| Revision as of 06:48, 28 January 2023 editClueBot NG (talk | contribs)Bots, Pending changes reviewers, Rollbackers6,439,788 editsm Reverting possible vandalism by 71.211.168.188 to version by Artem.G. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (4209899) (Bot)Tag: Rollback← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 01:54, 10 November 2024 edit undoGreenC bot (talk | contribs)Bots2,582,335 edits Rescued 1 archive link. Wayback Medic 2.5 per WP:URLREQ#foxnews.com/section/year/ | ||
| (48 intermediate revisions by 21 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Hiking path in Israel}} | |||
| {{Infobox hiking trail | {{Infobox hiking trail | ||
| |name |
| name = Israel National Trail | ||
| | photo = Israel_National_Trail-EN.png | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| | |
| photo_size = | ||
| |caption |
| caption = Route of Israel National Trail as of 2019 | ||
| |location |
| location = ] | ||
| |designation = | | designation = | ||
| |established = 1995 | | established = 1995 | ||
| |length |
| length = {{convert|1025|km|mi|1}} | ||
| | |
| trailheads = North: ], South: ] | ||
| |use |
| use = Hiking | ||
| |elev_gain_and_loss= | | elev_gain_and_loss = | ||
| |elev_change = | | elev_change = | ||
| |lowest |
| lowest = | ||
| |grade |
| grade = | ||
| |difficulty |
| difficulty = | ||
| | season = autumn, winter, spring; with caution and only northern parts also in summer | |||
| | |
| months = November to May<ref name=NatGeo>{{cite web |last= Schnitzspahn |first= Doug |title= World's Best Hikes: Epic Trails |publisher=] |url= http://adventure.nationalgeographic.com/adventure/trips/best-trails/worlds-best-grail-trails/#/israel-national-trail-hike_56712_600x450.jpg |archive-url= https://web.archive.org/web/20120801015838/http://adventure.nationalgeographic.com/adventure/trips/best-trails/worlds-best-grail-trails/#/israel-national-trail-hike_56712_600x450.jpg |url-status= dead |archive-date= August 1, 2012 |access-date= June 16, 2013}}</ref> | ||
| |months = November to May<ref name=NatGeo/> | |||
| |sights= | | sights = | ||
| |hazards= | | hazards = | ||
| |surface= | | surface = | ||
| |website |
| website = {{URL|http://www.israeltrail.net/}} | ||
| }} | }} | ||
| The '''Israel National Trail''' ({{ |
The '''Israel National Trail''' ({{langx|he|שביל ישראל}}, ''Shvil Yisra'el'') is a hiking trail that crosses the entire length of ],<ref>{{cite web|title=Israel National Trail|url=http://www.natureisrael.org/INT|publisher=]|access-date=21 April 2013|archive-date=10 March 2018|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180310234418/http://www.natureisrael.org/INT|url-status=dead}}</ref> with its northern end at ] in the far north of the country, extending to ] at the southernmost tip of Israel on the ], with a total length of {{convert|1040|km|abbr=on}}.<ref name="haaretz.com">, ]</ref><ref>, ]</ref> The trail was inaugurated in 1995. | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| The trail is marked with three stripes (white, blue, and orange), and takes an average of |
The trail is marked with three stripes (white, blue, and orange), and takes an average of 45–60 days to complete.<ref name="eretz.com"></ref> | ||
| The Israel National Trail has been listed in National Geographic's 20 most "epic trails." It is described as a trail that "delves into the grand scale of biblical landscapes as well as the everyday lives of the modern Israeli."<ref name="NatGeo-a">{{cite web | url=http://www.jpost.com/Travel/AroundIsrael/Article.aspx?id=281022 | title='National Geographic' calls Israel Trail 'epic' | publisher=The Jerusalem Post | date=August 13, 2012 | access-date=August 13, 2012 | author=Udasin, Sharon}}</ref> | The Israel National Trail has been listed in National Geographic's 20 most "epic trails." It is described as a trail that "delves into the grand scale of biblical landscapes as well as the everyday lives of the modern Israeli."<ref name="NatGeo-a">{{cite web | url=http://www.jpost.com/Travel/AroundIsrael/Article.aspx?id=281022 | title='National Geographic' calls Israel Trail 'epic' | publisher=The Jerusalem Post | date=August 13, 2012 | access-date=August 13, 2012 | author=Udasin, Sharon}}</ref> | ||
| Since January 2016, the Israel National Trail can be explored on Google Street View. . | Since January 2016, the Israel National Trail can be explored on Google Street View. .<ref>{{Cite web |last=Leichman |first=Abigail Klein |date=2015-05-11 |title=Israel National Trail gets Google Street View |url=https://www.israel21c.org/israel-national-trail-gets-google-street-view/ |access-date=2023-11-04 |website=ISRAEL21c |language=en-US}}</ref> | ||
| The best hiking seasons are either from mid-February to mid-May or from September to December. The summer months (mid-May to the end of August) are considered too hot. Winter is less popular due to rain, low temperatures and, in the southern sections of the trail, potential flash floods. | |||
| ==History == | ==History == | ||
| <mapframe text="Israel National Trail" width="270" height="850" latitude="31.585" longitude="34.994" align="right" zoom="8"> | |||
| ⚫ | The Israel National Trail (INT) is the brainchild of Avraham Tamir, a journalist and hiker who hiked the ] in the late 70's and Ori Dvir, hiker, educator and one of the founders of ] (SPNI). The INT is over 1000 kilometers long and is marked, managed and maintained by The Israel Trails Committee which also blazes, marks and maintains the 15,000 kilometers of hiking trails all over Israel. | ||
| { | |||
| "type": "ExternalData", | |||
| "service": "geoline", | |||
| "ids": "Q583897", | |||
| "properties": { | |||
| ⚫ | "title": "Israel National Trail", | ||
| "stroke": "#003e81", | |||
| "stroke-width": 5 | |||
| } | |||
| } | |||
| </mapframe> | |||
| ⚫ | The Israel National Trail (INT) is the brainchild of Avraham Tamir, a journalist and hiker who hiked the ] in the late 70's and Ori Dvir, hiker, educator and one of the founders of ] (SPNI). The INT is over 1000 kilometers long and is marked, managed and maintained by The Israel Trails Committee which also blazes, marks and maintains the 15,000 kilometers of hiking trails all over Israel. | ||
| The Israel National Trail was officially inaugurated by then ], ] in 1994. One of its purposes is to give Israelis a way to experience the entire breadth of the land firsthand. The various sections of the trail have been added progressively during this development. | The Israel National Trail was officially inaugurated by then ], ] in 1994. One of its purposes is to give Israelis a way to experience the entire breadth of the land firsthand. The various sections of the trail have been added progressively during this development. | ||
| ] | |||
| In 2003 a portion of the trail was diverted from the ] and now runs along the coast. The reasons for the change were the development of ], avoiding the security risk of walking along the ] and the desire to add to the trail sections with city and sea views. | In 2003 a portion of the trail was diverted from the ] and now runs along the coast. The reasons for the change were the development of ], avoiding the security risk of walking along the ] and the desire to add to the trail sections with city and sea views. | ||
| According to statistics compiled in 2010, only 4 out of 10 hikers complete the entire trail.<ref name="eretz.com"/> Recognizing this, the planners divided it into smaller sections that can be hiked separately. Some sections can be completed in day trips or over the weekend.<ref></ref> | According to statistics compiled in 2010, only 4 out of 10 hikers complete the entire trail.<ref name="eretz.com"/> Recognizing this, the planners divided it into smaller sections that can be hiked separately. Some sections can be completed in day trips or over the weekend.<ref></ref> | ||
| Because the southern section of the trail passes through many isolated areas, hikers cache supplies of food and water at designated points on the trail before beginning the hike or pay for supplies to be delivered. |
Because the southern section of the trail passes through many isolated areas, hikers cache supplies of food and water at designated points on the trail before beginning the hike or pay for supplies to be delivered. | ||
| Hikers can seek help from "trail angels". For example, at ] ], a soldier leaves the key to her room for hikers who need a place to sleep and a farmer in ] forest offers sleeping quarters in exchange for a day's work.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.hadassahmagazine.org/site/apps/nlnet/content2.aspx?c=twI6LmN7IzF&b=6216559&ct=8432343 |title=Israeli Life: Country Road, Take Me Home |access-date=2011-04-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110206162236/http://www.hadassahmagazine.org/site/apps/nlnet/content2.aspx?c=twI6LmN7IzF&b=6216559&ct=8432343 |archive-date=2011-02-06 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | Hikers can seek help from "trail angels". For example, at ] ], a soldier leaves the key to her room for hikers who need a place to sleep and a farmer in ] forest offers sleeping quarters in exchange for a day's work.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.hadassahmagazine.org/site/apps/nlnet/content2.aspx?c=twI6LmN7IzF&b=6216559&ct=8432343 |title=Israeli Life: Country Road, Take Me Home |access-date=2011-04-13 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20110206162236/http://www.hadassahmagazine.org/site/apps/nlnet/content2.aspx?c=twI6LmN7IzF&b=6216559&ct=8432343 |archive-date=2011-02-06 |url-status=dead }}</ref> | ||
| A unique phenomenon that developed with the increase in popularity of the trail is that of "trail angels" ({{langx|he|מלאכי שביל }}, ''Mal'ache Shvil''). This nickname refers to people who live along the trail and offer hikers assistance, such as providing accommodation with beds and a shower, allowing them to pitch a tent in their the yard or helping with transportation. Most of the "angels" do not require compensation for their support. | |||
| ==Awards and recognition== | ==Awards and recognition== | ||
| In 2012, National Geographic magazine included the trail on its best hiking trail list. It was praised for "connecting to something that often gets lost in all the headlines: the sublime beauty of the wilderness of the Middle East." According to the magazine, "the joy of the trail is meeting the Israelis hiking it, and spending some time in small kibbutzim where local people take hikers into their homes."<ref |
In 2012, National Geographic magazine included the trail on its best hiking trail list. It was praised for "connecting to something that often gets lost in all the headlines: the sublime beauty of the wilderness of the Middle East." According to the magazine, "the joy of the trail is meeting the Israelis hiking it, and spending some time in small kibbutzim where local people take hikers into their homes."<ref name="haaretz.com"/> | ||
| ==Route== | ==Route== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 74: | ||
| The trail is a continuous footpath across the entire country of ]. It mostly consists of dirt tracks, however, occasionally it includes quiet roads or pavements. The path is frequently marked by its unique striped markers. These are often painted on rocks and trees, or with signs and plates. | The trail is a continuous footpath across the entire country of ]. It mostly consists of dirt tracks, however, occasionally it includes quiet roads or pavements. The path is frequently marked by its unique striped markers. These are often painted on rocks and trees, or with signs and plates. | ||
| The trail is walked either North-to-South or South-to-North, both directions are common. However, the North-to-South is more frequently taken. Therefore a description of the route in that direction follows. | The trail is walked either North-to-South or South-to-North, both directions are common. However, the North-to-South is more frequently taken. Therefore, a description of the route in that direction follows. | ||
| ===Upper Galilee=== | ===Upper Galilee=== | ||
| ⚫ | The trail starts in ], behind the ]. It proceeds down to the Upper Galilee, passes through the city of ], and goes near ], where it passes by a memorial to ].<ref name="jacobsaarbook">{{Cite book|last=Saar|first=Jacob|url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/754709823|title=Israel National Trail and the Jerusalem Trail (Hike the Land of Israel)|date=2011|publisher=Eshkol|others=Yagil Henkin, Dany Gaspar|isbn=978-965-91249-4-7|edition=2nd|location=Israel|oclc=754709823}}</ref> | ||
| ⚫ | The |
||
| The path in this area is elevated, providing views of the ], a part of the ]. Further along, the path reaches ], and then a shrine, ] (Prophet Joshua). | The path in this area is elevated, providing views of the ], a part of the ]. Further along, the path reaches ], and then a shrine, ] (Prophet Joshua). | ||
| The trail continues up to ]. It passes by a rock formation known as Elijah's Chair, and the archaeological site of ]. Further, the trail sees exposed pipes of the ]. It then passes |
The trail continues up to ]. It passes by a rock formation known as Elijah's Chair, and the archaeological site of ]. Further, the trail sees exposed pipes of the ]. It then passes in ], more than two hundred meters below the city of ]. | ||
| ===Lower Galilee=== | ===Lower Galilee=== | ||
| Line 100: | Line 115: | ||
| ===Jerusalem to the Negev=== | ===Jerusalem to the Negev=== | ||
| Now pushing away from ], the path climbs up to ], a historical ruin on top of a hill. Continuing south, the route goes over a hill, with the ruin of ] on top. Onward, the route leads into ]; through the ancient town of ]. The route passes nearby to ], ruins of an ancient city. Further on, the route passes through the archaeological site of ]. | Now pushing away from ], the path climbs up to ], a historical ruin on top of a hill. Continuing south, the route goes over a hill, with the ruin of ] on top. Onward, the route leads into ]; through the ancient town of ]. The route passes nearby to ], ruins of an ancient city. Further on, the route passes through the archaeological site of ]. | ||
| The route follows the river of Nahal Adora'im it breaks away at the ruins of Tel Keshet, and then through Tel Nagila. It passes through ], then following the river of Nahal Shikma. Shortly afterwards, it goes through ], to enter the kibbutz of ]; within is the Joe Alon Centre and Museum of Bedouin Culture. Just leaving the kibbutz is Hirbat Rimon. | The route follows the river of Nahal Adora'im it breaks away at the ruins of Tel Keshet, and then through Tel Nagila. It passes through ], then following the river of Nahal Shikma. Shortly afterwards, it goes through ], to enter the kibbutz of ]; within is the Joe Alon Centre and Museum of Bedouin Culture. Just leaving the kibbutz is Hirbat Rimon. | ||
| Line 106: | Line 121: | ||
| Later the route goes through ], the largest forest in Israel. It passes through ], and then up to Mount Amasa, the second-highest point on the trail, at 859 m. | Later the route goes through ], the largest forest in Israel. It passes through ], and then up to Mount Amasa, the second-highest point on the trail, at 859 m. | ||
| Heading east onto the Arad Plateau, the route passes through the archaeological site of ], to then pass enter the city of ] itself.<ref name="jacobsaarbook" /> |
Heading east onto the Arad Plateau, the route passes through the archaeological site of ], to then pass enter the city of ] itself.<ref name="jacobsaarbook" /> | ||
| ===Negev=== | ===Negev=== | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| Leaving the city, the route passes into The ]. It goes over Mount Qina, and then along the river of Nahal Kanfan. Much later, it passes through the Roman archaeological site of ]. Heading south, it reaches an observation point on the rim of ], the first of the three ] the trail sees; it passes through and comes close to the gap (centre). | Leaving the city, the route passes into The ]. It goes over Mount Qina, and then along the river of Nahal Kanfan. Much later, it passes through the Roman archaeological site of ]. Heading south, it reaches an observation point on the rim of ], the first of the three ] the trail sees; it passes through and comes close to the gap (centre). | ||
| Later, the route passes through Mezad Tzafir, an ancient Roman stronghold that was a part of the ] (frontier). It follows ] for a short while, along which is the ], the highest dry waterfall in Israel, then passing another Roman stronghold, Meizad Yorkeam. | Later, the route passes through Mezad Tzafir, an ancient Roman stronghold that was a part of the ] (frontier). It follows ] for a short while, along which is the ], the highest dry waterfall in Israel, then passing another Roman stronghold, Meizad Yorkeam. | ||
| Next, the route climbs ], the collapsed southern rim of ], and then follows Nahal Afran. It then enters the Zin Valley, to cross Nahal Zin. It reaches the peak of Mount Akev, the spring of Ein Akev, and the river of Nahal Akev. It then passes through ]. | Next, the route climbs ], the collapsed southern rim of ], (''lit.'' The Big Crater) and then follows Nahal Afran. It then enters the Zin Valley, to cross Nahal Zin. It reaches the peak of Mount Akev, the spring of Ein Akev, and the river of Nahal Akev. It then passes through ]. | ||
| Further along, it passes by |
Further along, it passes by ], a fort used to protect spice trading routes. Then it enters the town of ]. | ||
| ] is on the edge of ], the largest ] in the world. The route |
] is on the edge of ], the largest ] in the world. The route takes around two days to cross it, and comes close to ], the deepest point of the Makhtesh. After leaving the Makhtesh, it passes by the ancient caravanserai of Moa, and goes through both ] and Vardit Canyons. It passes Kasui Sand Dunes, then into ], with Mount Timna and ], all within ]. | ||
| Lastly, the route reaches ], on the ], the final destination of the trail and its southern-most point.<ref name="jacobsaarbook" /> | Lastly, the route crosses Eilat mountain range and reaches ], on the ], the final destination of the trail and its southern-most point.<ref name="jacobsaarbook" /> | ||
| ==Cultural references== | ==Cultural references== | ||
| Line 134: | Line 150: | ||
| *] | *] | ||
| *] - the extension of the trail into Jerusalem | *] - the extension of the trail into Jerusalem | ||
| *] | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| ⚫ | {{Sister project links | wikt=no | commons=Category:Israel National Trail | b=no | n=no | q=no | s=no | v=no | voy=Israel National Trail | species=no | d=Q583897}} | ||
| {{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| Line 146: | Line 162: | ||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| ⚫ | {{Sister project links | wikt=no | commons=Category:Israel National Trail | b=no | n=no | q=no | s=no | v=no | voy=Israel National Trail | species=no | d=Q583897}} | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| Line 152: | Line 169: | ||
| * Israel National Trail at the Society for the Protection of Nature in Israel website (Hebrew) | * Israel National Trail at the Society for the Protection of Nature in Israel website (Hebrew) | ||
| * | * | ||
| * | * | ||
| {{coord|31|23|52|N|34|51|41|E|region:IL_type:landmark_source:kolossus-dewiki|display=title}} | {{coord|31|23|52|N|34|51|41|E|region:IL_type:landmark_source:kolossus-dewiki|display=title}} | ||
| {{Authority control}} | {{Authority control}} | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:54, 10 November 2024
Hiking path in Israel| Israel National Trail | |
|---|---|
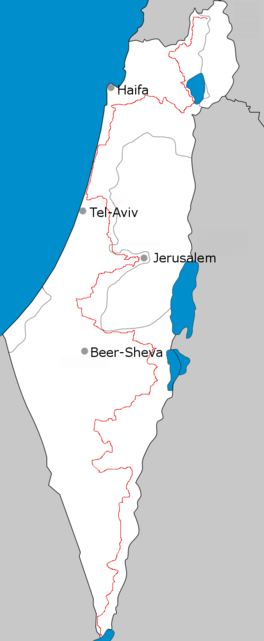 Route of Israel National Trail as of 2019 Route of Israel National Trail as of 2019 | |
| Length | 1,025 kilometres (636.9 mi) |
| Location | Israel |
| Established | 1995 |
| Trailheads | North: Dan, South: Eilat |
| Use | Hiking |
| Season | autumn, winter, spring; with caution and only northern parts also in summer |
| Months | November to May |
| Website | www |
The Israel National Trail (Hebrew: שביל ישראל, Shvil Yisra'el) is a hiking trail that crosses the entire length of Israel, with its northern end at Kibbutz Dan in the far north of the country, extending to Eilat at the southernmost tip of Israel on the Red Sea, with a total length of 1,040 km (650 mi). The trail was inaugurated in 1995.

The trail is marked with three stripes (white, blue, and orange), and takes an average of 45–60 days to complete.
The Israel National Trail has been listed in National Geographic's 20 most "epic trails." It is described as a trail that "delves into the grand scale of biblical landscapes as well as the everyday lives of the modern Israeli."
Since January 2016, the Israel National Trail can be explored on Google Street View. Israel National Trail on Google Street View.
The best hiking seasons are either from mid-February to mid-May or from September to December. The summer months (mid-May to the end of August) are considered too hot. Winter is less popular due to rain, low temperatures and, in the southern sections of the trail, potential flash floods.
History
Israel National TrailThe Israel National Trail (INT) is the brainchild of Avraham Tamir, a journalist and hiker who hiked the Appalachian Trail in the late 70's and Ori Dvir, hiker, educator and one of the founders of The Society for Protection of Nature in Israel (SPNI). The INT is over 1000 kilometers long and is marked, managed and maintained by The Israel Trails Committee which also blazes, marks and maintains the 15,000 kilometers of hiking trails all over Israel.
The Israel National Trail was officially inaugurated by then President of Israel, Ezer Weizmann in 1994. One of its purposes is to give Israelis a way to experience the entire breadth of the land firsthand. The various sections of the trail have been added progressively during this development.
In 2003 a portion of the trail was diverted from the Sharon and now runs along the coast. The reasons for the change were the development of Highway 6, avoiding the security risk of walking along the Green Line and the desire to add to the trail sections with city and sea views.
According to statistics compiled in 2010, only 4 out of 10 hikers complete the entire trail. Recognizing this, the planners divided it into smaller sections that can be hiked separately. Some sections can be completed in day trips or over the weekend.
Because the southern section of the trail passes through many isolated areas, hikers cache supplies of food and water at designated points on the trail before beginning the hike or pay for supplies to be delivered.
Hikers can seek help from "trail angels". For example, at Kibbutz Yagur, a soldier leaves the key to her room for hikers who need a place to sleep and a farmer in Hadera forest offers sleeping quarters in exchange for a day's work.
A unique phenomenon that developed with the increase in popularity of the trail is that of "trail angels" (Hebrew: מלאכי שביל, Mal'ache Shvil). This nickname refers to people who live along the trail and offer hikers assistance, such as providing accommodation with beds and a shower, allowing them to pitch a tent in their the yard or helping with transportation. Most of the "angels" do not require compensation for their support.
Awards and recognition
In 2012, National Geographic magazine included the trail on its best hiking trail list. It was praised for "connecting to something that often gets lost in all the headlines: the sublime beauty of the wilderness of the Middle East." According to the magazine, "the joy of the trail is meeting the Israelis hiking it, and spending some time in small kibbutzim where local people take hikers into their homes."
Route





The trail is a continuous footpath across the entire country of Israel. It mostly consists of dirt tracks, however, occasionally it includes quiet roads or pavements. The path is frequently marked by its unique striped markers. These are often painted on rocks and trees, or with signs and plates.
The trail is walked either North-to-South or South-to-North, both directions are common. However, the North-to-South is more frequently taken. Therefore, a description of the route in that direction follows.
Upper Galilee
The trail starts in Kibbutz Dan, behind the Beit Ussishkin Museum. It proceeds down to the Upper Galilee, passes through the city of Kiryat Shmona, and goes near Tel Hai, where it passes by a memorial to Joseph Trumpeldor.
The path in this area is elevated, providing views of the Hula Valley, a part of the Great Rift Valley. Further along, the path reaches Nabi Yusha fort/Metzudat Koach, and then a shrine, Al-Nabi Yusha' (Prophet Joshua).
The trail continues up to Mount Meron. It passes by a rock formation known as Elijah's Chair, and the archaeological site of Khirbet Shema. Further, the trail sees exposed pipes of the National Water Carrier of Israel. It then passes in Nahal Amud, more than two hundred meters below the city of Safed.
Lower Galilee
Now at a lower elevation, the route reaches close to the Sea of Galilee, at the town of Migdal. It then ascends briefly onto Mount Arbel, with views of the cliffs and natural caves below. From here, the route comes nearby to the Horns of Hattin, where the Battle of Hattin took place. Shortly afterwards, the route goes through Tiberias, the city directly next to the Sea of Galilee.
After following it for a while, the route departs from the Sea of Galilee, at Yardenit Baptismal Site, onto the Jordan River, which is follows very briefly. The route passes by what were the villages of Awlam and Sirin, as well as the archaeological site of Tel Rekhesh.
The route then continues over Mount Tabor, located at the top is the Church of the Transfiguration. After descending, the route again ascends, over Mount Devora, at the top of which is a monument to mark the silver wedding anniversary of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip. Shortly after, it passes by the Nazareth Iris Nature Reserve.
Here the route comes close to, but avoids the city of Nazareth, instead, it goes through Nof HaGalil (Nazareth Illit). After leaving, it passes by the archaeological site of Sepphoris (Zippori). Next passing by the ruins of a water mill, Tahanat Hanezirim.
Carmel and the Coast
The route passes through Kibbutz Yagur, to then enter, with a very steep ascent, Mount Carmel National Park. After crossing Mount Carmel itself, it passes by Isfiya, and then numerous other mountains. It then descends at the prehistoric Etzba Cave, and passes by the artist's colony of Ein Hod.
The route now turns south, and after passing many more prehistoric caves, it goes by the town of Zikhron Ya'akov. Shortly after, the route reaches an ancient Roman aqueduct, to then reach the Mediterranean Sea, at Jisr az-Zarqa. Along the coast a very short way, the route goes by Caesarea Maritima, the vast ruins of an ancient Roman city.
Going further south, the route goes through the city of Hadera. Afterwards, it crosses the river Nahal Alexander, going through the national park of the same name. Near here the route passes Hirbat Samara, the ruins of a building used by Ottoman customs officers. Next, the route passes the city of Netanya, on the coast, then crosses Nahal Poleg River.
Further along the coast, the route passes by the ruins of the ancient city of Apollonia–Arsuf. Shortly afterwards, it passes by Sidna Ali Mosque, to then go by the city of Herzliya. The route then enters Tel Aviv, where it turns east, away from the coast.
Tel Aviv to Jerusalem
The route turns at the mouth of the Yarkon River, which it follows for a while through Yarkon Park. Passing a British army Pillbox by a railway, it then passes into Yarkon Springs National Park. It then departs the river near the city of Rosh HaAyin.
The route goes by the Roman mausoleum of Hirbat Mazor. After a short while, it passes through the archaeological site of Tel Hadid. Next, it passes through Ben Shemen Forest, then passing nearby to the Roman ruins of Hirbat Anava and Hirbat Ragav. Further south, the route goes by Latrun Monastery, an old Crusader castle, and the village of Neve Shalom.
The route now begins to ascend, into the Judean Mountains National Park. Walking along Shayarot ridge, views are provided onto Highway 1, the main road from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem. The route follows Burma Road, a makeshift road used during the 1948 Siege of Jerusalem by Palmach soldiers of the Harel Brigade; passing by many military posts nearby. Shortly it passes by Bnei Brit Cave, a memorial dedicated to victims of the Holocaust.
Further east, the route goes through what was the village of Sataf, and then along Nahal Sorek. Shortly the route reaches as close as it gets to Jerusalem; from here, a separate trail, the Jerusalem Trail can be taken for a two-day site trip to see the city. The route passes by Yad Kennedy; a memorial to John F. Kennedy, and Hirbat Khanot, an old traveller's stop.
Jerusalem to the Negev
Now pushing away from Jerusalem, the path climbs up to Azekah, a historical ruin on top of a hill. Continuing south, the route goes over a hill, with the ruin of Tel Goded on top. Onward, the route leads into Beit Guvrin National Park; through the ancient town of Eleutheropolis/Beit Guvrin. The route passes nearby to Tel Maresha, ruins of an ancient city. Further on, the route passes through the archaeological site of Tel Lachish.
The route follows the river of Nahal Adora'im it breaks away at the ruins of Tel Keshet, and then through Tel Nagila. It passes through Pura Nature Reserve, then following the river of Nahal Shikma. Shortly afterwards, it goes through Lahav Forest, to enter the kibbutz of Lahav; within is the Joe Alon Centre and Museum of Bedouin Culture. Just leaving the kibbutz is Hirbat Rimon.
Later the route goes through Yatir Forest, the largest forest in Israel. It passes through Amasa, and then up to Mount Amasa, the second-highest point on the trail, at 859 m.
Heading east onto the Arad Plateau, the route passes through the archaeological site of Tel Arad, to then pass enter the city of Arad itself.
Negev


Leaving the city, the route passes into The Negev Desert. It goes over Mount Qina, and then along the river of Nahal Kanfan. Much later, it passes through the Roman archaeological site of Mezad Tamar. Heading south, it reaches an observation point on the rim of HaMakhtesh HaKatan, the first of the three Makhtesh the trail sees; it passes through and comes close to the gap (centre).
Later, the route passes through Mezad Tzafir, an ancient Roman stronghold that was a part of the Limes (frontier). It follows Nahal Hatira for a short while, along which is the Hatira Waterfall, the highest dry waterfall in Israel, then passing another Roman stronghold, Meizad Yorkeam.
Next, the route climbs Mount Karbolet, the collapsed southern rim of HaMakhtesh HaGadol, (lit. The Big Crater) and then follows Nahal Afran. It then enters the Zin Valley, to cross Nahal Zin. It reaches the peak of Mount Akev, the spring of Ein Akev, and the river of Nahal Akev. It then passes through Ein Shaviv Oasis.
Further along, it passes by Metzad Mahmal, a fort used to protect spice trading routes. Then it enters the town of Mizpe Ramon.
Mizpe Ramon is on the edge of Makhtesh Ramon, the largest Makhtesh in the world. The route takes around two days to cross it, and comes close to Ein Saharonim, the deepest point of the Makhtesh. After leaving the Makhtesh, it passes by the ancient caravanserai of Moa, and goes through both Barak and Vardit Canyons. It passes Kasui Sand Dunes, then into Timna Valley Park, with Mount Timna and Solomons Pillars, all within Timna Valley.
Lastly, the route crosses Eilat mountain range and reaches Eilat, on the Red Sea, the final destination of the trail and its southern-most point.
Cultural references
The trail is featured prominently in Israeli author David Grossman's 2008 novel To the End of the Land. In that story the mother of an Israeli soldier takes to the trail to occupy and distract herself while her son is engaged in a military operation.
See also
- Tourism in Israel
- Geography of Israel
- List of long-distance footpaths
- Derech HaTeva
- Wildlife of Israel
- Sea to sea trail
- Jerusalem Trail - the extension of the trail into Jerusalem
- Jordan Trail
References
- Schnitzspahn, Doug. "World's Best Hikes: Epic Trails". National Geographic. Archived from the original on August 1, 2012. Retrieved June 16, 2013.
- "Israel National Trail". Society for the Protection of Nature in Israel. Archived from the original on 10 March 2018. Retrieved 21 April 2013.
- ^ National Geographic names Israel National Trail as one of world's best, Haaretz
- Google Street View cameras to bring Israel National Trail alive, Jerusalem Post
- ^ Porcupines, Emperors, and the New Middle East, Eretz Magazine
- Udasin, Sharon (August 13, 2012). "'National Geographic' calls Israel Trail 'epic'". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved August 13, 2012.
- Leichman, Abigail Klein (2015-05-11). "Israel National Trail gets Google Street View". ISRAEL21c. Retrieved 2023-11-04.
- Hiking the Israel Trail
- "Israeli Life: Country Road, Take Me Home". Archived from the original on 2011-02-06. Retrieved 2011-04-13.
- ^ Saar, Jacob (2011). Israel National Trail and the Jerusalem Trail (Hike the Land of Israel). Yagil Henkin, Dany Gaspar (2nd ed.). Israel: Eshkol. ISBN 978-965-91249-4-7. OCLC 754709823.
Further reading
- Bortoletto, Linda (2019). Le Chemin des anges - Ma traversée d’Israël à pied, Payot, ISBN 2228924652, in French language
- Galblum Pex, Judith (2007). Walk the land : a journey on foot through Israel. Greeley, CO: Cladach Publishing. ISBN 978-0-9759619-5-7.
- Green, Aryeh (2018). My Israel Trail, Cedar Fort, ISBN 978-1462122011
- Saar, Jacob; Henkin, Yagil (2020). Israel National Trail (Hike the Land of Israel). Eshkol Publishing. p. 200. ISBN 978-96542059-1-7.
External links
- The INT Experience - Everything about the INT, in English
- Hiking the Israel National Trail - English language resources
- Der Israel Trail - German/ English resources
- The trail in Google maps
- Shvil Israel at SPNI Israel National Trail at the Society for the Protection of Nature in Israel website (Hebrew)
- Israel National Trail Hiking Journals - English
- Israel National Trail - Hebrew
31°23′52″N 34°51′41″E / 31.39778°N 34.86139°E / 31.39778; 34.86139
Categories: