004133003|last1=Shefton|first1=Brian Benjamin|last2=Lomas|first2=Kathryn|publisher=BRILL }}</ref> Conversely, ] of ] (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily.<ref>As reported in ] V,6,1-3.</ref> A third theory, put forward by some modern scholars, suggests that the Sicani were immigrants, who gained control of areas previously inhabited by native tribes.<ref>{{cite book|last=Fine|first=John|title=The ancient Greeks: a critical history|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NjeM0kcp8swC&q=most+scholars+now+believe+that+the+sicans+and+Sicels,+as+well+as+the&pg=PA72|year=1985|publisher=Harvard University Press|isbn=0-674-03314-0|page=72}}</ref> The testimony of a Sicanian migration by land is supported by ] geographer ], who does not seem to depend on Thucydides when he asserts that three peoples arrived in Sicily: Sicani, ] and ]: the first two came from Italy, while the third came from ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Pausanias, Description of Greece, Elis 1, chapter 25, section 6|url=http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Paus.%205.25.6&lang=original|access-date=2021-12-26|website=www.perseus.tufts.edu}}</ref> ] and ] also mention the Sicani, among the peoples of the Mount Albanus league in the ].<ref>], '']'', III, 56; III, 69.</ref><ref>{{Cite book|last=Arias|first=Paolo Enrico|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ADk_AQAAIAAJ|title=Problemi sui Siculi e sugli Etruschi|date=1943|publisher=Crisafulli|language=it}}</ref> The Sicans are mentioned in ]'s ] as allies of the ], ] and Sacrani of Old Latium.<ref>], '']'', VII, 795; VIII, 328; XI, 317;</ref> ] and ] remember them with the Aurunci and the ].<ref>], ''Attic Nights'', I, 10.</ref><ref>], '']'', I, 5.</ref> Archaeological research suggests that the Sicani were influenced at an early stage by the ] (prior to the Greek colonisation of Sicily).<ref>Fine, p.72</ref> | |||
| The Sicani are thought to be the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name.{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} Most modern scholars believe that the Sicani were originally an ] tribe that gained control of areas previously inhabited by native tribes.<ref>{{cite book|last=Fine|first=John|title=The ancient Greeks: a critical history|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=NjeM0kcp8swC&printsec=frontcover&dq=inauthor:%22John+Van+Antwerp+Fine%22&hl=el&ei=ZX5oTOWuM9GTOJKvzbgF&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=3&ved=0CDMQ6AEwAg#v=onepage&q=Sicans&f=false|year=1985|publisher=Harvard University Press|isbn=0674033140|page=72}}</ref> Archaeological excavation has shown that they had received some ] influence. The Greek historian ] claimed they immigrated from ], but his basis for saying this is unknown.<ref>{{cite news|http://books.google.com/books?id=L-VmL59CfkcC&pg=PA47&lpg=PA47&dq=Thucydides+Sicani&source=web&ots=pFiBFCDMUE&sig=Yhc2JLurSz8Is4r1lRLl3STfu4Q&hl=en&sa=X&oi=book_result&resnum=4&ct=result|title=Greek Identity in the Western Mediterranean|year=2004}}</ref> The ] are thought to be the next recorded people to settle Sicily, perhaps from the ] or ].{{Citation needed|date=August 2010}} They settled in the north-west of the island. The ] were the next to arrive, from mainland ], perhaps ]{{Citation needed|date=October 2009}}, and settled in the east. Historical records start with the Phoenicians, who established colonies in the 11th century BCE, and especially with the Greeks, who founded the colony of ], which eventually became the largest Greek city, in 734 BCE. Other Greek colonies were established around the island. The indigenous Sicilians were gradually absorbed by these colonizing peoples and finally disappeared as distinct peoples under Roman occupation. | |||
| It is generally agreed by scholars that the Sicani preceded other inhabitants of Sicily in prehistory, namely the ] and ]. The former are thought to be the next recorded people to settle Sicily. According to ], Elymians were a population of ] origin, who arrived in Sicily after having fought a war with the ].<ref>{{Cite web|title=Gli Elimi: storia e archeologia di Segesta, Erice, Entella|url=http://www.arkeomania.com/origineelimi.html|access-date=2021-12-26|website=www.arkeomania.com}}</ref> They settled in the north-west corner of the island, forcing the Sicanians to move across eastward. The Sicels were the next to arrive, from mainland ], and settled in the east. The arrival of the Sicels is thought to have occurred during the thirteenth or eleventh century BCE. The Sicanians area after this became limited to the south-western part of the island with settlements in the area of ] and ].<ref>{{cite book |last1=Le Glay |first1=Marcel |title=A history of Rome |date=2009 |publisher=Wiley-Blackwell |isbn=978-1-4051-8327-7 |oclc=760889060 }}{{pn|date=May 2020}}</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==Language== | ||
| A few short inscriptions using the ] have been found in the extinct Sicanian language.<ref>''The World's Writing Systems.'' 1996:301.</ref> Except for names they have not been translated, and the language is ] due to lack of data.<ref></ref> | |||
| The Sicani enter the historical record with the Phoenicians, who established colonies during the 11th century BCE – preceding the Greeks, who founded the colony of ]. While many other Greek colonies were established around the island, by ] Syracuse had become the largest city in the Greek-speaking world. The Sicani were gradually absorbed by these colonizing peoples. They disappeared as a distinct people following the annexation of Sicily by the Roman Republic. | |||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| ⚫ | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
| ==Herodotus and King Minos== | |||
| ], according to tradition, went to Sicania, or Sicily, as it is now called, in search of ], and there perished by a violent death.<ref>Herodotus, ''The History'', George Rawlinson, trans., (New York: Dutton & Co., 1862</ref> | |||
| ⚫ | ==Language== | ||
| {{Infobox language | |||
| | name = Sicanian | |||
| | altname = Sicana | |||
| | region = ] | |||
| | extinct = {{Citation needed span|approximately 300 BCE|date=November 2023}} | |||
| | familycolor = unclassified | |||
| | iso3 = sxc | |||
| | linglist = sxc | |||
| | glotto = sica1234 | |||
| | glottorefname = Sicana | |||
| | map = Sicily prehellenic topographic map.svg | |||
| | mapcaption = Approximate locations of the Sicani and their neighbors, the ] and the ], in ] around 11th century BC (before the arrival of the ] and the ]). | |||
| | map2 = Sicilia arcaica.jpg | |||
| | mapcaption2 = Tribes of Hellenic Sicily | |||
| | script = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| A few short inscriptions using the ] have been found in the extinct Sicanian language.<ref>''The World's Writing Systems.'' 1996:301.</ref> Except for names, they have not been translated, and the language is ] due to lack of data.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://linguistlist.org/forms/langs/LLDescription.cfm?code=sxc |title='Sicanian' at Linguist List |access-date=2008-07-28 |archive-date=2012-03-01 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120301201422/http://linguistlist.org/forms/langs/LLDescription.cfm?code=sxc |url-status=dead }}</ref> Due to the lack of clear linguistic or cultural boundaries between Sicani and Sicel areas to the east, the existence of Sicanian as a distinct language is open to question; it is also unclear whether Sicanian survived as a language as late as the classical period, even in spoken form. On the other hand, the term ''Sicanian'' remains useful as a means of identifying the older, possibly non-Indo-European linguistic substrate, geographically overlaid by later arrivals such as Sicel and Elymian.<ref name="Tribulato"/> Recurring suffixes like -''ina'', -''ana'', -''ara'', -''ssus'' and -''ssa'' are often found in Sicanian place names (e.g. Camarina, Telmissus and Cimissa), and are thus proposed as a good starting point for identifying Sicanian towns. These tentatively-identified "Sicanian" toponyms seem to display similarities with other non-Indo-European substratal languages within the proposed ], although these proposed connections remain nebulous.<ref name="Tribulato">{{cite book |last1=Tribulato |first1=Olga |title=Language and Linguistic Contact in Ancient Sicily |date=29 November 2012 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |isbn=9781139851930 |page=164-166}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 37: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| ⚫ | ==References== | ||
| ⚫ | {{Reflist|2}} | ||
| ==External links== | |||
| * | |||
| * by Vincenzo Salerno | |||
| {{Eurasian languages}} | |||
| {{Languages of Sicily|state=expanded}} | |||
| {{Coord missing|Italy}} | {{Coord missing|Italy}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ⚫ | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:45, 24 October 2024
Ancient people of Sicily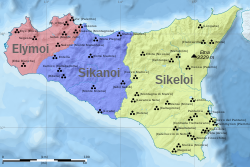
The Sicani or Sicanians were one of three ancient peoples of Sicily present at the time of Phoenician and Greek colonization. The Sicani dwelt east of the Elymians and west of the Sicels, having, according to Diodorus Siculus, the boundary with the last in the ancient Himera river (Salso) after a series of battles between these tribes.
History
The Sicani are the oldest inhabitants of Sicily with a recorded name. In the 5th century BCE, the Greek historian Thucydides, claims that the Sicani originated on the Iberian Peninsula, from around a river they called "Sicanus" and had migrated to Sicily following an invasion by the Ligurians. (The name Sicanus has been linked to the modern river known in Spanish as the Júcar.) Thucydides' source is unknown, although he often draws on the Sicilian historian Antiochus of Syracuse. Conversely, Timaeus of Tauromenium (writing c. 300 BCE) considers the Sicani to be indigenous to Sicily. A third theory, put forward by some modern scholars, suggests that the Sicani were immigrants, who gained control of areas previously inhabited by native tribes. The testimony of a Sicanian migration by land is supported by Greek geographer Pausanias, who does not seem to depend on Thucydides when he asserts that three peoples arrived in Sicily: Sicani, Sicels and Phrygians: the first two came from Italy, while the third came from Troy. Pliny the Elder and Gaius Julius Solinus also mention the Sicani, among the peoples of the Mount Albanus league in the Old Latium. The Sicans are mentioned in Virgil's Aeneid as allies of the Rutuli, Aurunci and Sacrani of Old Latium. Aulus Gellius and Macrobius remember them with the Aurunci and the Pelasgians. Archaeological research suggests that the Sicani were influenced at an early stage by the Mycenaeans (prior to the Greek colonisation of Sicily).
It is generally agreed by scholars that the Sicani preceded other inhabitants of Sicily in prehistory, namely the Elymians and Sicels. The former are thought to be the next recorded people to settle Sicily. According to Hellanicus of Lesbos, Elymians were a population of Italic origin, who arrived in Sicily after having fought a war with the Oenotrians. They settled in the north-west corner of the island, forcing the Sicanians to move across eastward. The Sicels were the next to arrive, from mainland Italy, and settled in the east. The arrival of the Sicels is thought to have occurred during the thirteenth or eleventh century BCE. The Sicanians area after this became limited to the south-western part of the island with settlements in the area of Gela and Agrigentum.
The Sicani enter the historical record with the Phoenicians, who established colonies during the 11th century BCE – preceding the Greeks, who founded the colony of Syracuse. While many other Greek colonies were established around the island, by 734 BCE Syracuse had become the largest city in the Greek-speaking world. The Sicani were gradually absorbed by these colonizing peoples. They disappeared as a distinct people following the annexation of Sicily by the Roman Republic.
Herodotus and King Minos
Minos, according to tradition, went to Sicania, or Sicily, as it is now called, in search of Daedalus, and there perished by a violent death.
Language
| Sicanian | |
|---|---|
| Sicana | |
| Region | Sicily |
| Extinct | approximately 300 BCE |
| Language family | unclassified
|
| Writing system | Greek script |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | sxc |
| Linguist List | sxc |
| Glottolog | sica1234 |
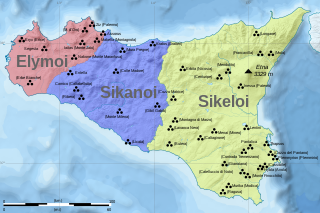 Approximate locations of the Sicani and their neighbors, the Elymians and the Sicels, in Sicily around 11th century BC (before the arrival of the Phoenicians and the Greeks). Approximate locations of the Sicani and their neighbors, the Elymians and the Sicels, in Sicily around 11th century BC (before the arrival of the Phoenicians and the Greeks). | |
 Tribes of Hellenic Sicily Tribes of Hellenic Sicily | |
A few short inscriptions using the Greek alphabet have been found in the extinct Sicanian language. Except for names, they have not been translated, and the language is unclassified due to lack of data. Due to the lack of clear linguistic or cultural boundaries between Sicani and Sicel areas to the east, the existence of Sicanian as a distinct language is open to question; it is also unclear whether Sicanian survived as a language as late as the classical period, even in spoken form. On the other hand, the term Sicanian remains useful as a means of identifying the older, possibly non-Indo-European linguistic substrate, geographically overlaid by later arrivals such as Sicel and Elymian. Recurring suffixes like -ina, -ana, -ara, -ssus and -ssa are often found in Sicanian place names (e.g. Camarina, Telmissus and Cimissa), and are thus proposed as a good starting point for identifying Sicanian towns. These tentatively-identified "Sicanian" toponyms seem to display similarities with other non-Indo-European substratal languages within the proposed Aegean language family, although these proposed connections remain nebulous.
See also
References
- Diod., v.6.3-4
- Thucydides, His. VI,2,3,4.
- "Sicily: Encyclopedia II – Sicily – History". Experience Festival. 7 October 2007. Archived from the original on 31 December 2013.
- "Aapologetico de la literatura española contra los opiniones". Ensayo historico. 7 October 2007.
- Shefton, Brian Benjamin; Lomas, Kathryn (2004). "Greek Identity in the Western Mediterranean". BRILL. ISBN 9004133003.
- As reported in Diodorus Siculus V,6,1-3.
- Fine, John (1985). The ancient Greeks: a critical history. Harvard University Press. p. 72. ISBN 0-674-03314-0.
- "Pausanias, Description of Greece, Elis 1, chapter 25, section 6". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2021-12-26.
- Pliny the Elder, Naturalis Historia, III, 56; III, 69.
- Arias, Paolo Enrico (1943). Problemi sui Siculi e sugli Etruschi (in Italian). Crisafulli.
- Virgil, Aeneid, VII, 795; VIII, 328; XI, 317;
- Aulus Gellius, Attic Nights, I, 10.
- Macrobius, Saturnalia, I, 5.
- Fine, p.72
- "Gli Elimi: storia e archeologia di Segesta, Erice, Entella". www.arkeomania.com. Retrieved 2021-12-26.
- Le Glay, Marcel (2009). A history of Rome. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-8327-7. OCLC 760889060.
- Herodotus, The History, George Rawlinson, trans., (New York: Dutton & Co., 1862
- The World's Writing Systems. 1996:301.
- "'Sicanian' at Linguist List". Archived from the original on 2012-03-01. Retrieved 2008-07-28.
- ^ Tribulato, Olga (29 November 2012). Language and Linguistic Contact in Ancient Sicily. Cambridge University Press. p. 164-166. ISBN 9781139851930.
External links
- The death of Minos in Sicily
- Sicilian Peoples: The Sicanians by Vincenzo Salerno
| Language families of Eurasia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | |||||||
| West Asia | |||||||
| Caucasus | |||||||
| South Asia | |||||||
| East Asia | |||||||
| Indian Ocean rim | |||||||
| North Asia |
| ||||||
| Proposed groupings |
| ||||||
| Substrata | |||||||
| |||||||
| Languages of Sicily | |
|---|---|
| Official languages | |
| Contemporary languages | |
| Historical languages | |
Categories: