| Revision as of 14:48, 21 March 2013 editCarolmooredc (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers31,944 edits →China: books/scholar/news/general google search show no use "separation barrier" relevant to China EXCEPT mirrors of or quotes from this article← Previous edit | Revision as of 03:09, 22 March 2013 edit undoReaper Eternal (talk | contribs)Edit filter managers, Checkusers, Administrators62,582 editsm Reverted edits by Jemkiranm (talk) to last version by GeorgeLouisNext edit → | ||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| ==Current separation barriers== | ==Current separation barriers== | ||
| ===Cyprus=== | ===Cyprus=== | ||
| Since ] ] has constructed and maintains a separation barrier of {{convert|300|km|mi}} along the 1974 Green Line (or ceasefire line) dividing the ] into two parts |
Since the ] ] has constructed and maintains a separation barrier of {{convert|300|km|mi}} along the 1974 Green Line (or ceasefire line) dividing the ] into two parts along the ].<ref>Rongxing Guo, ''Territorial Disputes and Resource Management: A Global Handbook'', Nova Publishers, 2006, , | ||
| ISBN 1600214452, 9781600214455</ref> | |||
| *] | |||
| ===Egypt=== | |||
| {{Unreferenced section|date=October 2010}} | |||
| A security fence around the Egyptian town of ] was constructed in response to a spate of terrorist attacks at the resort. Government officials say the fence, equipped with checkpoints to allow vehicles into the area, will deter terrorists. In addition South Sinai Governor Mustafa Afifi said the fence will help control the effect of heavy seasonal rains and will reduce the number of vehicle-camel crashes that occur on the Sharm el-Sheik highway. | |||
| ⚫ | The Rafah Border Crossing (Arabic: معبر رفح, Hebrew: מעבר רפיח) |
||
| ===Greece=== | |||
| {{See also|Greek–Turkish relations}} | |||
| After having made an agreement with ] on the guard of the maritime borders of ] with ]<ref>http://www.frontex.europa.eu/newsroom/news_releases/art74.html</ref>{{dead link|date=February 2013}} the Greek government decided a wall to be built at the land border with Turkey, the ].<ref>http://www.theinsider.gr/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=9282:wall-against-immigrants-in-evros&catid=3:society&Itemid=41</ref>{{Verify source|date=February 2013}} These actions have been made as a reaction to the illegal immigration to Greece through the Greco-Turkish borders. These immigrants are originated from ] ]n and ]n states. From January to the beginning of November 2010, 32,500 illegal migrants were intercepted in a single 12.5-kilometer stretch of the Turkish-Greek border along the Evros river.Actually this site is the main entrance of illegal immigrants to the ] from the Asian continent.<ref>http://www.hurriyetdailynews.com/n.php?n=greek--barrier-on-border-with-turkey-to-keep-out-migrants-2011-01-02</ref>{{Failed verification|date=February 2013}} Illegal immigration is a current subject between the two countries. | |||
| ===India=== | ===India=== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 29: | ||
| ===Iraq=== | ===Iraq=== | ||
| On 10 April 2007, the ] began constructing a 3.6 metre (12 ft) high concrete ] of {{convert|5|km|mi}} around the predominantly ] district of ] in ].{{Citation needed|date=March 2013}} | On 10 April 2007, the ] began constructing a 3.6 metre (12 ft) high concrete ] of {{convert|5|km|mi}} around the predominantly ] district of ] in ].{{Citation needed|date=March 2013}} | ||
| *] | |||
| Writer ] described as a "separation barrier" the ] constructed by the United Nations in 1991 after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. It is made of electrified fencing and concertina wire, and includes a 15 foot deep and wide trench and a high earthen berm. It runs 120 miles along the border between the two nations.<ref>Damon DiMarco, ''Heart of War: Soldiers? Voices'', Citadel Press, 2007, , ISBN 0806528141, 9780806528144</ref> | |||
| ===Israel=== | ===Israel=== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 41: | ||
| ** The barrier on the Syrian border on the ] reflects the situation in the aftermath of the ], when Israel retained the territory conquered in 1967 except for handing back the town of ]. The Syrian government has repeatedly demanded the return of the entire Golan, but has made no specific issue of Israel erecting a security barrier along the border as it presently stands. | ** The barrier on the Syrian border on the ] reflects the situation in the aftermath of the ], when Israel retained the territory conquered in 1967 except for handing back the town of ]. The Syrian government has repeatedly demanded the return of the entire Golan, but has made no specific issue of Israel erecting a security barrier along the border as it presently stands. | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ⚫ | * The ] includes the Rafah Border Crossing (Arabic: معبر رفح, Hebrew: מעבר רפיח), an international border crossing between Egyptian and Palestinian-controlled Rafah. It was built by the Israeli and Egyptian governments after the 1979 Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty and 1982 Israeli withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula, and was managed by the Israel Airports Authority until it was evacuated on 11 September 2005 as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan. It has since become the mission of the European Union Border Assistance Mission Rafah (EUBAM) to monitor the crossing. | ||
| * ]: Israel saw no need to fortify the ] border with Egypt after the 1979 Israeli-Egyptian Peace Treaty. The fence along that border was always more a marker than an effective barrier, and has become rusty and swamped by shifting sand dunes. The porous border has become the scene of extensive ] and the smuggling of women, typically from Third World and East European countries, who are subsequently forced into ], as well as the entry of various refugees, asylum-seekers and illegal immigrants from various African countries, notably ]ese fleeing the ] in ]. There were also isolated cases of infiltration by armed Palestinians, and apprehension that they would increase. In December 2005 the government of Israel proposed building a £200 million security barrier along the Egyptian border, but as of late 2007 the funds have not been actually allocated. | |||
| * ]: The border of Israel's territory with Jordan, mostly in the ] Desert along the ], is considered the most peaceful of the country's borders, due to traditional good relations with Jordan's ] Dynasty. In March 2004, Israel and Jordan commenced a joint project to build a desert science centre on their shared border. They have taken down a stretch of the border fence between the ] and the ] for the campus. | * ]: The border of Israel's territory with Jordan, mostly in the ] Desert along the ], is considered the most peaceful of the country's borders, due to traditional good relations with Jordan's ] Dynasty. In March 2004, Israel and Jordan commenced a joint project to build a desert science centre on their shared border. They have taken down a stretch of the border fence between the ] and the ] for the campus. | ||
| ** As well as the in the Negev, Israel also controls the ]'s border with Jordan in the ]. Along this border there is a security barrier with a two-way aim, designed to stop both infiltration from Jordan into the Israeli-controlled territory and the passage of West Bank Palestinians, uncontrolled by Israeli officials, into Jordan. | ** As well as the in the Negev, Israel also controls the ]'s border with Jordan in the ]. Along this border there is a security barrier with a two-way aim, designed to stop both infiltration from Jordan into the Israeli-controlled territory and the passage of West Bank Palestinians, uncontrolled by Israeli officials, into Jordan. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 48: | ||
| ** The ] involves a security barrier along Israel's ]. There is also the security barrier along the Gaza Strip's border with Egypt (see ]), erected when Israel was in direct military control of the area. Though Israeli forces were withdrawn in 2005, the Government of Israel retains a declared interest in the area, especially due to alleged large-scale smuggling of arms from Sinai into the Strip, and insists upon the Egyptians and Palestinians maintaining intact the barrier between their respective territories – such insistence backed by sometimes open threats to otherwise resume direct Israeli military control. This has been cited by Palestinians and others who assert that the Gaza Strip remains an Occupied Territory despite the Israeli ] in 2005. | ** The ] involves a security barrier along Israel's ]. There is also the security barrier along the Gaza Strip's border with Egypt (see ]), erected when Israel was in direct military control of the area. Though Israeli forces were withdrawn in 2005, the Government of Israel retains a declared interest in the area, especially due to alleged large-scale smuggling of arms from Sinai into the Strip, and insists upon the Egyptians and Palestinians maintaining intact the barrier between their respective territories – such insistence backed by sometimes open threats to otherwise resume direct Israeli military control. This has been cited by Palestinians and others who assert that the Gaza Strip remains an Occupied Territory despite the Israeli ] in 2005. | ||
| ** The ] is being built as a fence with wide margins and sophisticated electronic surveillance in rural areas, and an eight-meter-high wall in urban areas. Of all Israel's separation barriers, it is the most controversial – between Israelis and Palestinians, internationally, and also inside the Israeli society itself. The controversy stems mainly from the government's decision not to follow Israel's 1949 Armistice lines (]) but rather build the barrier within the West Bank - in some stretches, deeply within. Opponents of the project (who usually call it "The Wall" rather than "Barrier" or "Fence") say that this proves its purpose is not to stop suicide bombers – which would be equally served by a fence along the Green Line – but by the intention, effectively, to annexe parts of the West Bank, especially those where ]s have been established, as well as water sources – and to define the future borders with Palestine unilaterally and ahead of negotiations. This position was supported by the ] at ], which ruled that Israel had the right to fortify its own border but that building a barrier inside an Occupied Territory constituted a violation of ]; the government of Israel, however, disputes this interpretation and refuses to abide by this ruling. For its part, the ] held that building inside the West Bank is in itself legal, but it but ordered some changes to the route of the barrier where the judges considered the original route to cause severe damage to Palestinian daily life – especially in separating Palestinian villagers from their land. Some radical Israeli groups, such as ], actively participate in protests against the barrier together with the villagers. As of late 2007, the barrier – originally slated to be completed by the end of 2005 – is far from complete, and further construction was stopped, officially for lack of funds. | ** The ] is being built as a fence with wide margins and sophisticated electronic surveillance in rural areas, and an eight-meter-high wall in urban areas. Of all Israel's separation barriers, it is the most controversial – between Israelis and Palestinians, internationally, and also inside the Israeli society itself. The controversy stems mainly from the government's decision not to follow Israel's 1949 Armistice lines (]) but rather build the barrier within the West Bank - in some stretches, deeply within. Opponents of the project (who usually call it "The Wall" rather than "Barrier" or "Fence") say that this proves its purpose is not to stop suicide bombers – which would be equally served by a fence along the Green Line – but by the intention, effectively, to annexe parts of the West Bank, especially those where ]s have been established, as well as water sources – and to define the future borders with Palestine unilaterally and ahead of negotiations. This position was supported by the ] at ], which ruled that Israel had the right to fortify its own border but that building a barrier inside an Occupied Territory constituted a violation of ]; the government of Israel, however, disputes this interpretation and refuses to abide by this ruling. For its part, the ] held that building inside the West Bank is in itself legal, but it but ordered some changes to the route of the barrier where the judges considered the original route to cause severe damage to Palestinian daily life – especially in separating Palestinian villagers from their land. Some radical Israeli groups, such as ], actively participate in protests against the barrier together with the villagers. As of late 2007, the barrier – originally slated to be completed by the end of 2005 – is far from complete, and further construction was stopped, officially for lack of funds. | ||
| ===Northern Ireland=== | |||
| ] | |||
| In ], ] and other settlements in ], barriers called "]" have been built to separate the two main communities. Their purpose is to minimize inter-communal violence between ]/] (who mainly self-identify as ] and/or Catholic) and ]/] (who mainly self-identify as ] and/or Protestant). They were first built following the ] and beginning of the "]". They have continued to be built and expanded since the ] of 1998. In 2008 a public discussion began about how and when the barriers could be removed.<ref> | |||
| {{cite web | |||
| |author=Tony Macaulay | |||
| |date=July 2008 | |||
| |url=http://www.cain.ulst.ac.uk/issues/segregat/docs/macaulay200708.pdf | |||
| |title=A Process for Removing Interface Barriers: A discussion paper proposing a five phase process for the removal of ‘peace walls’ in Northern Ireland | |||
| |publisher=Macaulay Associates | |||
| |accessdate=2010-02-06 | |||
| }}</ref>{{Failed verification|date=February 2013}} | |||
| On 1 September 2011 Belfast City Council agreed to develop a strategy regarding the removal of peace walls.<ref></ref>{{Request quotation|date=February 2013}} | |||
| At the end of 2011 several local community initiatives resulted in several interface structures being opened for a trial period.<ref> | |||
| </ref>{{Failed verification|date=February 2013}} | |||
| In January 2012, the International Fund for Ireland launched a Peace Walls funding programme to support local communities who want to work towards beginning to remove the peace walls. | |||
| <ref> Quote: "There are almost 90 barriers separating Protestant and Catholic neighbourhoods across the region..."</ref> | |||
| ===Pakistan=== | ===Pakistan=== | ||
| Line 105: | Line 79: | ||
| As of July 2009 it was reported that Saudis will pay $3.5 billion for security fence.<ref></ref>{{dead link|date=February 2013}} | As of July 2009 it was reported that Saudis will pay $3.5 billion for security fence.<ref></ref>{{dead link|date=February 2013}} | ||
| ===South Africa=== | |||
| {{Synthesis|date=March 2013}} | |||
| A treaty signed on December 9, 2002 by the presidents of three countries - South Africa, Mozambique, and Zimbabwe allowed for the fence to be torn down in order to open the ancient ] migration route between South Africa and Mozambique which was disrupted by the fence. The ] of {{convert|35000|km2|sqmi}} will connect the parks of three countries: South Africa's ], Mozambique's ], and Zimbabwe's ].<ref>.</ref>{{dead link|date=February 2013}} | |||
| In 2005 it was reported that only a relatively small portion of the high-security border fence separating South Africa's Kruger National Park with Zimbabwe's Gonarezhou Park has been removed. Security concerns, especially about illegal immigrants and the smuggling of weapons and four-wheel-drive vehicles, have been hindering the removal of more sections of the border fence between the Kruger and Limpopo parks.<ref>.</ref>{{dead link|date=February 2013}} | |||
| ===Spain=== | |||
| {{unreferencedsection|date=March 2013}} | |||
| The ] and ] have constructed barriers between the Spanish exclaves of ] and ] and ] to prevent illegal immigration and smuggling. | |||
| *] | |||
| *] | |||
| Even though both the United Kingdom and Spain are part of the European Union, the border fence separating ] and ] is still relevant since Gibraltar is not part of the ] and is outside of the customs union and VAT area. The border crossing is open twenty-four hours a day to facilitate customs collection by Spain. | |||
| ===United Nations=== | |||
| The United Nations has constructed a demilitarized zone to stop ] from re-invading ]; Kuwait plans to install a new separation barrier as well.{{Citation needed|date=March 2013}} | |||
| *] | |||
| ===United States=== | ===United States=== | ||
| ] at the American-Mexican border, before security upgrades were installed.]] | ] at the American-Mexican border, before security upgrades were installed.]] | ||
| The ] has constructed a |
The ] has constructed a ] along {{convert|130|km|mi}} of its ] with ] of {{convert|3169|km|mi}} to prevent unauthorized immigration into the United States and to deter smuggling of contraband. The ] has referred to it as a "separation barrier" and suggests that while it is "revolting to many as an ugly face of separation" it could be used as an opportunity if part of a larger program of "foreign aid, infrastructure investment and regional development."<ref>The Georgetown Journal of Law & Public Policy, Volume 5, ], 2007, .</ref> | ||
| *] | |||
| ===Uzbekistan=== | |||
| {{unreferencedsection|date=March 2013}} | |||
| In 1999 ] began construction of a barbed wire fence to secure their border with ]. | |||
| *] | |||
| In 2001 Uzbekistan fortified the border fence with ]. | |||
| *] | |||
| ==See also== | ==See also== | ||
Revision as of 03:09, 22 March 2013
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

The term separation barrier refers to a wall or fence constructed to limit the movement of people across a certain line or border, or to separate two populations. These structures vary in placement with regard to international borders and topography.
The term originated to describe the various fences, walls and other barriers Israel created to separate Palestinians in the Israeli-occupied territories of the West Bank and Gaza from Israel, to separate various Palestinian towns and villages within the occupied territories from each other, as well as to separate Egypt from Israel.
The term "separation barrier" also has been applied to other such walls or fences.
Current separation barriers
Cyprus
Since the 1974 Turkey has constructed and maintains a separation barrier of 300 kilometres (190 mi) along the 1974 Green Line (or ceasefire line) dividing the Republic of Cyprus into two parts along the United Nations Buffer Zone.
India
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Since the mid-1990s, India has been involved in the construction of some of the lengthiest separation barriers along its international borders. Six of the nine countries neighboring India are classified as Least Developed Countries. As a consequence, thousands of people from these countries, especially from Bangladesh, Nepal and Burma, illegally immigrate into India.
The Indo-Bangladeshi barrier and Indo-Burma barrier are being built to check smuggling, illegal immigration stealing Indian jobs and possible infiltration by Islamist terrorists. The refugee crisis could also ensue should a climate catastrophe ravage South Asia.
In addition, India completed the construction of the Indian Kashmir barrier which runs along the Line of Control in Kashmir. The purpose of this barrier is to prevent infiltration by armed militants. Many Kashmiris both in Jammu and Kashmir of India and Pakistan Occupied Kashmir in Pakistan are against the separation barrier since Kashmir is a disputed territory.
Iran
The Iran-Pakistan barrier wall is 700 kilometer long, which Iran claims is to stop the flow of illegal border crossings, stem the flow of drugs and prevent terror attacks from Pakistan. However, the Provincial Assembly of Balochistan, whose lands straddle the border region strongly opposes the construction of the wall and maintains that the wall would create problems for the Baloch people by dividing their community politically and socially, with their trade and social activities being seriously impeded. Leader of the Opposition, Kachkol Ali, said the governments of the two countries had not taken the Baloch into their confidence on this matter and demanded that the construction of the wall be stopped immediately and he also appealed to the international community to help the Baloch people. Residents of the Sorap locality in the Mand area of western Mekran region in Balochistan province rely on edible goods from Iran for their livelihood but Iranian border security forces vacate the town . The Balochistanis, who live on both sides of the border and in the area where both countries neighbour Afghanistan, have had their communities divided by the wall.
Iraq
On 10 April 2007, the U.S. military began constructing a 3.6 metre (12 ft) high concrete wall of 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) around the predominantly Sunni district of Adhamiya in Baghdad.
Writer Damon DiMarco described as a "separation barrier" the Kuwait-Iraq barrier constructed by the United Nations in 1991 after the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait. It is made of electrified fencing and concertina wire, and includes a 15 foot deep and wide trench and a high earthen berm. It runs 120 miles along the border between the two nations.
Israel
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (March 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
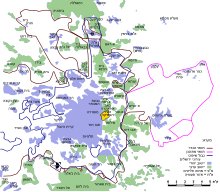
Due to Israel's specific situation of being at war and conflict with much of its Middle Eastern environment, separation barriers and walls have been and remain an issue of major military (and often also political) concern:
- Jerusalem: During the 1950s and 1960s a fortified separation barrier also divided much of Jerusalem to separate Jordanian and Israeli-controlled sectors of the city. It was pulled down in the immediate aftermath of the 1967 Six Day War, when the eastern part of the city came under Israeli rule. Currently, the route of the separation barrier in Jerusalem cuts off residents of the Jerusalem municipality from Jerusalem proper.
- Lebanon and Syria: Israel's borders with Lebanon and Syria have sophisticated security barriers, including electronic surveillance and warning systems. The barrier along the Lebanese border follows the lines of the 1949 Armistice and was laid down in coordination with the UN, the government anxious to make clear that it had withdrawn completely from Lebanese territory (excepting the ongoing dispute on the Shaba Farms).
- The barrier on the Syrian border on the Golan Heights reflects the situation in the aftermath of the Yom Kippur War, when Israel retained the territory conquered in 1967 except for handing back the town of Kuneitra. The Syrian government has repeatedly demanded the return of the entire Golan, but has made no specific issue of Israel erecting a security barrier along the border as it presently stands.

- The Israel and Egypt – Gaza Strip barrier includes the Rafah Border Crossing (Arabic: معبر رفح, Hebrew: מעבר רפיח), an international border crossing between Egyptian and Palestinian-controlled Rafah. It was built by the Israeli and Egyptian governments after the 1979 Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty and 1982 Israeli withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula, and was managed by the Israel Airports Authority until it was evacuated on 11 September 2005 as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan. It has since become the mission of the European Union Border Assistance Mission Rafah (EUBAM) to monitor the crossing.
- Jordan: The border of Israel's territory with Jordan, mostly in the Negev Desert along the Arabah, is considered the most peaceful of the country's borders, due to traditional good relations with Jordan's Hashemite Dynasty. In March 2004, Israel and Jordan commenced a joint project to build a desert science centre on their shared border. They have taken down a stretch of the border fence between the Red Sea and the Dead Sea for the campus.
- As well as the in the Negev, Israel also controls the West Bank's border with Jordan in the Jordan Valley. Along this border there is a security barrier with a two-way aim, designed to stop both infiltration from Jordan into the Israeli-controlled territory and the passage of West Bank Palestinians, uncontrolled by Israeli officials, into Jordan.

- Occupied Territories: Israel's most critical and volatile relations are with its direct neighbors, the Palestinians, which are reflected in maintaining separation barriers between Israel proper and the Occupied Territories, with the declared aim of and subsequent success in preventing infiltration by suicide bombers.
- The Israeli Gaza Strip barrier involves a security barrier along Israel's 1949 Armistice lines. There is also the security barrier along the Gaza Strip's border with Egypt (see Philadelphi Route), erected when Israel was in direct military control of the area. Though Israeli forces were withdrawn in 2005, the Government of Israel retains a declared interest in the area, especially due to alleged large-scale smuggling of arms from Sinai into the Strip, and insists upon the Egyptians and Palestinians maintaining intact the barrier between their respective territories – such insistence backed by sometimes open threats to otherwise resume direct Israeli military control. This has been cited by Palestinians and others who assert that the Gaza Strip remains an Occupied Territory despite the Israeli Disengagement from Gaza in 2005.
- The Israeli West Bank barrier is being built as a fence with wide margins and sophisticated electronic surveillance in rural areas, and an eight-meter-high wall in urban areas. Of all Israel's separation barriers, it is the most controversial – between Israelis and Palestinians, internationally, and also inside the Israeli society itself. The controversy stems mainly from the government's decision not to follow Israel's 1949 Armistice lines (Green Line) but rather build the barrier within the West Bank - in some stretches, deeply within. Opponents of the project (who usually call it "The Wall" rather than "Barrier" or "Fence") say that this proves its purpose is not to stop suicide bombers – which would be equally served by a fence along the Green Line – but by the intention, effectively, to annexe parts of the West Bank, especially those where Israeli settlements have been established, as well as water sources – and to define the future borders with Palestine unilaterally and ahead of negotiations. This position was supported by the International Court of Justice at The Hague, which ruled that Israel had the right to fortify its own border but that building a barrier inside an Occupied Territory constituted a violation of International Law; the government of Israel, however, disputes this interpretation and refuses to abide by this ruling. For its part, the Israeli Supreme Court held that building inside the West Bank is in itself legal, but it but ordered some changes to the route of the barrier where the judges considered the original route to cause severe damage to Palestinian daily life – especially in separating Palestinian villagers from their land. Some radical Israeli groups, such as Anarchists Against the Wall, actively participate in protests against the barrier together with the villagers. As of late 2007, the barrier – originally slated to be completed by the end of 2005 – is far from complete, and further construction was stopped, officially for lack of funds.
Pakistan
In September 2005, Pakistan stated it has plans to build a 1,500-mile (2,400 km) fence along its border with Afghanistan to prevent Islamic insurgents and drug smugglers slipping between the two countries. Former Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf has subsequently offered to mine the border as well.
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has begun construction of a Saudi-Yemen barrier between its territory and Yemen to prevent the unauthorized movement of people and goods into and out of the Kingdom. Anthony H. Cordesman has called it a "separation barrier."
In 2006 Saudi Arabia proposed plans for the construction of a security fence along the entire length of its desert border of 900 kilometres (560 mi) with Iraq in a multi-million dollar project to secure the Kingdom's borders in order to improve internal security, control illegal immigration and bolster its defences against external threats.

As of July 2009 it was reported that Saudis will pay $3.5 billion for security fence.
United States

The United States has constructed a barrier along 130 kilometres (81 mi) of its border with Mexico of 3,169 kilometres (1,969 mi) to prevent unauthorized immigration into the United States and to deter smuggling of contraband. The Georgetown Journal of Law has referred to it as a "separation barrier" and suggests that while it is "revolting to many as an ugly face of separation" it could be used as an opportunity if part of a larger program of "foreign aid, infrastructure investment and regional development."
See also
- Defensive walls
- List of fortifications
- List of walls
- List of cities with defensive walls
- Buffer zone
- Israel and Egypt–Gaza Strip barrier
- Israeli West Bank barrier
- Israel–Egypt barrier
External links
- Security Fences around the World
- Security Fences in The Atlantic Monthly
- Article about CityWalls on Erasmuspc
- "Obama's Border Fence", NOW on PBS, July 3, 2009.
- "Around Globe, Walls Spring Up to Divide Neighbors" Page Not Found, Reuters, April 30, 2007.
- Border to Border, Wall to Wall, Fence to Fence
References
- Steven Poole, Unspeak: How Words Become Weapons, How Weapons Become a Message, and How That Message Becomes Reality, Grove Press, 2007, p. 81, ISBN 0802143059, 9780802143051
- Fiona de Londras, Detention in the 'War on Terror': Can Human Rights Fight Back?, Cambridge University Press, 2011, p. 177-178, ISBN 1139500031, 9781139500036
- Robert Zelnick, Israel's Unilateralism: Beyond Gaza, Hoover Press, 2006, p 30-31, ISBN 0817947736, 9780817947736
- Rongxing Guo, Territorial Disputes and Resource Management: A Global Handbook, Nova Publishers, 2006, p 91, ISBN 1600214452, 9781600214455
- http://www.unpo.org/members/7922
- http://www.ostomaan.org/articles/news-and-views/4359
- Damon DiMarco, Heart of War: Soldiers? Voices, Citadel Press, 2007, p. 129, ISBN 0806528141, 9780806528144
- "Behind the Wall- Shuafat Camp", Ir Amim Special Report. 2006. http://www.ir-amim.org.il/eng/?CategoryID=330
- "Pakistan doing all it can in terror war - Musharraf". Turkish weekly. February 28, 2006. Retrieved 2006-12-03.
WASHINGTON (Reuters) - Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf said on Monday his country was doing all it could in the U.S.-led war against terrorism and offered to fence and mine its border with Afghanistan to stem Taliban infiltration. "I have been telling Karzai and the United States, 'Let us fence the border and let us mine it.' Today I say it again. Let us mine their entire border. Let us fence it. It's not difficult", Musharraf said, referring to Afghan President Hamid Karzai.
- Plett, Barbara (March 1, 2006). "Musharraf interview: Full transcript". BBC News. Retrieved 2006-12-03.
Now the other thing that I've said: if he thinks everyone is crossing from here, I've been saying let us fence the border and let us also mine the border. We are experts at mining, they should mine the border on their side. We will fence it on our side. If that is all right I am for it, so that they are not allowed to go across at all. And then let us see what is happening in Afghanistan. Why don't they agree to this, I've said this openly many times before, they don't do it, for whatever are their reasons. I know how effective the fence, the Indian fence which is about 1,800 kilometres, and they are fencing the Kashmir mountains also, it is so difficult. Why are they doing that, are they mad, they are spending billions of rupees. Because it is effective. Let's fence this border so that this blame game is killed once for ever.
- Anthony H. Cordesman, Saudi Arabia: National Security in a Troubled Region, p. 276.
- Saudis plan to fence off border with chaos, The Times, April 10, 2006.
- Saudis will pay $3.5 billion for security fence
- The Georgetown Journal of Law & Public Policy, Volume 5, Georgetown University Law Center, 2007, p. 347.