| Revision as of 08:26, 7 November 2022 editMztourist (talk | contribs)Autopatrolled, Extended confirmed users72,311 edits →Bridgehead: rmv dupl links← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 20:32, 26 November 2024 edit undoTurgidson (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users61,595 edits c/eTag: 2017 wikitext editor | ||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
| | map_label = | | map_label = | ||
| | territory = | | territory = | ||
| | result = |
| result = Axis withdrawal to Crimea in October 1943 | ||
| | status = | | status = | ||
| | combatants_header = Belligerents | | combatants_header = Belligerents | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''Kuban Bridgehead''' ({{ |
The '''Kuban Bridgehead''' ({{langx|de|Kuban-Brückenkopf}}), also known as the "Goth's head position" ({{lang|de|Gotenkopfstellung}}),<ref>{{Cite book|title = A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II Second Edition|last = Weinberg|first = Gerhard L.|publisher = ]|year = 2005|isbn = 978-0-521-61826-7|location = New York, NY|pages = 456}}</ref> was a German military position on the ], Russia, between the ] and the ]. Existing from January to October 1943, the ] formed after the ] of the ]. The heavily fortified position was intended as a staging area for the '']'' which was to be used to renew attacks towards the oil wells of the Caucasus. Axis positions in the bridgehead were repeatedly subjected to large Soviet offensives, but none ever comprehensively broke the Axis defensive lines. The bridgehead was abandoned when the ] breached the ], forcing an evacuation of the German forces across the ] to ]. | ||
| ==Prelude== | ==Prelude== | ||
| ] (''Fall Blau''), launched 28 June 1942, saw ] divided into two ]s, ] and ], the former participating in the ]. Throughout the operation the German situation, especially that of Army Group B centered on ], began to deteriorate.<ref name="War II 2005. p. 307">Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. {{ISBN|1-57607-999-6}}.</ref> As Army Group B began collapsing in the North, Army Group A quickly found itself at risk of being flanked. It was forced to abandon its task of securing the oilfields of the Caspian, and began withdrawing down the Terek River toward the Taman Peninsula.<ref name="War II 2005. p. 307">Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. {{ISBN|1-57607-999-6}}.</ref> | ] (''Fall Blau''), launched 28 June 1942, saw ] divided into two ]s, ] and ], the former participating in the ]. Throughout the operation the German situation, especially that of Army Group B centered on ], began to deteriorate.<ref name="War II 2005. p. 307">Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. {{ISBN|1-57607-999-6}}.</ref> As Army Group B began collapsing in the North, Army Group A quickly found itself at risk of being flanked. It was forced to abandon its task of securing the oilfields of the Caspian, and began withdrawing down the ] toward the Taman Peninsula.<ref name="War II 2005. p. 307">Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. {{ISBN|1-57607-999-6}}.</ref> | ||
| == Bridgehead == | == Bridgehead == | ||
| {{Campaignbox Crimea and Caucasus}} | {{Campaignbox Crimea and Caucasus}} | ||
| Following the encirclement of the ] at Stalingrad, Army Group A withdrew towards the Black Sea and Crimea.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title = Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History.|publisher = ABC-CLIO|year = 2005|isbn = 1-57607-999-6|location = Oxford, England|pages = 307}}</ref> The ], commanded by ] and ], constructed a defensive position across the ] delta in the Taman Peninsula, which was completed in January 1943. The main, first defense line started by ] and ran roughly northwards all the way across the peninsula. Consisting of 5 defense lines, the total depth of the defense area was up to 60 km.<ref name=ntoEncMil></ref> German forces, moving from positions along the ], fully occupied the new defensive network in February 1943 while under constant attack by the Red Army.<ref name=":0" /> |
Following the encirclement of the ] at Stalingrad, Army Group A withdrew towards the Black Sea and Crimea.<ref name=":0">{{Cite book|title = Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History.|publisher = ABC-CLIO|year = 2005|isbn = 1-57607-999-6|location = Oxford, England|pages = 307}}</ref> The ], commanded by ] and ], constructed a defensive position across the ] delta in the Taman Peninsula, which was completed in January 1943. The main, first defense line started by ] and ran roughly northwards all the way across the peninsula. Consisting of 5 defense lines, the total depth of the defense area was up to 60 km.<ref name=ntoEncMil></ref> German forces, moving from positions along the ], fully occupied the new defensive network in February 1943 while under constant attack by the Red Army.<ref name=":0" /> The bridgehead, originally intended to provide a staging area for future attempts to gain control of the Caspian oil fields, was re-tasked on 3 September 1943,''<ref>{{Cite book|title = A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II Second Edition|last = Weinberg|first = Gerhard L.|publisher = ]|year = 2005|isbn = 978-0-521-61826-7|location = New York, NY|pages = 605}}</ref>'' as the German situation on the Eastern Front continued to deteriorate.<ref name=":0" /> The Kuban Bridgehead then served to evacuate German forces as the withdrawal of Army Group South to the ] had become inevitable.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
| The first defenses of the Kuban Bridgehead were breached on September |
The first defenses of the Kuban Bridgehead were breached on 15–16 September 1943 in the area of Novorossiysk during the {{Interlanguage link multi|Novorossiysk–Taman Operation|ru|3=Новороссийско-Таманская операция}} of the Soviet ]. The Taman Peninsula was completely cleared of German forces on 9 October 1943.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://mural.maynoothuniversity.ie/5581/1/DGalbraithKubanBridgehead.pdf |title=The Defence and Evacuation of the Kuban Bridgehead, January – October 1943 |author=David R. Galbraith |date=July 2014 |work=David R. Galbraith - Master of Arts thesis |publisher=National University of Ireland, Maynooth |access-date=July 19, 2022}}</ref><ref name=ntoEncMil/> | ||
| == See also == | == See also == | ||
| * ] |
* ] — a military decoration given to those who fought in the Kuban bridgehead | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | * ] | ||
| * ] | |||
| == References == | == References == | ||
Latest revision as of 20:32, 26 November 2024
1943 German military position on the Eastern Front of World War II| The Kuban Bridgehead | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Battle of the Caucasus on the Eastern Front of World War II | |||||||
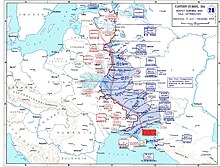 Map of July–December 1943 positions of the Eastern Front. The Kuban Bridgehead starts by Novorossiysk | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
The Kuban Bridgehead (German: Kuban-Brückenkopf), also known as the "Goth's head position" (Gotenkopfstellung), was a German military position on the Taman Peninsula, Russia, between the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea. Existing from January to October 1943, the bridgehead formed after the Germans were pushed out of the Caucasus. The heavily fortified position was intended as a staging area for the Wehrmacht which was to be used to renew attacks towards the oil wells of the Caucasus. Axis positions in the bridgehead were repeatedly subjected to large Soviet offensives, but none ever comprehensively broke the Axis defensive lines. The bridgehead was abandoned when the Red Army breached the Panther–Wotan line, forcing an evacuation of the German forces across the Kerch Strait to Crimea.
Prelude
Case Blue (Fall Blau), launched 28 June 1942, saw Army Group South divided into two Army Groups, Army Group A and Army Group B, the former participating in the Battle of the Caucasus. Throughout the operation the German situation, especially that of Army Group B centered on Stalingrad, began to deteriorate. As Army Group B began collapsing in the North, Army Group A quickly found itself at risk of being flanked. It was forced to abandon its task of securing the oilfields of the Caspian, and began withdrawing down the Terek River toward the Taman Peninsula.
Bridgehead
| Invasion of Crimea and Caucasus | |
|---|---|
Following the encirclement of the 6th Army at Stalingrad, Army Group A withdrew towards the Black Sea and Crimea. The 17th Army, commanded by Richard Ruoff and Erwin Jaenecke, constructed a defensive position across the Kuban River delta in the Taman Peninsula, which was completed in January 1943. The main, first defense line started by Novorossiysk and ran roughly northwards all the way across the peninsula. Consisting of 5 defense lines, the total depth of the defense area was up to 60 km. German forces, moving from positions along the Terek River, fully occupied the new defensive network in February 1943 while under constant attack by the Red Army. The bridgehead, originally intended to provide a staging area for future attempts to gain control of the Caspian oil fields, was re-tasked on 3 September 1943, as the German situation on the Eastern Front continued to deteriorate. The Kuban Bridgehead then served to evacuate German forces as the withdrawal of Army Group South to the Dnieper Line had become inevitable.
The first defenses of the Kuban Bridgehead were breached on 15–16 September 1943 in the area of Novorossiysk during the Novorossiysk–Taman Operation [ru] of the Soviet North Caucasian Front. The Taman Peninsula was completely cleared of German forces on 9 October 1943.
See also
- Kuban Shield — a military decoration given to those who fought in the Kuban bridgehead
- Kerch–Eltigen operation
- Courland Pocket
- Malaya Zemlya
- 2nd Guards Taman Motor Rifle Division
References
- ^ Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. ISBN 1-57607-999-6.
- ^ Tessin, G., Verbänd und Truppen der deutschen Wehrmacht und Waffen - SS im Zweiten Weltkrieg 1939-1945, Biblo Verlag, Osnabruck, 1977. taken from http://www.cgsc.edu/CARL/nafziger/939GXXP.PDF Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine pg 10
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. (2005). A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II Second Edition. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. p. 456. ISBN 978-0-521-61826-7.
- ^ Encyclopedia of World War II: A Political, Social, and Military History. Oxford, England: ABC-CLIO. 2005. p. 307. ISBN 1-57607-999-6.
- ^ "Новороссийско-Таманская наступательная операция (9 сентября — 9 октября 1943 г.)"
- Weinberg, Gerhard L. (2005). A World at Arms: A Global History of World War II Second Edition. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. p. 605. ISBN 978-0-521-61826-7.
- David R. Galbraith (July 2014). "The Defence and Evacuation of the Kuban Bridgehead, January – October 1943" (PDF). David R. Galbraith - Master of Arts thesis. National University of Ireland, Maynooth. Retrieved July 19, 2022.