| Revision as of 06:26, 14 January 2011 edit24.17.170.181 (talk) →Astrology← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 00:14, 2 January 2025 edit undoSkeptic2 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users, Pending changes reviewers5,711 edits Reverted non-encyclopedic additionTag: Undo | ||
| (674 intermediate revisions by more than 100 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Constellation straddling the celestial equator}} | |||
| {{about|the constellation|the astrological sign|Ophiuchus (astrology)|the roots rock music group|Ophiuchus (band)|the manga character|Ophiuchus Shaina}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=September 2021}} | |||
| {{Infobox Constellation | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| {{Sky|17|00|00|+|00|00|00|10}} | |||
| {{Infobox constellation | |||
| | name = Ophiuchus | | name = Ophiuchus | ||
| | abbreviation = Oph | | abbreviation = Oph | ||
| | genitive = Ophiuchi | | genitive = Ophiuchi | ||
| | pronounce = {{ |
| pronounce = {{IPAc-en|ˌ|ɒ|f|i|ˈ|juː|k|ə|s}}<br/>genitive: {{IPAc-en|ˌ|ɒ|f|i|ˈ|juː|k|aɪ}} | ||
| | symbolism = |
| symbolism = the serpent-bearer | ||
| | RA = 17 | | RA = {{RA|17}} | ||
| | dec= −8 | | dec= {{DEC|−8}} | ||
| | family = ] | | family = ] | ||
| | quadrant = SQ3 | | quadrant = SQ3 | ||
| Line 13: | Line 16: | ||
| | arearank = 11th | | arearank = 11th | ||
| | numbermainstars = 10 | | numbermainstars = 10 | ||
| | numberbfstars = |
| numberbfstars = 65 | ||
| |ophicues = 15 | |||
| | numberstarsplanets = 7 | |||
| | numberbrightstars = 5 | | numberbrightstars = 5 | ||
| | numbernearbystars = 11 | | numbernearbystars = 11 | ||
| | brighteststarname = ] ( |
| brighteststarname = ] (Rasalhague) | ||
| | starmagnitude = 2.08 | | starmagnitude = 2.08 | ||
| | neareststarname = ] | | neareststarname = ] | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
| | stardistancepc = 1.83 | | stardistancepc = 1.83 | ||
| | numbermessierobjects = 7 | | numbermessierobjects = 7 | ||
| | meteorshowers = ] |
| meteorshowers = {{ubl|]|Northern ]|Southern May Ophiuchids|]}} | ||
| | bordering = ] |
| bordering = {{ubl|]|]|]|]|]|]|]}} | ||
| | latmax = ] | | latmax = ] | ||
| | latmin = ] | | latmin = ] | ||
| | month = July | | month = July | ||
| }} | |||
| | notes=}} | |||
| '''Ophiuchus''' is a large ] |
'''Ophiuchus''' ({{IPAc-en|ˌ|ɒ|f|i|ˈ|juː|k|ə|s}}) is a large ] straddling the ]. Its name comes from the ] {{wikt-lang|grc|ὀφιοῦχος}} ({{grc-transl|ὀφιοῦχος}}), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation ]. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer ], and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was '''Serpentarius'''.<ref>{{cite web |title=Star Tales – Ophiuchus |url=http://www.ianridpath.com/startales/ophiuchus.html |access-date=2021-06-25}}</ref> | ||
| ==Location== | ==Location== | ||
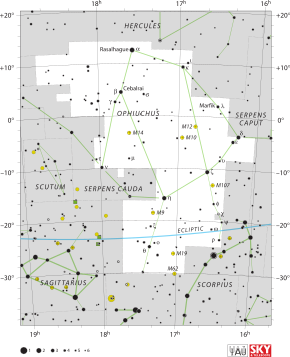
| ], shown with a surrounding bluish cloud slightly above a pentagon of stars in Scorpius, with the main band of the Milky Way much further to the left]] | |||
| It is located between ], ] and ], northwest of the center of the ]. The southern part lies between ] to the west and ] to the east. It is best visible in the northern summer and located opposite ] in the sky. Ophiuchus is depicted as a man grasping a ]; the interposition of his body divides the snake constellation Serpens into two parts, Serpens Caput and Serpens Cauda, which are nonetheless counted as one constellation. | |||
| Ophiuchus lies between ], ], ], ], and ], northwest of the center of the ]. The southern part lies between ] to the west and ] to the east.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Nightwatch A practical Guide to Viewing the Universe Revised Fourth Edition: Updated for use Through 2025 |last=Dickinson |first=Terence |publisher=Firefly Books |isbn=1-55407-147-X |location=US |pages=185 |year=2006}}</ref> In the ], it is best visible in summer.<ref>{{Cite book |title=Nightwatch A Practical Guide to Viewing the Universe Revised Fourth Edition: Updated for Use Through 2025 |last=Dickinson |first=Terence |publisher=Firefly Books|isbn=1-55407-147-X |location=US |pages=44–59 |year=2006}}</ref> It is opposite of ]. Ophiuchus is depicted as a man grasping a ]; the interposition of his body divides the snake constellation Serpens into two parts, ] and ]. Ophiuchus straddles the equator with the majority of its ] lying in the southern hemisphere. ], its brightest star, lies near the northern edge of Ophiuchus at about {{dec|+12|30}} declination.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://in-the-sky.org/data/object.php?id=TYC1000-2508-1 |title=Rasalhague (Star) |last=Ford |first=Dominic |website=in-the-sky.org |language=en |access-date=2018-06-23}}</ref> The constellation extends southward to −30° declination. Segments of the ecliptic within Ophiuchus are south of −20° declination (see chart at right). | |||
| In contrast to Orion, from November to January (summer in the Southern Hemisphere, winter in the Northern Hemisphere), Ophiuchus is in the daytime sky and thus not visible at most latitudes. However, for much of the polar region north of the ] in the Northern Hemisphere's winter months, the Sun is below the horizon even at midday. Stars (and thus parts of Ophiuchus, especially Rasalhague) are then visible at twilight for a few hours around local noon, low in the south. In the Northern Hemisphere's spring and summer months, when Ophiuchus is normally visible in the night sky, the constellation is actually not visible, because the ] obscures the stars at those times and places in the Arctic. In countries close to the equator, Ophiuchus appears overhead in June around midnight and in the October evening sky.{{citation needed|date=February 2021}} | |||
| ==Notable features== | |||
| {{clear left}} | |||
| ]] | |||
| ==Features== | |||
| ===Stars=== | ===Stars=== | ||
| {{See also|List of stars in Ophiuchus}} | |||
| ]'s drawing depicting the location of the ''stella nova'' in the foot of Ophiuchus.]] | |||
| The brightest stars in Ophiuchus include ], called Rasalhague ("head of the serpent charmer"), at magnitude 2.07, and ], known as Sabik ("the preceding one"), at magnitude 2.43.<ref>Chartrand III, Mark R.; (1983) ''Skyguide: A Field Guide for Amateur Astronomers'', p. 170 ({{ISBN|0-307-13667-1}}).</ref><ref name="Hoffleit 1991">{{cite web | url=http://vizier.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR-S?HR%202491 | title=Entry for HR 2491 | work=Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Preliminary Version) |author1=Hoffleit, D. |author2=Warren, W. H. Jr. | date=1991 | publisher=] }} ID .</ref> Alpha Ophiuchi is composed of an A-type (bluish-white) giant star<ref name=aj74_375>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Cowley | first1=A. | last2=Cowley | first2=C. | last3=Jaschek | first3=M. | last4=Jaschek | first4=C. | title=A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications | journal=Astronomical Journal | volume=74 | pages=375–406 |date=April 1969 | doi=10.1086/110819 | bibcode=1969AJ.....74..375C }}</ref> and a ].<ref name=apj726_2_104>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Hinkley | first1=Sasha | last2=Monnier | first2=John D. | last3=Oppenheimer | first3=Ben R. | last4=Roberts | first4=Lewis C. Jr. | last5=Ireland | first5=Michael | last6=Zimmerman | first6=Neil | last7=Brenner | first7=Douglas | last8=Parry | first8=Ian R. | last9=Martinache | first9=Frantz | title=Establishing α Oph as a Prototype Rotator: Improved Astrometric Orbit | journal=The Astrophysical Journal | volume=726 | issue=2 | page=104 |date=January 2011 | doi=10.1088/0004-637X/726/2/104 | bibcode=2011ApJ...726..104H |arxiv = 1010.4028 | s2cid=50830196 | url=http://authors.library.caltech.edu/21951/1/Hinkley2011p12486Astrophys_J.pdf }}</ref> The primary is a rapid rotator<ref name=monnierrasalhague>{{cite journal|doi=10.1088/0004-637X/725/1/1192|arxiv=1012.0787|title=Rotationally Modulated g-modes in the Rapidly Rotating δ Scuti Star Rasalhague (α Ophiuchi)|journal=The Astrophysical Journal|volume=725|issue=1|pages=1192–1201|year=2010|last1=Monnier|first1=J. D|last2=Townsend|first2=R. H. D|last3=Che|first3=X|last4=Zhao|first4=M|last5=Kallinger|first5=T|last6=Matthews|first6=J|last7=Moffat|first7=A. F. J|bibcode=2010ApJ...725.1192M|s2cid=51105576}}</ref> with an inclined axis of rotation.<ref name=rmaa38_117>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Zhao | first1=M. | last2=Monnier | first2=J. D. | last3=Pedretti | first3=E. | last4=Thureau | first4=N. | last5=Mérand | first5=A. | last6=Ten Brummelaar | first6=T. | last7=McAlister | first7=H. | last8=Ridgway | first8=S. T. | last9=Turner | first9=N. | title=Imaging and Modeling Rapid Rotators: α Cep and α Oph | department=The Interferometric View on Hot Stars | editor1-first=Th. | editor1-last=Rivinius | editor2-first=M. | editor2-last=Curé | journal=Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica, Serie de Conferencias | volume=38 | pages=117–118 |date=February 2010 | bibcode=2010RMxAC..38..117Z }}</ref> Eta Ophiuchi is a binary system.<ref name=aj133_4_1209>{{citation | last1=Docobo | first1=J. A. | last2=Ling | first2=J. F. | title=Orbits and System Masses of 14 Visual Double Stars with Early-Type Components | journal=The Astronomical Journal | volume=133 | issue=4 | pages=1209–1216 |date=April 2007 | doi=10.1086/511070 | bibcode=2007AJ....133.1209D | s2cid=120821801 | doi-access=free }}</ref> Other bright stars in the constellation include ], Cebalrai ("dog of the shepherd")<ref>{{cite book |author1=Paul Kunitzsch |author2=Tim Smart |title=A Dictionary of Modern Star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XVspPwAACAAJ |year=2006 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-931559-44-7 |page=44}}</ref> and ], or Marfik ("the elbow").<ref>Chartrand, at p. 170.</ref> Beta Ophiuchi is an evolved ] star that is slightly more massive than the Sun.<ref name=aaa352_555>{{citation | last1=Allende Prieto | first1=C. | last2=Lambert | first2=D. L. | title=Fundamental parameters of nearby stars from the comparison with evolutionary calculations: masses, radii and effective temperatures | journal=] | volume=352| pages=555–562 | year=1999 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/200811242 | bibcode=1999A&A...352..555A | arxiv=0809.0359 | s2cid=14531031 }}</ref><ref name=aaa480_1_91>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Soubiran | first1=C. | last2=Bienaymé | first2=O. | last3=Mishenina | first3=T. V. | last4=Kovtyukh | first4=V. V. | title=Vertical distribution of Galactic disk stars. IV. AMR and AVR from clump giants | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | year=2008 | volume=480 | issue=1 | pages=91–101 | bibcode=2008A&A...480...91S | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20078788 |arxiv = 0712.1370 | s2cid=16602121 }}</ref> Lambda Ophiuchi is a binary star system with the primary being more massive and luminous than the Sun.<ref name=zorec2012>{{cite journal | |||
| The brightest stars in Ophiuchus include ], called Rasalhague (at the figure's head), and ]. | |||
| | last1=Zorec | first1=J. | last2=Royer | first2=F. | |||
| | last3=Asplund | first3=Martin | last4=Cassisi | first4=Santi | |||
| | last5=Ramirez | first5=Ivan | last6=Melendez | first6=Jorge | |||
| | last7=Bensby | first7=Thomas | last8=Feltzing | first8=Sofia | |||
| | title=Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities | |||
| | display-authors=1 | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | |||
| | volume=537 | pages=A120 | year=2012 | |||
| | bibcode=2012A&A...537A.120Z | arxiv=1201.2052 | |||
| | doi=10.1051/0004-6361/201117691 | s2cid=55586789 }}</ref><ref name=aaa388>{{cite journal |author1=Lastennet, E. |author2=Fernandes, J. |author3=Lejeune, Th. | title=A revised HRD for individual components of binary systems from BaSeL BVRI synthetic photometry. Influence of interstellar extinction and stellar rotation | journal=Astronomy and Astrophysics | volume=388 | pages=309–319 |date=June 2002 | doi=10.1051/0004-6361:20020439 | bibcode=2002A&A...388..309L |arxiv = astro-ph/0203341 |s2cid=14376211 }}</ref> | |||
| ] is part of a class called recurrent ]e, whose brightness increase at irregular intervals by hundreds of times in a period of just a few days. It is thought to be at the brink of becoming a type-1a ].<ref> |
] is part of a class called recurrent ]e, whose brightness increase at irregular intervals by hundreds of times in a period of just a few days. It is thought to be at the brink of becoming a type-1a ].<ref>{{cite news |url=http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5204676.stm |title=Star 'soon to become supernova' |publisher=] |date=23 July 2006}}</ref> It erupts around every 15 years and usually has a magnitude of around 5.0 during eruptions, most recently in 2021.<ref>{{Cite web|title= Outburst of RS Ophiuchi|url=http://ooruri.kusastro.kyoto-u.ac.jp/mailarchive/vsnet-alert/26131|access-date=2021-08-09|website=ooruri.kusastro.kyoto-u.ac.jp}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|title=ATel #14834: Fermi-LAT Gamma-ray Detection of the Recurrent Nova RS Oph|url=https://astronomerstelegram.org/?read=14834|access-date=2021-08-09|website=ATel}}</ref> | ||
| ], one of the ] to the ] (the only stars closer are the ] ] system and ]), lies in Ophiuchus. |
], one of the ] to the ] (the only stars closer are the ] ] system and ]), lies in Ophiuchus. It is located to the left of β and just north of the V-shaped group of stars in an area that was once occupied by the now-obsolete constellation of ] (Poniatowski's Bull). It is thought that an exoplanet orbits around the star,<ref name=BarnardPlanet>{{cite journal | ||
| | last1 = Ribas | first1 = I. | |||
| | last2 = Tuomi | first2 = M. | |||
| | last3 = Reiners | first3 = Ansgar | |||
| | last4 = Butler | first4 = R. P. | |||
| | last5 = Morales | first5 = J. C. | |||
| | last6 = Perger | first6 = M. | |||
| | last7 = Dreizler | first7 = S. | |||
| | last8 = Rodríguez-López | first8 = C. | |||
| | last9 = González Hernández | first9 = J. I. | |||
| | last10 = Rosich | first10 = A. | |||
| | last11 = Feng | first11 = F. | |||
| | last12 = Trifonov | first12 = T. | |||
| | last13 = Vogt | first13 = S. S. | |||
| | last14 = Caballero | first14 = J. A. | |||
| | last15 = Hatzes | first15 = A. | |||
| | last16 = Herrero | first16 = E. | |||
| | last17 = Jeffers | first17 = S. V. | |||
| | last18 = Lafarga | first18 = M. | |||
| | last19 = Murgas | first19 = F. | |||
| | last20 = Nelson | first20 = R. P. | |||
| | last21 = Rodríguez | first21 = E. | |||
| | last22 = Strachan | first22 = J. B. P. | |||
| | last23 = Tal-Or | first23 = L. | |||
| | last24 = Teske | first24 = J. | |||
| | last25 = Toledo-Padrón | first25 = B. | |||
| | last26 = Zechmeister | first26 = M. | |||
| | last27 = Quirrenbach | first27 = A. | |||
| | last28 = Amado | first28 = P. J. | |||
| | last29 = Azzaro | first29 = M. | |||
| | last30 = Béjar | first30 = V. J. S. | |||
| | last31 = Barnes | first31 = J. R. | |||
| | last32 = Berdiñas | first32 = Z. M. | |||
| | last33 = Burt | first33 = J. | |||
| | last34 = Coleman | first34 = G. | |||
| | last35 = Cortés-Contreras | first35 = M. | |||
| | last36 = Crane | first36 = J. | |||
| | last37 = Engle | first37 = S. G. | |||
| | last38 = Guinan | first38 = E. F. | |||
| | last39 = Haswell | first39 = C. A. | |||
| | last40 = Henning | first40 = Th. | |||
| | last41 = Holden | first41 = B. | |||
| | last42 = Jenkins | first42 = J. | |||
| | last43 = Jones | first43 = H. R. A. | |||
| | last44 = Kaminski | first44 = A. | |||
| | last45 = Kiraga | first45 = M. | |||
| | last46 = Kürster | first46 = Martin | |||
| | last47 = Lee | first47 = M. H. | |||
| | last48 = López-González | first48 = M. J. | |||
| | last49 = Montes | first49 = D. | |||
| | last50 = Morin | first50 = J. | |||
| | last51 = Ofir | first51 = A. | |||
| | last52 = Pallé | first52 = E. | |||
| | last53 = Rebolo | first53 = Rafael | |||
| | last54 = Reffert | first54 = S. | |||
| | last55 = Schweitzer | first55 = A. | |||
| | last56 = Seifert | first56 = W. | |||
| | last57 = Shectman | first57 = S. A. | |||
| | last58 = Staab | first58 = D. | |||
| | last59 = Street | first59 = R. A. | |||
| | last60 = Suárez Mascareño | first60 = A. | |||
| | last61 = Tsapras | first61 = Y. | |||
| | last62 = Wang | first62 = S. X. | |||
| | last63 = Anglada-Escudé | first63 = G. | |||
| | display-authors = 4 | |||
| | date = 2018-11-14 | |||
| | title = A candidate super-Earth planet orbiting near the snow line of Barnard's star | |||
| | url = https://www.eso.org/public/archives/releases/sciencepapers/eso1837/eso1837a.pdf | |||
| | url-status = live | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | publisher = ] | |||
| | volume = 563 | |||
| | issue = 7731 | |||
| | pages = 365–368 | |||
| | arxiv = 1811.05955 | |||
| | bibcode = 2018Natur.563..365R | |||
| | doi = 10.1038/s41586-018-0677-y | |||
| | issn = 0028-0836 | |||
| | oclc = 716177853 | |||
| | archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20190326185022/https://www.eso.org/public/archives/releases/sciencepapers/eso1837/eso1837a.pdf | |||
| | archive-date = 2019-03-26 | |||
| | pmid = 30429552 | |||
| | hdl = 2299/21132 | |||
| | s2cid = 256769911}}</ref> | |||
| but later studies have refuted this claim.<ref name=Lubin2021>{{cite journal | last1=Lubin | first1=Jack | last2=Robertson | first2=Paul | last3=Stefansson | first3=Gudmundur | last4=Ninan | first4=Joe | last5=Mahadevan | first5=Suvrath | last6=Endl | first6=Michael | last7=Ford | first7=Eric | last8=Wright | first8=Jason T. | last9=Beard | first9=Corey | last10=Bender | first10=Chad | last11=Cochran | first11=William D. | last12=Diddams | first12=Scott A. | last13=Fredrick | first13=Connor | last14=Halverson | first14=Samuel | last15=Kanodia | first15=Shubham | last16=Metcalf | first16=Andrew J. | last17=Ramsey | first17=Lawrence | last18=Roy | first18=Arpita | last19=Schwab | first19=Christian | last20=Terrien | first20=Ryan |display-authors=3 | title=Stellar Activity Manifesting at a One-year Alias Explains Barnard b as a False Positive | journal=The Astronomical Journal | publisher=American Astronomical Society | volume=162 | issue=2 | date=15 July 2021 | doi=10.3847/1538-3881/ac0057|issn=0004-6256 | pages=61 | arxiv=2105.07005| bibcode=2021AJ....162...61L | s2cid=234741985 | doi-access=free }}</ref> In 1998, an intense flare was observed.<ref name=PaulsonBarnard>{{cite journal|first1=Diane B.|last1=Paulson|year=2006|title=Optical Spectroscopy of a Flare on Barnard's Star|journal=]|volume=118|issue=1|page=227|doi=10.1086/499497|last2=Allred|first2=Joel C.|last3=Anderson|first3=Ryan B.|last4=Hawley|first4=Suzanne L.|last5=Cochran|first5=William D.|last6=Yelda|first6=Sylvana|bibcode=2006PASP..118..227P|arxiv=astro-ph/0511281|s2cid=17926580}}</ref><ref name=BenedictBarnard>{{cite journal|last1=Benedict|first1=G. Fritz|year=1998|title=Photometry of Proxima Centauri and Barnard's star using Hubble Space Telescope fine guidance senso 3|journal=The Astronomical Journal|bibcode=1998AJ....116..429B|volume=116|issue=1|page=429|doi=10.1086/300420|last2=McArthur|first2=Barbara|last3=Nelan|first3=E.|last4=Story|first4=D.|last5=Whipple|first5=A. L.|last6=Shelus|first6=P. J.|last7=Jefferys|first7=W. H.|last8=Hemenway|first8=P. D.|last9=Franz|first9=Otto G.|last10=Wasserman|first10=L. H.|last11=Duncombe|first11=R. L.|last12=Van Altena|first12=W.|last13=Fredrick|first13=L. W.|arxiv=astro-ph/9806276|s2cid=15880053}}</ref> The star has also been a target of plans for interstellar travel such as ].<ref name=Daedalus76>{{cite journal|last1=Bond|first1=A.|last2=Martin|first2=A. R.|name-list-style=amp|year=1976|title=Project Daedalus – The mission profile|journal=]|url=http://md1.csa.com/partners/viewrecord.php?requester=gs&collection=TRD&recid=A7618970AH&q=project+daedalus&uid=788304424&setcookie=yes|volume=9|issue=2|page=101|access-date=15 August 2006|bibcode=1976JBIS...29..101B|url-status=dead|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20071020144727/http://md1.csa.com/partners/viewrecord.php?requester=gs&collection=TRD&recid=A7618970AH&q=project+daedalus&uid=788304424&setcookie=yes|archive-date=20 October 2007}}</ref><ref name=DarlingDaedalus>{{cite encyclopedia|first=David|last=Darling|url=http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/D/Daedalus.html|title=Daedalus, Project|date=July 2005|encyclopedia=The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight|access-date=10 August 2006|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060831043940/http://www.daviddarling.info/encyclopedia/D/Daedalus.html|archive-date=31 August 2006|url-status=live}}</ref> In 2005, astronomers using data from the ] discovered a ] so large that it extends beyond the plane of the galaxy.<ref name='huge superbubble'>{{cite news |title=Huge 'Superbubble' of Gas Blowing Out of Milky Way |date=13 January 2006 |url=http://www.physorg.com/news9882.html|work=] |access-date=4 July 2008}}</ref> It is called the ]. | |||
| In April 2007, ]s announced that the ]-built ] had made the first detection of clouds of ] ] in space, following observations in the constellation Ophiuchus.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/04/070417080835.htm |title=Molecular Oxygen Detected for the First Time in the Interstellar Medium |access-date=28 September 2016}}</ref> The ] was first observed on 9 October 1604, near θ Ophiuchi. ] saw it first on 16 October and studied it so extensively that the ] was subsequently called ''Kepler's Supernova''. He published his findings in a book titled ''De stella nova in pede Serpentarii'' (''On the New Star in Ophiuchus's Foot''). ] used its brief appearance to counter the ] ] that the heavens are changeless. It was a Type Ia supernova<ref name = "Reynolds2007">{{Cite journal | last1 = Reynolds | first1 = S. P. | last2 = Borkowski | first2 = K. J. | last3 = Hwang | first3 = U. | last4 = Hughes | first4 = J. P. | last5 = Badenes | first5 = C. | last6 = Laming | first6 = J. M. | last7 = Blondin | first7 = J. M. | date = 2 October 2007 | title = A Deep ''Chandra'' Observation of Kepler's Supernova Remnant: A Type Ia Event with Circumstellar Interaction | journal = ] | volume = 668 | issue = 2 | pages = L135–L138 | doi = 10.1086/522830 |doi-access=free|arxiv = 0708.3858 |bibcode = 2007ApJ...668L.135R |bibcode-access=free}}</ref> and the most recent Milky Way supernova visible to the unaided eye.<ref>{{cite web|title=Kepler's Supernova: Recently Observed Supernova|url=http://www.universeforfacts.com/2013/12/keplers-supernova-sn-1064-most-recently.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190104220659/http://www.universeforfacts.com/2013/12/keplers-supernova-sn-1064-most-recently.html|url-status=dead|archive-date=4 January 2019|website=Universe for Facts|access-date=21 December 2014}}</ref> In 2009 it was announced that ], a star in Ophiuchus, undergoes repeated, cyclical dimming with a period of about 1.5 days consistent with the transit of a small orbiting planet.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Charbonneau |first1=David |display-authors=etal <!-- Zachory K. Berta, Jonathan Irwin, Christopher J. Burke, Philip Nutzman, Lars A. Buchhave, Christophe Lovis, Xavier Bonfils, David W. Latham, Stéphane Udry, Ruth A. Murray-Clay, Matthew J. Holman, Emilio E. Falco, Joshua N. Winn, Didier Queloz, Francesco Pepe, Michel Mayor, Xavier Delfosse, Thierry Forveille --> |title=A super-Earth transiting a nearby low-mass star |journal=Nature |volume=462 |issue=7275 |pages=891–894 |doi=10.1038/nature08679 |pmid=20016595 |date=December 2009 |arxiv=0912.3229 |bibcode=2009Natur.462..891C|s2cid=4360404 }}</ref> The planet's low density (about 40% that of Earth) suggests that the planet might have a substantial component of low-density gas—possibly ] or ].<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Rogers |first1=Leslie A. |last2=Seager |first2=Sara |title=Three Possible Origins for the Gas Layer on GJ 1214b |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |volume=716 |issue=2 |pages=1208–1216 |doi=10.1088/0004-637x/716/2/1208 |bibcode=2010ApJ...716.1208R |arxiv=0912.3243 |year=2010|s2cid=15288792 }}</ref> The proximity of this star to Earth (42 light years) makes it a feasible target for further observations. The host star emits X-rays which could have removed mass from the exoplanet.<ref name=Lalitha2014>{{cite journal | |||
| In 2005, astronomers using data from the ] discovered a ] so large that it extends beyond the plane of the galaxy.<ref name='huge superbubble'>{{cite news | title=Huge 'Superbubble' of Gas Blowing Out of Milky Way | date=2006-01-13 | publisher= | url =http://www.physorg.com/news9882.html | work =] | accessdate = 2008-07-04 }}</ref> It is called the Ophiuchus Superbubble. | |||
| | title=X-Ray Emission from the Super-Earth Host GJ 1214 | |||
| | display-authors=1 | |||
| | last1=Lalitha | first1=S. | |||
| | last2=Poppenhaeger | first2=K. | |||
| | last3=Singh | first3=K. P. | |||
| | last4=Czesla | first4=S. | |||
| | last5=Schmitt | first5=J. H. M. M. | |||
| | journal=The Astrophysical Journal Letters | |||
| | volume=790 | |||
| | issue=1 | |||
| | id=L11 | |||
| | pages=5 | |||
| | date=July 2014 | |||
| | doi=10.1088/2041-8205/790/1/L11 | |||
| | bibcode=2014ApJ...790L..11L | |||
| |arxiv = 1407.2741 | s2cid=118774018 | |||
| }}</ref> In April 2010, the naked-eye star ] was occulted by the asteroid ].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.skyandtelescope.com/resources/proamcollab/astroalert/89599442.html |title=Asteroid To Hide Naked-Eye Star |access-date=2019-07-17 |date=31 March 2010 }}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.skyandtelescope.com/observing/highlights/89690067.html |title=Asteroid To Hide Bright Star |access-date=2019-07-17|date=31 March 2010 }}</ref><ref name=IOTA>{{cite web |url=http://asteroidoccultation.com/2010_04_si.htm |title=(824) Anastasia / HIP 81377 event on 2010 Apr 06, 10:21 UT |access-date=2019-07-17 |archive-date=17 July 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190717141423/http://asteroidoccultation.com/2010_04_si.htm |url-status=dead }}</ref> | |||
| <gallery widths="140px" heights="200px"> | |||
| In April 2007, ] announced that the ]-built ] had made the first detection of clouds of ] ] in space, following observations in the constellation Ophiuchus.<ref></ref> | |||
| Image:OphiuchusCC.jpg|The constellation Ophiuchus as it can be seen by naked eye<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.allthesky.com/constellations/ophiuchus.html |title=Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer – Constellations – Digital Images of the Sky }}</ref> | |||
| Image:Kepler Drawing of SN 1604.png|]'s drawing depicting the location of the ''stella nova'' in the foot of Ophiuchus | |||
| Image:Stjärnbild på Herkules, 1602 - Skoklosters slott - 102426.tif|Hercules and Ophiuchus, 1602 by ] | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| ===Deep-sky objects=== | |||
| The ] was first observed on October 9, 1604, near θ Ophiuchi. ] saw it first on October 16 and studied it so extensively that the ] was subsequently called Kepler's Supernova. He published his findings in a book titled ''De stella nova in pede Serpentarii'' (On the New Star in Ophiuchus' Foot). ] used its brief appearance to counter the ] ] that the heavens are changeless. | |||
| ] ] complex from ]]] | |||
| ] ] complex]] | |||
| Ophiuchus contains several ]s, such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ], as well as the ] IC 4603-4604. | |||
| In approximately 40,000 years '']'' probe will pass within 1.6 ]s of the star AC+79 3888, which is located in Ophiuchus.<ref></ref> | |||
| ] is a globular cluster which may have an extra-galactic origin.<ref name=mnras434_2_1220>{{citation | |||
| In 2009 it was announced that ], a star in Ophiuchus, undergoes repeated, cyclical dimming with a period of about 1.5 days consistent with the transit of a small orbiting planet.<ref></ref> Further, the authors conclude that the planet must have a low density consistent with vast quantities of water. The proximity of this star to Earth (42 light years) makes it a tempting target for further astronomic observations. | |||
| | display-authors=1 | last1=Arellano Ferro | first1=A. | |||
| | last2=Bramich | first2=D. M. | last3=Figuera Jaimes | first3=R. | |||
| | last4=Giridhar | first4=Sunetra | last5=Kains | first5=N. | |||
| | last6=Kuppuswamy | first6=K. | last7=Jørgensen | first7=U. G. | |||
| | last8=Alsubai | first8=K. A. | last9=Andersen | first9=J. M. | |||
| | last10=Bozza | first10=V. | last11=Browne | first11=P. | |||
| | last12=Calchi Novati | first12=S. | last13=Damerdji | first13=Y. | |||
| | last14=Diehl | first14=C. | last15=Dominik | first15=M. | |||
| | last16=Dreizler | first16=S. | last17=Elyiv | first17=A. | |||
| | last18=Giannini | first18=E. | last19=Harpsøe | first19=K. | |||
| | last20=Hessman | first20=F. V. | last21=Hinse | first21=T. C. | |||
| | last22=Hundertmark | first22=M. | last23=Juncher | first23=D. | |||
| | last24=Kerins | first24=E. | last25=Korhonen | first25=H. | |||
| | last26=Liebig | first26=C. | last27=Mancini | first27=L. | |||
| | last28=Mathiasen | first28=M. | last29=Penny | first29=M. T. | |||
| | last30=Rabus | first30=M. | last31=Rahvar | first31=S. | |||
| | last32=Ricci | first32=D. | last33=Scarpetta | first33=G. | |||
| | last34=Skottfelt | first34=J. | last35=Snodgrass | first35=C. | |||
| | last36=Southworth | first36=J. | last37=Surdej | first37=J. | |||
| | last38=Tregloan-Reed | first38=J. | last39=Vilela | first39=C. | |||
| | last40=Wertz | first40=O. | last41=Mindstep Consortium | |||
| | title=A detailed census of variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 6333 (M9) from CCD differential photometry | |||
| | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | |||
| | volume=434 | issue=2 | pages=1220–1238 | date=September 2013 | |||
| | doi=10.1093/mnras/stt1080 | doi-access=free | bibcode=2013MNRAS.434.1220A | |||
| | arxiv=1306.3206 | postscript=. }}</ref> ] is a fairly close ], only 20,000 light-years from Earth. It has a magnitude of 6.6 and is a Shapley class VII cluster. This means that it has "intermediate" concentration; it is only somewhat concentrated towards its center.{{sfn|Levy|2005|pp=153-54}} M12 is a globular cluster which is around 5 kiloparsecs from the Solar System.<ref name=M12Gontcharov>{{cite journal | doi=10.1093/mnras/stab2756 | title=Isochrone fitting of Galactic globular clusters – III. NGC 288, NGC 362, and NGC 6218 (M12) | year=2021 | last1=Gontcharov | first1=George A. | last2=Khovritchev | first2=Maxim Yu | last3=Mosenkov | first3=Aleksandr V. | last4=Il'In | first4=Vladimir B. | last5=Marchuk | first5=Alexander A. | last6=Savchenko | first6=Sergey S. | last7=Smirnov | first7=Anton A. | last8=Usachev | first8=Pavel A. | last9=Poliakov | first9=Denis M. | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | volume=508 | issue=2 | pages=2688–2705| doi-access=free | arxiv=2109.13115 }}</ref> ] is another globular cluster which is somewhat farther away.<ref name=apj742_1_51>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Boyles | first1=J. | last2=Lorimer | first2=D. R. | last3=Turk | first3=P. J. | last4=Mnatsakanov | first4=R. | last5=Lynch | first5=R. S. | last6=Ransom | first6=S. M. | last7=Freire | first7=P. C. | last8=Belczynski | first8=K. | title=Young Radio Pulsars in Galactic Globular Clusters | journal=The Astrophysical Journal | volume=742 | issue=1 | page=51 |date=November 2011 | doi=10.1088/0004-637X/742/1/51 | bibcode=2011ApJ...742...51B | postscript=. |arxiv = 1108.4402 | s2cid=118649860 }}</ref> Globular cluster M19 is ]<ref name=burnham1978>{{citation | first1=Robert | last1=Burnham | title=Burnham's Celestial Handbook: An Observer's Guide to the Universe Beyond the Solar System | volume=2 | series=Dover Books on Astronomy | edition=2nd | publisher=] | date=1978 | isbn=978-0486235684 | page=1263 | url=https://books.google.com/books?id=wB9uZ9lH5bgC&pg=PA1263 | postscript=. }}</ref> with multiple different types of variable stars.<ref name=aj122_5_2587>{{citation | display-authors=1 | last1=Clement | first1=Christine M. | last2=Muzzin | first2=Adam | last3=Dufton | first3=Quentin | last4=Ponnampalam | first4=Thivya | last5=Wang | first5=John | last6=Burford | first6=Jay | last7=Richardson | first7=Alan | last8=Rosebery | first8=Tara | last9=Rowe | first9=Jason | last10=Hogg | first10=Helen Sawyer | title=Variable Stars in Galactic Globular Clusters | journal=The Astronomical Journal | volume=122 | issue=5 | pages=2587–2599 |date=November 2001 | doi=10.1086/323719 | bibcode=2001AJ....122.2587C | postscript=. |arxiv = astro-ph/0108024 | s2cid=38359010 }}</ref> M62 is a globular cluster rich in ]s such as ]<ref name=Contreras2010>{{citation | |||
| | title=Time-series Photometry of Globular Clusters: M62 (NGC 6266), the Most RR Lyrae-rich Globular Cluster in the Galaxy? | |||
| | last1=Contreras | first1=R. | last2=Catelan | first2=M. | |||
| | last3=Smith | first3=H. A. | last4=Pritzl | first4=B. J. | |||
| | last5=Borissova | first5=J. | last6=Kuehn | first6=C. A. | |||
| | journal=The Astronomical Journal | display-authors=1 | |||
| | volume=140 | issue=6 | pages=1766–1786 | date=December 2010 | |||
| | doi=10.1088/0004-6256/140/6/1766 | bibcode=2010AJ....140.1766C | arxiv=1009.4206 | s2cid=118515997 }}</ref> and has two generations of stars with different element abundances.<ref name=Milone2015>{{citation | |||
| | title=Helium and multiple populations in the massive globular cluster NGC 6266 (M 62) | |||
| | last1=Milone | first1=A. P. | |||
| | journal=Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society | |||
| | volume=446 | issue=2 | pages=1672–1684 | date=January 2015 | |||
| | bibcode=2015MNRAS.446.1672M | arxiv=1409.7230 | |||
| | doi=10.1093/mnras/stu2198 | doi-access=free | postscript=. }}</ref> M107 is also rich in variable stars.<ref name=McCombs2013>{{citation | |||
| | contribution=Variable Stars in the Globular Cluster M107: The Discovery of a Probable SX Phoenicis | |||
| | last1=McCombs | first1=Thayne | last2=Reinhart | first2=E. | |||
| | last3=Murphy | first3=B. W. | display-authors=1 | |||
| | title=AAS Meeting #221 | volume=221 | pages=250.22 | id=250.22 | date=January 2013 | |||
| | publisher=American Astronomical Society | |||
| | bibcode=2013AAS...22125022M | postscript=. }}</ref> | |||
| The unusual ] merger remnant and ] ] is also in Ophiuchus. At a distance of 400 million light-years, this "butterfly-shaped" galaxy has two ]s 3,000 light-years apart. Confirmation of the fact that both ] contain black holes was obtained by ] from the ]. Astronomers estimate that the black holes will ] in another billion years. NGC 6240 also has an unusually high rate of ], classifying it as a ]. This is likely due to the heat generated by the orbiting black holes and the aftermath of the ].<ref name="objects">{{cite book |title=300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe |first1=Jamie |last1=Wilkins |first2=Robert |last2=Dunn |publisher=Firefly Books |date=2006 |location=Buffalo, New York |isbn=978-1-55407-175-3}}</ref> Both have ].<ref name="komossaetal 2003"> | |||
| In April 2010, the naked-eye star ] was occulted by ]. | |||
| {{cite journal | |||
| | last1 = Komossa | first1 = Stefanie | |||
| | last2 = Burwitz | first2 = Vadim | |||
| | last3 = Hasinger | first3 = Guenther | |||
| | last4 = Predehl | first4 = Peter | |||
| | last5 = Kaastra | first5 = Jelle S. | |||
| | last6 = Ikebe | first6 = Yasushi | |||
| | display-authors = 4 | |||
| | title = Discovery of a Binary Active Galactic Nucleus in the Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy NGC 6240 Using Chandra | |||
| | date = 2003 | |||
| | journal = ] | |||
| | volume = 582 | |||
| | issue = 1 | |||
| | pages = L15–L19 | |||
| | arxiv = astro-ph/0212099 | |||
| | bibcode = 2003ApJ...582L..15K | |||
| | doi = 10.1086/346145 | |||
| | s2cid = 16697327 | |||
| }}</ref> | |||
| In 2006, a new nearby ] was discovered associated with the 4th magnitude star ].<ref>{{cite journal |title=A New Nearby Candidate Star Cluster in Ophiuchus at d = 170 pc |last=Mamajek |first=Eric E. |date=2006 |journal=Astronomical Journal |volume=132 |issue=5 |pages=2198–2205 |bibcode=2006AJ....132.2198M |doi=10.1086/508205 |arxiv=astro-ph/0609064|s2cid=14070978 }}</ref> The ] cluster appears to be a poor cluster remnant analogous to the ], but 7 times more distant (approximately 170 parsecs away). Mamajek 2 appears to have formed in the same star-forming complex as the ] cluster roughly 135 million years ago.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Dynamical Evolution and Spectral Characteristics of the Stellar Group Mamajek 2 |last1=Jilinski |first1=Evgueni |last2=Ortega |first2=Vladimir G. |last3=de la Reza |first3=Jorge Ramiro |last4=Drake |first4=Natalia A. |last5=Bazzanella |first5=Bruno |name-list-style=amp |date=2009 |journal=The Astrophysical Journal |volume=691 |issue=1 |pages=212–218 |bibcode=2009ApJ...691..212J |doi=10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/212 |arxiv=0810.1198|s2cid=15570695 }}</ref> | |||
| ===Deep-sky objects=== | |||
| Ophiuchus contains several ]s, such as ], ], ], ], ], ], ], ], and ], as well as the ] IC 4603-4604. The unusual ] merger remnant ] is also in Ophiuchus. | |||
| In 2006, a new nearby ] was discovered associated with the 4th magnitude star ].<ref>{{cite journal|title=A New Nearby Candidate Star Cluster in Ophiuchus at d = 170 pc|author=Mamajek, Eric E.|year=2006|journal=Astronomical | |||
| ] is a large ], located 410 light-years from Earth. Despite its diameter of 0.4 light-years, Barnard 68 only has twice the mass of the Sun, making it both very diffuse and very cold, with a temperature of about 16 ]s. Though it is currently stable, Barnard 68 will eventually collapse, inciting the process of ]. One unusual feature of Barnard 68 is its vibrations, which have a period of 250,000 years. Astronomers speculate that this phenomenon is caused by the ] from a ].<ref name="objects"/> Barnard 68 has blocked thousands of stars visible at other wavelengths<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.eso.org/public/images/eso9934b/ |title= The Dark Cloud B68 at Different Wavelengths |publisher= ]|accessdate= January 30, 2012}}</ref> and the distribution of dust in Barnard 68 has been mapped.<ref> | |||
| Journal|volume=132|pages=2198|url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006AJ....132.2198M|doi=10.1086/508205}}</ref> The ] cluster appears to be a poor cluster remnant analogous to the ], but 7 times more distant (approximately 170 parsecs away). ] appears to have formed in the same star-forming complex as the ] cluster roughly 135 million years ago.<ref>{{cite journal|title=Dynamical Evolution and Spectral Characteristics of the Stellar Group Mamajek 2|author=Jilinski, E., Ortega, V.G., de la Reza, R., Drake, N.A., and Bazzanella, B.|year=2009|journal=Astrophysical Journal|volume=691|pages=212|url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009ApJ...691..212J|doi=10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/212}}</ref> | |||
| {{cite journal | |||
| |title=Seeing the light through the dark | |||
| |last1=Alves|first1=João | |||
| |last2=Lada|first2=Charles | |||
| |last3=Lada|first3=Elizabeth | |||
| |journal=The Messenger | |||
| |date=March 2001 | |||
| |volume=103 | |||
| |pages=15–20 | |||
| |bibcode=2001Msngr.103....1A | |||
| |url=http://www.eso.org/sci/publications/messenger/archive/no.103-mar01/messenger-no103-1-1.pdf | |||
| }}</ref><ref> | |||
| {{cite journal | |||
| |title=Internal structure of a cold dark molecular cloud inferred from the extinction of background starlight | |||
| |last1=Alves|first1=João F. | |||
| |last2=Lada|first2=Charles J. | |||
| |last3=Lada|first3=Elizabeth A. | |||
| |journal=Nature | |||
| |date=January 2001 | |||
| |volume=409 | |||
| |issue=6817 | |||
| |pages=159–161 | |||
| |bibcode=2001Natur.409..159A | |||
| |doi=10.1038/35051509 | |||
| |pmid=11196632 | |||
| |s2cid=4318459 }}</ref> | |||
| The space probe ], the furthest man-made object from earth, is traveling in the direction of Ophiuchus. It is located between ], ] and ] at right ascension 17h 13m and declination +12° 25’ (July 2020).<ref>Coordinates available at .</ref> | |||
| ==Mythology== | |||
| {{Section OR|date=December 2008}} | |||
| In November 2022, the USA's ] NOIRLab (]) announced the unambiguous identification of the nearest ] orbited by a ], the system identified as ] at around 1,560 ]s from the Sun.<ref name="2022-11-04_NSF">, Dr ] et al, USA ] NOIRLab (]), 2022-11-04</ref> | |||
| , a set of constellation cards published in London c.1825. Above the tail of the serpent is the now-obsolete constellation ] while below it is ].]] | |||
| ==History and mythology== | |||
| There exist a number of theories as to whom the figure represents. | |||
| There is no evidence of the constellation preceding the ], and in ], a "Sitting Gods" constellation seems to have been located in the general area of Ophiuchus. However, Gavin White proposes that Ophiuchus may in fact be remotely descended from this Babylonian constellation, representing ], a serpent-god who was sometimes depicted with his upper half human but with serpents for legs.<ref>White, Gavin; ''Babylonian Star-lore'', Solaria Pubs, 2008, p. 187f</ref> | |||
| The earliest mention of the constellation is in ], informed by the lost catalogue of ] (4th century BC):<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |author1=Liddell, Henry George |author2=Scott, Robert |dictionary=A Greek-English Lexicon |publisher=perseus.tufts.edu |url=https://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus%3Atext%3A1999.04.0057%3Aentry%3Do%29fiou%3Dxos |title=ὀφιοῦχος}}</ref> {{blockquote|To the Phantom's back the ] is near, but by his head mark near at hand the head of Ophiuchus, and then from it you can trace the starlit Ophiuchus himself: so brightly set beneath his head appear his gleaming shoulders. They would be clear to mark even at the midmonth moon, but his hands are not at all so bright; for faint runs the gleam of stars along on this side and on that. Yet they too can be seen, for they are not feeble. Both firmly clutch the ], which encircles the waist of Ophiuchus, but he, steadfast with both his feet well set, tramples a huge monster, even the ]n, standing upright on his eye and breast. Now the Serpent is wreathed about his two hands – a little above his right hand, but in many folds high above his left.<ref>translation by Mair, Alexander W.; & Mair, Gilbert R.; Loeb Classical Library, volume 129, William Heinemann, London, 1921 </ref>}} | |||
| The most recent interpretation is that the figure represents the healer ], who learned the secrets of keeping death at bay after observing one serpent bringing another healing herbs. To prevent the entire human race from becoming ] under Asclepius' care, ] killed him with a bolt of ], but later placed his image in the heavens to honor his good works. It has also been noted that the constellation Ophiuchus is close to that of ], which has at times been believed to represent ] (the mentor of Asclepius and many other Greek ]s), though Chiron was originally associated with the constellation ]. | |||
| To the ], the constellation represented the god ] struggling with a huge snake that guarded the ].<ref name="Thompson">{{cite book |last=Thompson |first=Robert |title=Illustrated Guide to Astronomical Wonders: From Novice to Master Observer|date=2007|publisher=O'Reilly Media, Inc.|isbn=9780596526856|page=326}}</ref> | |||
| Another possibility is that the figure represents the ] priest ], who was killed by a pair of sea serpents sent by the gods after he warned the Trojans not to accept the ]. This event was also memorialized by the sculptors ], ], and ] in the famous marble sculpture '']'', which stands in the ]. | |||
| Later myths identified Ophiuchus with ], the ] priest of ], who warned his fellow Trojans about the ] and was later slain by a pair of sea serpents sent by the gods to punish him.<ref name="Thompson"/> According to ] mythography,<ref>Hyginus, ''Astronomica'' 2, 14, Latin Mythography, 2nd century AD</ref> the figure represents the healer ], who learned the secrets of keeping death at bay after observing one serpent bringing another healing herbs. To prevent the entire human race from becoming ] under Asclepius' care, ] killed him with a bolt of ], but later placed his image in the heavens to honor his good works. In medieval ] (]'s '']'', 10th century), the constellation was known as ''Al-Ḥawwa''', "the snake-charmer".<ref>{{Cite web|title=Snake-Charmer|url=https://brickthology.com/category/snake-charmer/|access-date=2022-02-01|website=Brickthology|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| A third possibility is ] wrestling with the ] to take control of the ] at ]. | |||
| ] describes Ophiuchus as trampling on ] with his feet. This is depicted in Renaissance to Early Modern ]s, beginning with ] in 1515; in some depictions (such as that of ] in '']'', 1606), Scorpius also seems to threaten to sting Serpentarius in the foot. This is consistent with ], who already included ] and ] as the snake-charmer's "left foot", and ] and ] as his "right foot", making Ophiuchus a ] at least as regards his feet.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.icoproject.org/cons.html |title=Manuscript reproduction |access-date=2019-07-17 |archive-date=6 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190506142015/http://www.icoproject.org/cons.html |url-status=dead }}</ref> This arrangement has been taken as symbolic in later literature and placed in relation to the words spoken by God to the serpent in the ] (Genesis 3:15).<ref>]; ''Astronomy of the Bible'', 1908, p. 164f</ref> | |||
| A fourth is the story of ], a Thessalonian who rescued the people of the island of ] from a plague of ] and was granted a place in the sky in honor of this deed. | |||
| <gallery widths="200px" heights="150px"> | |||
| According to Gavin White, Ophiuchus may represent the Babylonian constellation known as the Sitting Gods (Mul.Dingir.Tush.A.Mesh), which he proposes was originally a human figure whose legs have been replaced by the tail of a huge serpent.<ref>''Babylonian Star-lore'' by Gavin White, Solaria Pubs, 2008, page 191</ref> | |||
| File:Azophi Ophiuchus.jpg|Ophiuchus in a manuscript copy of ]'s ], 18th century copy of a manuscript prepared for ] in 1417 (note that as in all pre-modern ]s, the constellation is mirrored, with ] on the left and ] on the right). | |||
| File:Sidney Hall - Urania's Mirror - Taurus Poniatowski, Serpentarius, Scutum Sobiesky, and Serpens.jpg|Ophiuchus holding the serpent, Serpens, as depicted in '']'', a set of constellation cards published in London c. 1825. Above the tail of the serpent is the now-obsolete constellation ] while below it is ]. | |||
| </gallery> | |||
| == |
==Zodiac== | ||
| {{main|Ophiuchus (astrology)}} | {{main|Ophiuchus (astrology)}} | ||
| Ophiuchus is one of the 13 constellations that cross the ].<ref>Shapiro, Lee T. , in ''The Space Place'' (NASA, last updated 22 July 2011)</ref> It has sometimes been suggested as the "13th sign of the ]". However, this confuses ] with ].<ref>{{cite web|url=https://earthsky.org/sky-archive/ophiuchus-highest-on-august-evenings-2|title=Ophiuchus, 13th constellation of zodiac|work= Earth Sky | access-date = 2019-07-19}}</ref> The signs of the zodiac are a 12-fold division of the ecliptic, so that each sign spans 30° of celestial longitude, approximately the distance the Sun travels in a month, and (in the Western tradition) are aligned with the seasons so that the ] always falls on the boundary between Pisces and Aries.<ref>{{Cite web|last=Gleason|first=Edward|title=Why is the vernal equinox called the "First Point of Aries" when the Sun is actually in Pisces on this date? {{!}} Planetarium|url=https://usm.maine.edu/planet/why-vernal-equinox-called-first-point-aries-when-sun-actually-pisces-date|access-date=2022-03-25|website=University of Southern Maine}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Campbell|first=Tina|date=2020-07-15|title=Has your star sign changed following the discovery of a 'new' Zodiac sign?|url=https://metro.co.uk/2020/07/15/what-new-zodiac-sign-ophichius-mean-what-dates-cover-12990848/|access-date=2021-04-29|website=Metro|language=en}}</ref> Constellations, on the other hand, are unequal in size and are based on the positions of the stars. The ] have only a loose association with the signs of the zodiac, and do not in general coincide with them.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://astrologyclub.org/ophiuchus-13th-zodiac-sign-no/ |title=Ophiuchus – a 13th Zodiac Sign? No! |work=Astrology Club |access-date=2016-10-18 |date=2 March 2016}}</ref> In Western astrology the constellation of Aquarius, for example, largely corresponds to the sign of Pisces. Similarly, the constellation of Ophiuchus occupies most (29 November – 18 December<ref>{{cite web |url=http://earthsky.org/constellations/born-between-november-29-and-december-18-heres-your-constellation |title=Born under the sign of Ophiuchus? |date=16 August 2021 |publisher=EarthSky.org}}</ref>) of the sign of Sagittarius (23 November – 21 December). The differences are due to the fact that the time of year that the Sun passes through a particular zodiac constellation's position has slowly changed (because of the ]) over the centuries from when the ] originally developed the zodiac.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Aitken |first=Robert G. |title=Edmund Halley and Stellar Proper Motions |journal=Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets |date=October 1942 |volume=4 |issue=164 |pages=103 |bibcode=1942ASPL....4..103A}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Redd |first=Nola Taylor |title=Constellations: The Zodiac Constellation Names |url=http://www.space.com/15722-constellations.html |publisher=space.com |access-date=3 August 2012}}</ref> | |||
| Until recently, Ophiuchus was not included in standard astrological zodiacs, which divide the ecliptic into abstract 30-degree segments (implying exactly 12 signs), rather than using the physical constellations. Only a few astrologers, those using a ], use it as the 13th zodiacal sign. | |||
| January 2011, Ophiuchus was officially recognized as the 13th sign, falling between Scorpio and Sagittarius, beginning November 29 and ending December 17. | |||
| ==Symbol== | |||
| ] is often used as a symbol for Ophiuchus.]] | |||
| ] | |||
| Two symbols have been proposed for Ophiuchus, one based on the ] (Unicode ⚕, U+2695) and the other in general use in Japanese astrology (Unicode ⛎, U+26CE). | |||
| Since Ophiuchus is identified with ], the Rod of Asclepius is often used as a symbol for Ophiuchus. In Japan, an astrological symbol for Ophiuchus is in widespread use. The symbol is sufficiently common to be included in ]. | |||
| ==Citations== | ==Citations== | ||
| {{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
| http://newsfeed.time.com/2011/01/13/ophiuchus-what-all-saggitarius-and-capricorns-need-to-know-about-their-new-zodiac/ | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| * ] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| * {{cite book |first=David H. |last=Levy |title=Deep Sky Objects |publisher=Prometheus Books |date=2005 |isbn=1-59102-361-0 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/deepskyobjects00davi}} | |||
| * Ian Ridpath and Wil Tirion (2007). ''Stars and Planets Guide'', Collins, London. ISBN 978-0007251209. Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 978-0691135564. | |||
| * Ridpath, Ian; and Tirion, Wil; (2007) ''Stars and Planets Guide'', Collins, London; {{ISBN|978-0-00-725120-9}}, Princeton University Press, Princeton; {{ISBN|978-0-691-13556-4}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{ |
{{EB1911 poster|Serpentarius}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Commons category|Ophiuchus (constellation)}} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | |||
| {{Stars of Ophiuchus}} | {{Stars of Ophiuchus}} | ||
| {{navconstel}} | {{navconstel}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Zodiac}} | ||
| {{Portal bar|Astronomy|Stars|Spaceflight|Outer space|Solar System}} | |||
| {{Authority control}} | |||
| {{DEFAULTSORT:Ophiuchus}} | |||
| {{Sky|17|00|00|+|00|00|00|10}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 00:14, 2 January 2025
Constellation straddling the celestial equatorFor other uses, see Ophiuchus (disambiguation).
| Constellation | |
 List of stars in Ophiuchus List of stars in Ophiuchus | |
| Abbreviation | Oph |
|---|---|
| Genitive | Ophiuchi |
| Pronunciation | /ˌɒfiˈjuːkəs/ genitive: /ˌɒfiˈjuːkaɪ/ |
| Symbolism | the serpent-bearer |
| Right ascension | 17 |
| Declination | −8° |
| Quadrant | SQ3 |
| Area | 948 sq. deg. (11th) |
| Main stars | 10 |
| Bayer/Flamsteed stars | 65 |
| Stars brighter than 3.00 | 5 |
| Stars within 10.00 pc (32.62 ly) | 11 |
| Brightest star | α Oph (Rasalhague) (2.08) |
| Messier objects | 7 |
| Meteor showers |
|
| Bordering constellations | |
| Visible at latitudes between +80° and −80°. Best visible at 21:00 (9 p.m.) during the month of July. | |
Ophiuchus (/ˌɒfiˈjuːkəs/) is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek ὀφιοῦχος (ophioûkhos), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was Serpentarius.
Location

Ophiuchus lies between Aquila, Serpens, Scorpius, Sagittarius, and Hercules, northwest of the center of the Milky Way. The southern part lies between Scorpius to the west and Sagittarius to the east. In the northern hemisphere, it is best visible in summer. It is opposite of Orion. Ophiuchus is depicted as a man grasping a serpent; the interposition of his body divides the snake constellation Serpens into two parts, Serpens Caput and Serpens Cauda. Ophiuchus straddles the equator with the majority of its area lying in the southern hemisphere. Rasalhague, its brightest star, lies near the northern edge of Ophiuchus at about +12° 30′ declination. The constellation extends southward to −30° declination. Segments of the ecliptic within Ophiuchus are south of −20° declination (see chart at right).
In contrast to Orion, from November to January (summer in the Southern Hemisphere, winter in the Northern Hemisphere), Ophiuchus is in the daytime sky and thus not visible at most latitudes. However, for much of the polar region north of the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere's winter months, the Sun is below the horizon even at midday. Stars (and thus parts of Ophiuchus, especially Rasalhague) are then visible at twilight for a few hours around local noon, low in the south. In the Northern Hemisphere's spring and summer months, when Ophiuchus is normally visible in the night sky, the constellation is actually not visible, because the midnight sun obscures the stars at those times and places in the Arctic. In countries close to the equator, Ophiuchus appears overhead in June around midnight and in the October evening sky.
Features
Stars
See also: List of stars in OphiuchusThe brightest stars in Ophiuchus include α Ophiuchi, called Rasalhague ("head of the serpent charmer"), at magnitude 2.07, and η Ophiuchi, known as Sabik ("the preceding one"), at magnitude 2.43. Alpha Ophiuchi is composed of an A-type (bluish-white) giant star and a K-type main sequence star. The primary is a rapid rotator with an inclined axis of rotation. Eta Ophiuchi is a binary system. Other bright stars in the constellation include β Ophiuchi, Cebalrai ("dog of the shepherd") and λ Ophiuchi, or Marfik ("the elbow"). Beta Ophiuchi is an evolved red giant star that is slightly more massive than the Sun. Lambda Ophiuchi is a binary star system with the primary being more massive and luminous than the Sun.
RS Ophiuchi is part of a class called recurrent novae, whose brightness increase at irregular intervals by hundreds of times in a period of just a few days. It is thought to be at the brink of becoming a type-1a supernova. It erupts around every 15 years and usually has a magnitude of around 5.0 during eruptions, most recently in 2021.
Barnard's Star, one of the nearest stars to the Solar System (the only stars closer are the Alpha Centauri binary star system and Proxima Centauri), lies in Ophiuchus. It is located to the left of β and just north of the V-shaped group of stars in an area that was once occupied by the now-obsolete constellation of Taurus Poniatovii (Poniatowski's Bull). It is thought that an exoplanet orbits around the star, but later studies have refuted this claim. In 1998, an intense flare was observed. The star has also been a target of plans for interstellar travel such as Project Daedalus. In 2005, astronomers using data from the Green Bank Telescope discovered a superbubble so large that it extends beyond the plane of the galaxy. It is called the Ophiuchus Superbubble.
In April 2007, astronomers announced that the Swedish-built Odin satellite had made the first detection of clouds of molecular oxygen in space, following observations in the constellation Ophiuchus. The supernova of 1604 was first observed on 9 October 1604, near θ Ophiuchi. Johannes Kepler saw it first on 16 October and studied it so extensively that the supernova was subsequently called Kepler's Supernova. He published his findings in a book titled De stella nova in pede Serpentarii (On the New Star in Ophiuchus's Foot). Galileo used its brief appearance to counter the Aristotelian dogma that the heavens are changeless. It was a Type Ia supernova and the most recent Milky Way supernova visible to the unaided eye. In 2009 it was announced that GJ 1214, a star in Ophiuchus, undergoes repeated, cyclical dimming with a period of about 1.5 days consistent with the transit of a small orbiting planet. The planet's low density (about 40% that of Earth) suggests that the planet might have a substantial component of low-density gas—possibly hydrogen or steam. The proximity of this star to Earth (42 light years) makes it a feasible target for further observations. The host star emits X-rays which could have removed mass from the exoplanet. In April 2010, the naked-eye star ζ Ophiuchi was occulted by the asteroid 824 Anastasia.
-
 The constellation Ophiuchus as it can be seen by naked eye
The constellation Ophiuchus as it can be seen by naked eye
-
 Johannes Kepler's drawing depicting the location of the stella nova in the foot of Ophiuchus
Johannes Kepler's drawing depicting the location of the stella nova in the foot of Ophiuchus
-
 Hercules and Ophiuchus, 1602 by Willem Blaeu
Hercules and Ophiuchus, 1602 by Willem Blaeu
Deep-sky objects


Ophiuchus contains several star clusters, such as IC 4665, NGC 6633, M9, M10, M12, M14, M19, M62, and M107, as well as the nebula IC 4603-4604.
M9 is a globular cluster which may have an extra-galactic origin. M10 is a fairly close globular cluster, only 20,000 light-years from Earth. It has a magnitude of 6.6 and is a Shapley class VII cluster. This means that it has "intermediate" concentration; it is only somewhat concentrated towards its center. M12 is a globular cluster which is around 5 kiloparsecs from the Solar System. M14 is another globular cluster which is somewhat farther away. Globular cluster M19 is oblate-shaped with multiple different types of variable stars. M62 is a globular cluster rich in variable stars such as RR Lyrae variables and has two generations of stars with different element abundances. M107 is also rich in variable stars.
The unusual galaxy merger remnant and starburst galaxy NGC 6240 is also in Ophiuchus. At a distance of 400 million light-years, this "butterfly-shaped" galaxy has two supermassive black holes 3,000 light-years apart. Confirmation of the fact that both nuclei contain black holes was obtained by spectra from the Chandra X-ray Observatory. Astronomers estimate that the black holes will merge in another billion years. NGC 6240 also has an unusually high rate of star formation, classifying it as a starburst galaxy. This is likely due to the heat generated by the orbiting black holes and the aftermath of the collision. Both have active galactic nuclei.
In 2006, a new nearby star cluster was discovered associated with the 4th magnitude star Mu Ophiuchi. The Mamajek 2 cluster appears to be a poor cluster remnant analogous to the Ursa Major Moving Group, but 7 times more distant (approximately 170 parsecs away). Mamajek 2 appears to have formed in the same star-forming complex as the NGC 2516 cluster roughly 135 million years ago.
Barnard 68 is a large dark nebula, located 410 light-years from Earth. Despite its diameter of 0.4 light-years, Barnard 68 only has twice the mass of the Sun, making it both very diffuse and very cold, with a temperature of about 16 kelvins. Though it is currently stable, Barnard 68 will eventually collapse, inciting the process of star formation. One unusual feature of Barnard 68 is its vibrations, which have a period of 250,000 years. Astronomers speculate that this phenomenon is caused by the shock wave from a supernova. Barnard 68 has blocked thousands of stars visible at other wavelengths and the distribution of dust in Barnard 68 has been mapped.
The space probe Voyager 1, the furthest man-made object from earth, is traveling in the direction of Ophiuchus. It is located between α Herculis, α Ophiuchi and κ Ophiuchi at right ascension 17h 13m and declination +12° 25’ (July 2020).
In November 2022, the USA's NSF NOIRLab (National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory) announced the unambiguous identification of the nearest stellar black hole orbited by a G-type main-sequence star, the system identified as Gaia BH1 at around 1,560 light years from the Sun.
History and mythology
There is no evidence of the constellation preceding the classical era, and in Babylonian astronomy, a "Sitting Gods" constellation seems to have been located in the general area of Ophiuchus. However, Gavin White proposes that Ophiuchus may in fact be remotely descended from this Babylonian constellation, representing Nirah, a serpent-god who was sometimes depicted with his upper half human but with serpents for legs.
The earliest mention of the constellation is in Aratus, informed by the lost catalogue of Eudoxus of Cnidus (4th century BC):
To the Phantom's back the Crown is near, but by his head mark near at hand the head of Ophiuchus, and then from it you can trace the starlit Ophiuchus himself: so brightly set beneath his head appear his gleaming shoulders. They would be clear to mark even at the midmonth moon, but his hands are not at all so bright; for faint runs the gleam of stars along on this side and on that. Yet they too can be seen, for they are not feeble. Both firmly clutch the Serpent, which encircles the waist of Ophiuchus, but he, steadfast with both his feet well set, tramples a huge monster, even the Scorpion, standing upright on his eye and breast. Now the Serpent is wreathed about his two hands – a little above his right hand, but in many folds high above his left.
To the ancient Greeks, the constellation represented the god Apollo struggling with a huge snake that guarded the Oracle of Delphi.
Later myths identified Ophiuchus with Laocoön, the Trojan priest of Poseidon, who warned his fellow Trojans about the Trojan Horse and was later slain by a pair of sea serpents sent by the gods to punish him. According to Roman era mythography, the figure represents the healer Asclepius, who learned the secrets of keeping death at bay after observing one serpent bringing another healing herbs. To prevent the entire human race from becoming immortal under Asclepius' care, Jupiter killed him with a bolt of lightning, but later placed his image in the heavens to honor his good works. In medieval Islamic astronomy (Azophi's Uranometry, 10th century), the constellation was known as Al-Ḥawwa', "the snake-charmer".
Aratus describes Ophiuchus as trampling on Scorpius with his feet. This is depicted in Renaissance to Early Modern star charts, beginning with Albrecht Dürer in 1515; in some depictions (such as that of Johannes Kepler in De Stella Nova, 1606), Scorpius also seems to threaten to sting Serpentarius in the foot. This is consistent with Azophi, who already included ψ Oph and ω Oph as the snake-charmer's "left foot", and θ Oph and ο Oph as his "right foot", making Ophiuchus a zodiacal constellation at least as regards his feet. This arrangement has been taken as symbolic in later literature and placed in relation to the words spoken by God to the serpent in the Garden of Eden (Genesis 3:15).
-
 Ophiuchus in a manuscript copy of Azophi's Uranometry, 18th century copy of a manuscript prepared for Ulugh Beg in 1417 (note that as in all pre-modern star charts, the constellation is mirrored, with Serpens Caput on the left and Serpens Cauda on the right).
Ophiuchus in a manuscript copy of Azophi's Uranometry, 18th century copy of a manuscript prepared for Ulugh Beg in 1417 (note that as in all pre-modern star charts, the constellation is mirrored, with Serpens Caput on the left and Serpens Cauda on the right).
-
 Ophiuchus holding the serpent, Serpens, as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c. 1825. Above the tail of the serpent is the now-obsolete constellation Taurus Poniatovii while below it is Scutum.
Ophiuchus holding the serpent, Serpens, as depicted in Urania's Mirror, a set of constellation cards published in London c. 1825. Above the tail of the serpent is the now-obsolete constellation Taurus Poniatovii while below it is Scutum.
Zodiac
Main article: Ophiuchus (astrology)Ophiuchus is one of the 13 constellations that cross the ecliptic. It has sometimes been suggested as the "13th sign of the zodiac". However, this confuses zodiac or astrological signs with constellations. The signs of the zodiac are a 12-fold division of the ecliptic, so that each sign spans 30° of celestial longitude, approximately the distance the Sun travels in a month, and (in the Western tradition) are aligned with the seasons so that the March equinox always falls on the boundary between Pisces and Aries. Constellations, on the other hand, are unequal in size and are based on the positions of the stars. The constellations of the zodiac have only a loose association with the signs of the zodiac, and do not in general coincide with them. In Western astrology the constellation of Aquarius, for example, largely corresponds to the sign of Pisces. Similarly, the constellation of Ophiuchus occupies most (29 November – 18 December) of the sign of Sagittarius (23 November – 21 December). The differences are due to the fact that the time of year that the Sun passes through a particular zodiac constellation's position has slowly changed (because of the precession of the Earth's rotational axis) over the centuries from when the Babylonians originally developed the zodiac.
Citations
- "Star Tales – Ophiuchus". Retrieved 25 June 2021.
- Dickinson, Terence (2006). Nightwatch A practical Guide to Viewing the Universe Revised Fourth Edition: Updated for use Through 2025. US: Firefly Books. p. 185. ISBN 1-55407-147-X.
- Dickinson, Terence (2006). Nightwatch A Practical Guide to Viewing the Universe Revised Fourth Edition: Updated for Use Through 2025. US: Firefly Books. pp. 44–59. ISBN 1-55407-147-X.
- Ford, Dominic. "Rasalhague (Star)". in-the-sky.org. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- Chartrand III, Mark R.; (1983) Skyguide: A Field Guide for Amateur Astronomers, p. 170 (ISBN 0-307-13667-1).
- Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W. H. Jr. (1991). "Entry for HR 2491". Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Preliminary Version). CDS. ID V/50.
- Cowley, A.; et al. (April 1969), "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications", Astronomical Journal, 74: 375–406, Bibcode:1969AJ.....74..375C, doi:10.1086/110819
- Hinkley, Sasha; et al. (January 2011), "Establishing α Oph as a Prototype Rotator: Improved Astrometric Orbit" (PDF), The Astrophysical Journal, 726 (2): 104, arXiv:1010.4028, Bibcode:2011ApJ...726..104H, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/726/2/104, S2CID 50830196
- Monnier, J. D; Townsend, R. H. D; Che, X; Zhao, M; Kallinger, T; Matthews, J; Moffat, A. F. J (2010). "Rotationally Modulated g-modes in the Rapidly Rotating δ Scuti Star Rasalhague (α Ophiuchi)". The Astrophysical Journal. 725 (1): 1192–1201. arXiv:1012.0787. Bibcode:2010ApJ...725.1192M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/725/1/1192. S2CID 51105576.
- Zhao, M.; et al. (February 2010), Rivinius, Th.; Curé, M. (eds.), "Imaging and Modeling Rapid Rotators: α Cep and α Oph", The Interferometric View on Hot Stars, Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica, Serie de Conferencias, 38: 117–118, Bibcode:2010RMxAC..38..117Z
- Docobo, J. A.; Ling, J. F. (April 2007), "Orbits and System Masses of 14 Visual Double Stars with Early-Type Components", The Astronomical Journal, 133 (4): 1209–1216, Bibcode:2007AJ....133.1209D, doi:10.1086/511070, S2CID 120821801
- Paul Kunitzsch; Tim Smart (2006). A Dictionary of Modern Star Names: A Short Guide to 254 Star Names and Their Derivations. Sky Publishing Corporation. p. 44. ISBN 978-1-931559-44-7.
- Chartrand, at p. 170.
- Allende Prieto, C.; Lambert, D. L. (1999), "Fundamental parameters of nearby stars from the comparison with evolutionary calculations: masses, radii and effective temperatures", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 352: 555–562, arXiv:0809.0359, Bibcode:1999A&A...352..555A, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200811242, S2CID 14531031
- Soubiran, C.; et al. (2008), "Vertical distribution of Galactic disk stars. IV. AMR and AVR from clump giants", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 480 (1): 91–101, arXiv:0712.1370, Bibcode:2008A&A...480...91S, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078788, S2CID 16602121
- Zorec, J.; et al. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars. IV. Evolution of rotational velocities". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 537: A120. arXiv:1201.2052. Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.120Z. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. S2CID 55586789.
- Lastennet, E.; Fernandes, J.; Lejeune, Th. (June 2002). "A revised HRD for individual components of binary systems from BaSeL BVRI synthetic photometry. Influence of interstellar extinction and stellar rotation". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 388: 309–319. arXiv:astro-ph/0203341. Bibcode:2002A&A...388..309L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20020439. S2CID 14376211.
- "Star 'soon to become supernova'". BBC News. 23 July 2006.
- "[vsnet-alert 26131] Outburst of RS Ophiuchi". ooruri.kusastro.kyoto-u.ac.jp. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- "ATel #14834: Fermi-LAT Gamma-ray Detection of the Recurrent Nova RS Oph". ATel. Retrieved 9 August 2021.
- Ribas, I.; Tuomi, M.; Reiners, Ansgar; Butler, R. P.; et al. (14 November 2018). "A candidate super-Earth planet orbiting near the snow line of Barnard's star" (PDF). Nature. 563 (7731). Holtzbrinck Publishing Group: 365–368. arXiv:1811.05955. Bibcode:2018Natur.563..365R. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0677-y. hdl:2299/21132. ISSN 0028-0836. OCLC 716177853. PMID 30429552. S2CID 256769911. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 March 2019.
- Lubin, Jack; Robertson, Paul; Stefansson, Gudmundur; et al. (15 July 2021). "Stellar Activity Manifesting at a One-year Alias Explains Barnard b as a False Positive". The Astronomical Journal. 162 (2). American Astronomical Society: 61. arXiv:2105.07005. Bibcode:2021AJ....162...61L. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ac0057. ISSN 0004-6256. S2CID 234741985.
- Paulson, Diane B.; Allred, Joel C.; Anderson, Ryan B.; Hawley, Suzanne L.; Cochran, William D.; Yelda, Sylvana (2006). "Optical Spectroscopy of a Flare on Barnard's Star". Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific. 118 (1): 227. arXiv:astro-ph/0511281. Bibcode:2006PASP..118..227P. doi:10.1086/499497. S2CID 17926580.
- Benedict, G. Fritz; McArthur, Barbara; Nelan, E.; Story, D.; Whipple, A. L.; Shelus, P. J.; Jefferys, W. H.; Hemenway, P. D.; Franz, Otto G.; Wasserman, L. H.; Duncombe, R. L.; Van Altena, W.; Fredrick, L. W. (1998). "Photometry of Proxima Centauri and Barnard's star using Hubble Space Telescope fine guidance senso 3". The Astronomical Journal. 116 (1): 429. arXiv:astro-ph/9806276. Bibcode:1998AJ....116..429B. doi:10.1086/300420. S2CID 15880053.
- Bond, A. & Martin, A. R. (1976). "Project Daedalus – The mission profile". Journal of the British Interplanetary Society. 9 (2): 101. Bibcode:1976JBIS...29..101B. Archived from the original on 20 October 2007. Retrieved 15 August 2006.
- Darling, David (July 2005). "Daedalus, Project". The Encyclopedia of Astrobiology, Astronomy, and Spaceflight. Archived from the original on 31 August 2006. Retrieved 10 August 2006.
- "Huge 'Superbubble' of Gas Blowing Out of Milky Way". PhysOrg.com. 13 January 2006. Retrieved 4 July 2008.
- "Molecular Oxygen Detected for the First Time in the Interstellar Medium". Retrieved 28 September 2016.
- Reynolds, S. P.; Borkowski, K. J.; Hwang, U.; Hughes, J. P.; Badenes, C.; Laming, J. M.; Blondin, J. M. (2 October 2007). "A Deep Chandra Observation of Kepler's Supernova Remnant: A Type Ia Event with Circumstellar Interaction". The Astrophysical Journal. 668 (2): L135 – L138. arXiv:0708.3858. Bibcode:2007ApJ...668L.135R. doi:10.1086/522830.
- "Kepler's Supernova: Recently Observed Supernova". Universe for Facts. Archived from the original on 4 January 2019. Retrieved 21 December 2014.
- Charbonneau, David; et al. (December 2009). "A super-Earth transiting a nearby low-mass star". Nature. 462 (7275): 891–894. arXiv:0912.3229. Bibcode:2009Natur.462..891C. doi:10.1038/nature08679. PMID 20016595. S2CID 4360404.
- Rogers, Leslie A.; Seager, Sara (2010). "Three Possible Origins for the Gas Layer on GJ 1214b". The Astrophysical Journal. 716 (2): 1208–1216. arXiv:0912.3243. Bibcode:2010ApJ...716.1208R. doi:10.1088/0004-637x/716/2/1208. S2CID 15288792.
- Lalitha, S.; et al. (July 2014). "X-Ray Emission from the Super-Earth Host GJ 1214". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 790 (1): 5. arXiv:1407.2741. Bibcode:2014ApJ...790L..11L. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/790/1/L11. S2CID 118774018. L11.
- "Asteroid To Hide Naked-Eye Star". 31 March 2010. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- "Asteroid To Hide Bright Star". 31 March 2010. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- "(824) Anastasia / HIP 81377 event on 2010 Apr 06, 10:21 UT". Archived from the original on 17 July 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- "Ophiuchus, the Serpent Bearer – Constellations – Digital Images of the Sky".
- Arellano Ferro, A.; et al. (September 2013), "A detailed census of variable stars in the globular cluster NGC 6333 (M9) from CCD differential photometry", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 434 (2): 1220–1238, arXiv:1306.3206, Bibcode:2013MNRAS.434.1220A, doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1080.
- Levy 2005, pp. 153–54.
- Gontcharov, George A.; Khovritchev, Maxim Yu; Mosenkov, Aleksandr V.; Il'In, Vladimir B.; Marchuk, Alexander A.; Savchenko, Sergey S.; Smirnov, Anton A.; Usachev, Pavel A.; Poliakov, Denis M. (2021). "Isochrone fitting of Galactic globular clusters – III. NGC 288, NGC 362, and NGC 6218 (M12)". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 508 (2): 2688–2705. arXiv:2109.13115. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab2756.
- Boyles, J.; et al. (November 2011), "Young Radio Pulsars in Galactic Globular Clusters", The Astrophysical Journal, 742 (1): 51, arXiv:1108.4402, Bibcode:2011ApJ...742...51B, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/742/1/51, S2CID 118649860.
- Burnham, Robert (1978), Burnham's Celestial Handbook: An Observer's Guide to the Universe Beyond the Solar System, Dover Books on Astronomy, vol. 2 (2nd ed.), Courier Dover Publications, p. 1263, ISBN 978-0486235684.
- Clement, Christine M.; et al. (November 2001), "Variable Stars in Galactic Globular Clusters", The Astronomical Journal, 122 (5): 2587–2599, arXiv:astro-ph/0108024, Bibcode:2001AJ....122.2587C, doi:10.1086/323719, S2CID 38359010.
- Contreras, R.; et al. (December 2010), "Time-series Photometry of Globular Clusters: M62 (NGC 6266), the Most RR Lyrae-rich Globular Cluster in the Galaxy?", The Astronomical Journal, 140 (6): 1766–1786, arXiv:1009.4206, Bibcode:2010AJ....140.1766C, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/140/6/1766, S2CID 118515997
- Milone, A. P. (January 2015), "Helium and multiple populations in the massive globular cluster NGC 6266 (M 62)", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 446 (2): 1672–1684, arXiv:1409.7230, Bibcode:2015MNRAS.446.1672M, doi:10.1093/mnras/stu2198.
- McCombs, Thayne; et al. (January 2013), "Variable Stars in the Globular Cluster M107: The Discovery of a Probable SX Phoenicis", AAS Meeting #221, vol. 221, American Astronomical Society, p. 250.22, Bibcode:2013AAS...22125022M, 250.22.
- ^ Wilkins, Jamie; Dunn, Robert (2006). 300 Astronomical Objects: A Visual Reference to the Universe. Buffalo, New York: Firefly Books. ISBN 978-1-55407-175-3.
- Komossa, Stefanie; Burwitz, Vadim; Hasinger, Guenther; Predehl, Peter; et al. (2003). "Discovery of a Binary Active Galactic Nucleus in the Ultraluminous Infrared Galaxy NGC 6240 Using Chandra". Astrophysical Journal. 582 (1): L15 – L19. arXiv:astro-ph/0212099. Bibcode:2003ApJ...582L..15K. doi:10.1086/346145. S2CID 16697327.
- Mamajek, Eric E. (2006). "A New Nearby Candidate Star Cluster in Ophiuchus at d = 170 pc". Astronomical Journal. 132 (5): 2198–2205. arXiv:astro-ph/0609064. Bibcode:2006AJ....132.2198M. doi:10.1086/508205. S2CID 14070978.
- Jilinski, Evgueni; Ortega, Vladimir G.; de la Reza, Jorge Ramiro; Drake, Natalia A. & Bazzanella, Bruno (2009). "Dynamical Evolution and Spectral Characteristics of the Stellar Group Mamajek 2". The Astrophysical Journal. 691 (1): 212–218. arXiv:0810.1198. Bibcode:2009ApJ...691..212J. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/691/1/212. S2CID 15570695.
- "The Dark Cloud B68 at Different Wavelengths". European Southern Observatory. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- Alves, João; Lada, Charles; Lada, Elizabeth (March 2001). "Seeing the light through the dark" (PDF). The Messenger. 103: 15–20. Bibcode:2001Msngr.103....1A.
- Alves, João F.; Lada, Charles J.; Lada, Elizabeth A. (January 2001). "Internal structure of a cold dark molecular cloud inferred from the extinction of background starlight". Nature. 409 (6817): 159–161. Bibcode:2001Natur.409..159A. doi:10.1038/35051509. PMID 11196632. S2CID 4318459.
- Coordinates available at The Sky Live.
- Astronomers Discover Closest Black Hole to Earth Gemini North telescope on Hawai‘i reveals first dormant, stellar-mass black hole in our cosmic backyard, Dr Kareem El-Badry et al, USA National Science Foundation NOIRLab (National Optical-Infrared Astronomy Research Laboratory), 2022-11-04
- White, Gavin; Babylonian Star-lore, Solaria Pubs, 2008, p. 187f
- Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert. "ὀφιοῦχος". A Greek-English Lexicon. perseus.tufts.edu.
- translation by Mair, Alexander W.; & Mair, Gilbert R.; Loeb Classical Library, volume 129, William Heinemann, London, 1921 theoi.com
- ^ Thompson, Robert (2007). Illustrated Guide to Astronomical Wonders: From Novice to Master Observer. O'Reilly Media, Inc. p. 326. ISBN 9780596526856.
- Hyginus, Astronomica 2, 14, Latin Mythography, 2nd century AD
- "Snake-Charmer". Brickthology. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- "Manuscript reproduction". Archived from the original on 6 May 2019. Retrieved 17 July 2019.
- Maunder, Edward Walter; Astronomy of the Bible, 1908, p. 164f
- Shapiro, Lee T. "Constellations in the zodiac", in The Space Place (NASA, last updated 22 July 2011)
- "Ophiuchus, 13th constellation of zodiac". Earth Sky. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- Gleason, Edward. "Why is the vernal equinox called the "First Point of Aries" when the Sun is actually in Pisces on this date? | Planetarium". University of Southern Maine. Retrieved 25 March 2022.
- Campbell, Tina (15 July 2020). "Has your star sign changed following the discovery of a 'new' Zodiac sign?". Metro. Retrieved 29 April 2021.
- "Ophiuchus – a 13th Zodiac Sign? No!". Astrology Club. 2 March 2016. Retrieved 18 October 2016.
- "Born under the sign of Ophiuchus?". EarthSky.org. 16 August 2021.
- Aitken, Robert G. (October 1942). "Edmund Halley and Stellar Proper Motions". Astronomical Society of the Pacific Leaflets. 4 (164): 103. Bibcode:1942ASPL....4..103A.
- Redd, Nola Taylor. "Constellations: The Zodiac Constellation Names". space.com. Retrieved 3 August 2012.
See also
References
- Levy, David H. (2005). Deep Sky Objects. Prometheus Books. ISBN 1-59102-361-0.
- Ridpath, Ian; and Tirion, Wil; (2007) Stars and Planets Guide, Collins, London; ISBN 978-0-00-725120-9, Princeton University Press, Princeton; ISBN 978-0-691-13556-4
External links
- The Deep Photographic Guide to the Constellations: Ophiuchus
- Star Tales – Ophiuchus
- Warburg Institute Iconographic Database (ca 160 medieval and early modern images of Ophiuchus under the Latin name Serpentarius)
| The 88 modern constellations | |
|---|---|
| |
| Constellation history | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||
| |||||||||
|
| Zodiac | |
|---|---|
| Astrological signs | |
| Concepts in Western astrology | |
| Related | |